File
... The gods were differentiated from heroes not so much by their strength as by their supernatural power. They demanded worship from heroes and people alike and, in return, were able to perform miracles, offer supernatural protection, or give magical gifts. These supernatural beings often disagreed wit ...
... The gods were differentiated from heroes not so much by their strength as by their supernatural power. They demanded worship from heroes and people alike and, in return, were able to perform miracles, offer supernatural protection, or give magical gifts. These supernatural beings often disagreed wit ...
Mycenaeans
... identity. Greeks grew up thinking of themselves as residents of a given place or town and only secondary as Greeks sharing a common culture and language with other inhabitants of the peninsula. ...
... identity. Greeks grew up thinking of themselves as residents of a given place or town and only secondary as Greeks sharing a common culture and language with other inhabitants of the peninsula. ...
classical civilisation
... If you displeased the gods the Greeks believed that you would be punished. There are many stories in Greek mythology where people have been punished for being to proud or ambitious. ...
... If you displeased the gods the Greeks believed that you would be punished. There are many stories in Greek mythology where people have been punished for being to proud or ambitious. ...
Ancient Greece (1 of 4) - Pineda Ancient History
... Greece's geography directly shaped its traditions and customs. The sea was like a liquid highway helping Greek sailors travel and trade with other societies. 75% of Greece is covered in mountains. These mountains made it difficult for Greece to unite. Unable to unite politically they developed into ...
... Greece's geography directly shaped its traditions and customs. The sea was like a liquid highway helping Greek sailors travel and trade with other societies. 75% of Greece is covered in mountains. These mountains made it difficult for Greece to unite. Unable to unite politically they developed into ...
File
... lesson, natural phenomenon, human conflict) 2. An explanation…….does it explain how something came to be? If so, how? 3. Connection……does this myth connect to another story or yourself? (place, time, meaning) ...
... lesson, natural phenomenon, human conflict) 2. An explanation…….does it explain how something came to be? If so, how? 3. Connection……does this myth connect to another story or yourself? (place, time, meaning) ...
Ancient Greece Eras
... The Mycenaean Greeks were Indo-Europeans who came to the area around 1900 B.C. They were warriors and took over the mainland of Greece. The Mycenaean fought against one another. This, coupled with an earthquake and invasion from the north, resulted in a collapse of the civilization by 1100 B.C. Gree ...
... The Mycenaean Greeks were Indo-Europeans who came to the area around 1900 B.C. They were warriors and took over the mainland of Greece. The Mycenaean fought against one another. This, coupled with an earthquake and invasion from the north, resulted in a collapse of the civilization by 1100 B.C. Gree ...
Greece is a land of mountains and dry, rocky soil.
... •Women and slaves could not vote •People voted for a council of 500 men •Citizens voted after each law was discussed •If enough people voted for the law, the law would pass ...
... •Women and slaves could not vote •People voted for a council of 500 men •Citizens voted after each law was discussed •If enough people voted for the law, the law would pass ...
Writing A Greek Myth
... Gods tended to have special powers; for instance, Zeus could transform himself into other forms, such as animals, and was said to be behind the rain and drought. Meanwhile, the heroes were also remarkable. Heracles, for example, was a demi-God -his father was Zeus but his mother was a mortal -- and ...
... Gods tended to have special powers; for instance, Zeus could transform himself into other forms, such as animals, and was said to be behind the rain and drought. Meanwhile, the heroes were also remarkable. Heracles, for example, was a demi-God -his father was Zeus but his mother was a mortal -- and ...
Mythology
... • The time period around 1400 B.C. was an era where Mycenae, the traditional home of Agamemnon, brother of Menelaus and leader of the Greek warriors in Troy, dominated the mainland, and his island of Crete assumed the political and military status of master of the eastern Mediterranean. A golden age ...
... • The time period around 1400 B.C. was an era where Mycenae, the traditional home of Agamemnon, brother of Menelaus and leader of the Greek warriors in Troy, dominated the mainland, and his island of Crete assumed the political and military status of master of the eastern Mediterranean. A golden age ...
The_Greeks - DebHarperPortfolio
... • The adventures of Odysseus returning from Trojan wars to his wife Penelope • Land of the Lotus eaters • Circe the enchantress • Polyphemus the Cyclops • Scylla and Charybdids • The Sirens • Zeus v Aphrodite ...
... • The adventures of Odysseus returning from Trojan wars to his wife Penelope • Land of the Lotus eaters • Circe the enchantress • Polyphemus the Cyclops • Scylla and Charybdids • The Sirens • Zeus v Aphrodite ...
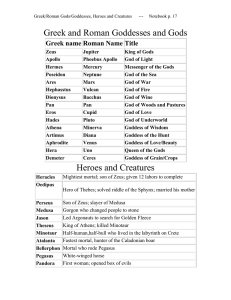
Greek and Roman Goddesses and Gods
... Gorgon who changed people to stone Led Argonauts to search for Golden Fleece King of Athens; killed Minotaur Half-human,half-bull who lived in the labyrinth on Crete Fastest mortal, hunter of the Caladonian boar Mortal who rode Pegasus White-winged horse First woman; opened box of evils ...
... Gorgon who changed people to stone Led Argonauts to search for Golden Fleece King of Athens; killed Minotaur Half-human,half-bull who lived in the labyrinth on Crete Fastest mortal, hunter of the Caladonian boar Mortal who rode Pegasus White-winged horse First woman; opened box of evils ...
File - Brother Murray Hunt
... All questions are either T/F or Multiple Choice/Multiple Answer. 1. The Minoan civilization disappeared just after the Trojan War came to a close. 2. Which of the following were Greeks who fought against Troy? a. Priam b. Agamemnon c. Menelaus d. Odysseus 3. Find Troy on the map. The city of Troy wa ...
