Exam 1 Solutions
... Suggestion: some of the problems say: show something. Be guided in your answer by how much space I have left for your work. In particular, nearly all of these problems require little space to solve. In order to maximize the credit you receive, show all of your steps, write neatly and give some reaso ...
... Suggestion: some of the problems say: show something. Be guided in your answer by how much space I have left for your work. In particular, nearly all of these problems require little space to solve. In order to maximize the credit you receive, show all of your steps, write neatly and give some reaso ...
Solutions - Math Berkeley
... (a) If AB = 0 for two square matrices A, B, then either A = 0 or B = 0. (b) The set P2 [X, Y ] of all polynomials in X and Y of degree at most 2 (together with the usual addition and multiplication by a constant) is a vector space of dimension 6. Proof. ...
... (a) If AB = 0 for two square matrices A, B, then either A = 0 or B = 0. (b) The set P2 [X, Y ] of all polynomials in X and Y of degree at most 2 (together with the usual addition and multiplication by a constant) is a vector space of dimension 6. Proof. ...
Notes on Matrix Multiplication and the Transitive Closure
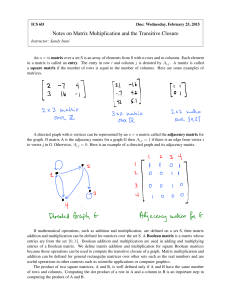
... length k − 1 from vertex i to vertex j. We will show that (Ak )i,j = 1 if and only if there is a walk of length k in G from vertex i to vertex j. Suppose that (Ak )i,j = 1. Since Ak = Ak−1 · A, by definition of matrix multiplication, (Ak )i,j = (Ak−1 )i,1 A1,j + (Ak−1 )i,2 A2,j + · · · + (Ak−1 )i,n ...
... length k − 1 from vertex i to vertex j. We will show that (Ak )i,j = 1 if and only if there is a walk of length k in G from vertex i to vertex j. Suppose that (Ak )i,j = 1. Since Ak = Ak−1 · A, by definition of matrix multiplication, (Ak )i,j = (Ak−1 )i,1 A1,j + (Ak−1 )i,2 A2,j + · · · + (Ak−1 )i,n ...
Caches and matrix multiply performance; norms
... (2N 2 + 2N 3 )b2 = 2n2 + 2n3 /b element transfers into fast memory. That is, the number of transfers into fast memory is about 1/b times the total number of element transfers. We could consider using different block shapes, but it turns out that roughly square blocks are roughly optimal. It also tur ...
... (2N 2 + 2N 3 )b2 = 2n2 + 2n3 /b element transfers into fast memory. That is, the number of transfers into fast memory is about 1/b times the total number of element transfers. We could consider using different block shapes, but it turns out that roughly square blocks are roughly optimal. It also tur ...
Algebra II Quiz 6
... MISMATCH. This means the multiplication is not possible. Why is that? The dimensions of each matrix are 3 x 1 and 3 x 1. Because the inner dimensions are not the same, it is NOT possible to multiply. Finding the Inverse of a Matrix: Enter the matrix in your calculator. Use (2nd)MATRIX 1A (or whichev ...
... MISMATCH. This means the multiplication is not possible. Why is that? The dimensions of each matrix are 3 x 1 and 3 x 1. Because the inner dimensions are not the same, it is NOT possible to multiply. Finding the Inverse of a Matrix: Enter the matrix in your calculator. Use (2nd)MATRIX 1A (or whichev ...
Non-negative matrix factorization

NMF redirects here. For the bridge convention, see new minor forcing.Non-negative matrix factorization (NMF), also non-negative matrix approximation is a group of algorithms in multivariate analysis and linear algebra where a matrix V is factorized into (usually) two matrices W and H, with the property that all three matrices have no negative elements. This non-negativity makes the resulting matrices easier to inspect. Also, in applications such as processing of audio spectrograms non-negativity is inherent to the data being considered. Since the problem is not exactly solvable in general, it is commonly approximated numerically.NMF finds applications in such fields as computer vision, document clustering, chemometrics, audio signal processing and recommender systems.








![perA= ]TY[aMi)` « P^X = ^ = xW - American Mathematical Society](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/014142501_1-23faff90adae754bbfcc6088c2128850-300x300.png)