PyProp - A Python Framework for Propagating the Time
... By solving the equations of classical mechanics, scientists had huge success in predicting planetary trajectories, the motion of rigid bodies, etc. Despite this success, it became inceasingly clear towards the end of the 19th century that classical mechanics was not sufficient to describe motion on t ...
... By solving the equations of classical mechanics, scientists had huge success in predicting planetary trajectories, the motion of rigid bodies, etc. Despite this success, it became inceasingly clear towards the end of the 19th century that classical mechanics was not sufficient to describe motion on t ...
pdf
... The advantage of the symplectic/Hamiltonian viewpoint is that we make use of the arsenal of tools for Hamiltonian systems; see e.g., Abraham and Marsden [1] and Marsden and Ratiu [21]. Most notably, symmetry and conservation laws in Hamiltonian systems are linked via Noether’s theorem: Practically s ...
... The advantage of the symplectic/Hamiltonian viewpoint is that we make use of the arsenal of tools for Hamiltonian systems; see e.g., Abraham and Marsden [1] and Marsden and Ratiu [21]. Most notably, symmetry and conservation laws in Hamiltonian systems are linked via Noether’s theorem: Practically s ...
lecture notes on applied mathematics
... magnitude scale for the brightness of stars) but we can convert this to an underlying linear scale. In other cases, qualitative scales are used (such as the Beaufort wind force scale), but these scales (“leaves rustle” or “umbrella use becomes difficult”) are not susceptible to a quantitative analys ...
... magnitude scale for the brightness of stars) but we can convert this to an underlying linear scale. In other cases, qualitative scales are used (such as the Beaufort wind force scale), but these scales (“leaves rustle” or “umbrella use becomes difficult”) are not susceptible to a quantitative analys ...
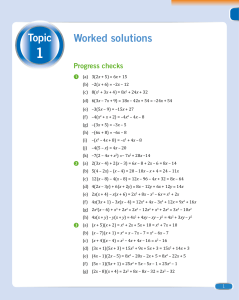
Topic 1 - Illuminate Publishing
... Divide top and bottom by 8xy4. Divide top and bottom by 5c. Divide top and bottom by 4x. Divide top and bottom by 3pqr. Divide top and bottom by 2x2y. Divide top and bottom by 9abc. Divide top and bottom by (x + 5). Divide top and bottom by (x + 3)(x + 5). ...
... Divide top and bottom by 8xy4. Divide top and bottom by 5c. Divide top and bottom by 4x. Divide top and bottom by 3pqr. Divide top and bottom by 2x2y. Divide top and bottom by 9abc. Divide top and bottom by (x + 5). Divide top and bottom by (x + 3)(x + 5). ...
Parabola
... Ex 3: Write the standard form of the equation of the parabola with focus at (0, 3) and vertex at the origin. Since the focus is on the y axis,(and vertex at the origin) the parabola goes up or down… x2 = 4py Since p = 3, the standard form of the equation is x2 = 12y Ex 4: Write the standard form of ...
... Ex 3: Write the standard form of the equation of the parabola with focus at (0, 3) and vertex at the origin. Since the focus is on the y axis,(and vertex at the origin) the parabola goes up or down… x2 = 4py Since p = 3, the standard form of the equation is x2 = 12y Ex 4: Write the standard form of ...