... All questions are either T/F or Multiple Choice/Multiple Answer. 1. The Minoan civilization disappeared just after the Trojan War came to a close. 2. Which of the following were Greeks who fought against Troy? a. Priam b. Agamemnon c. Menelaus d. Odysseus 3. Find Troy on the map. The city of Troy wa ...
ancient greece - Barren County Schools
... ___________________ overthrew them. This was more of a direct _________________. a. The ________________ was the major political institution. All citizens were __________and guaranteed __________ and could belong to the Assembly. The Assembly passed _______ and acted as the ________________. They ch ...
... ___________________ overthrew them. This was more of a direct _________________. a. The ________________ was the major political institution. All citizens were __________and guaranteed __________ and could belong to the Assembly. The Assembly passed _______ and acted as the ________________. They ch ...
The Curse of the House of Atreus
... Standing shoulder-to shoulder with the incestuous brood of Oedipus is the House of Atreus, the ancient royal family of Mycenae in Greece. Arguably the most important family in western literature, the descendants of Atreus suffered from an ancestral crime, variously described, that caused disastrous ...
... Standing shoulder-to shoulder with the incestuous brood of Oedipus is the House of Atreus, the ancient royal family of Mycenae in Greece. Arguably the most important family in western literature, the descendants of Atreus suffered from an ancestral crime, variously described, that caused disastrous ...
Ancient Greece
... 5. Athletic festivals such as the Olympic Games had religious connection by honoring various of the Greek Gods. 6. The funeral games (described by Stull and Lewis) describe specific events as well as role delineation within sport. 7. Achilles (Iliad) and Odysseus (Odyssey) represented the man of act ...
... 5. Athletic festivals such as the Olympic Games had religious connection by honoring various of the Greek Gods. 6. The funeral games (described by Stull and Lewis) describe specific events as well as role delineation within sport. 7. Achilles (Iliad) and Odysseus (Odyssey) represented the man of act ...
Name of Greek God, Goddess or Creature
... •How many gods and goddesses did the Ancient Greeks believe in? •How many of them lived on Mt. Olympus? •Who was the leader of the all the gods? • In what ways did Ancient Greeks worship the gods? ...
... •How many gods and goddesses did the Ancient Greeks believe in? •How many of them lived on Mt. Olympus? •Who was the leader of the all the gods? • In what ways did Ancient Greeks worship the gods? ...
Chapter 4 Power
... rocks were what became Greece. What is the land like of Ancient Greece prior to expanding to entire Mediterranean? ...
... rocks were what became Greece. What is the land like of Ancient Greece prior to expanding to entire Mediterranean? ...
The Ancient Greeks
... husbands. If the people of Athens felt that a politician was becoming too powerful, they wrote his name on piece of pottery (called ostrakon) and if he got enough of these, he was exiled for 10 years. Athens had a strong army and a very powerful navy. It was a great trading centre ...
... husbands. If the people of Athens felt that a politician was becoming too powerful, they wrote his name on piece of pottery (called ostrakon) and if he got enough of these, he was exiled for 10 years. Athens had a strong army and a very powerful navy. It was a great trading centre ...
Greek Notes
... reflects harmony in the universe Most famous work is the Parthenon, dedicated to Athena Simple rectangle, tall columns, sloping roof, delicate curves ...
... reflects harmony in the universe Most famous work is the Parthenon, dedicated to Athena Simple rectangle, tall columns, sloping roof, delicate curves ...
Social Studies Study Guide: Chapter 6
... -Where were the Mycenaeans from? mainland of Greece -Minoans gained power through trade and the Mycenaeans gained power through conquest. The Trojan War: p.171 -The Trojan War was fought between the Greeks and the Trojans (from Troy). -What did the Greeks give the Trojans as a gift that helped them ...
... -Where were the Mycenaeans from? mainland of Greece -Minoans gained power through trade and the Mycenaeans gained power through conquest. The Trojan War: p.171 -The Trojan War was fought between the Greeks and the Trojans (from Troy). -What did the Greeks give the Trojans as a gift that helped them ...
Greek Mythology Notes
... Goddess worship replaced by male sky god Goddess remains in many myths By 1000 B.C.Zeus, the father god, was supreme. ...
... Goddess worship replaced by male sky god Goddess remains in many myths By 1000 B.C.Zeus, the father god, was supreme. ...
Chapter 2 The Cultural Context of
... continued… • in cultural matters the aristocracy clung to power - as the most literate citizens, its members were the creators or sponsors of most Greek literature, art, and philosophy. • What we know of Greek culture comes from the aristoi, the free male citizens descended from old families • there ...
... continued… • in cultural matters the aristocracy clung to power - as the most literate citizens, its members were the creators or sponsors of most Greek literature, art, and philosophy. • What we know of Greek culture comes from the aristoi, the free male citizens descended from old families • there ...
Mycenae

Mycenae (/maɪˈsiːni/; Greek: Μυκῆναι Mykēnai or Μυκήνη Mykēnē) is an archaeological site in Greece, located about 90 kilometres (56 miles) southwest of Athens, in the north-eastern Peloponnese. Argos is 11 kilometres (7 miles) to the south; Corinth, 48 kilometres (30 miles) to the north. From the hill on which the palace was located, one can see across the Argolid to the Saronic Gulf.In the second millennium BC, Mycenae was one of the major centres of Greek civilization, a military stronghold which dominated much of southern Greece. The period of Greek history from about 1600 BC to about 1100 BC is called Mycenaean in reference to Mycenae. At its peak in 1350 BC, the citadel and lower town had a population of 30,000 and an area of 32 hectares.