Membrane and Transport
... concentration of solute same inside cell as outside (balanced) water moves in and out When things transport to attempt to become isotonic it’s called: moving across the concentration gradient ...
... concentration of solute same inside cell as outside (balanced) water moves in and out When things transport to attempt to become isotonic it’s called: moving across the concentration gradient ...
Biological Membranes
... This causes an electrical as well as chemical gradient across the cell membrane – an electrochemical gradient This gradient stores energy for the cell and can be used to help drive other transport ...
... This causes an electrical as well as chemical gradient across the cell membrane – an electrochemical gradient This gradient stores energy for the cell and can be used to help drive other transport ...
Osmosis and diffusion webquest
... After salt (in reality there would be many Na+ and Cl- ions) is added, how do the water molecules move across the membrane? Is there an overall direction of movement (where do most of the molecules end up?) ...
... After salt (in reality there would be many Na+ and Cl- ions) is added, how do the water molecules move across the membrane? Is there an overall direction of movement (where do most of the molecules end up?) ...
Review for Cell Theory and Cell Organelle Exam
... Describe the role of the nucleus in cell activity Explain the role of each organelle in the cell Summarize the importance of mitochondria in eukaryotic cells Identify 3 structures on plant cells that are not present in animal cells ...
... Describe the role of the nucleus in cell activity Explain the role of each organelle in the cell Summarize the importance of mitochondria in eukaryotic cells Identify 3 structures on plant cells that are not present in animal cells ...
cell wall - HCC Learning Web
... • Chloroplasts contain the green pigment chlorophyll, as well as enzymes and other molecules that function in photosynthesis • Chloroplasts are found in leaves and other green organs of plants and in algae • Chloroplast structure includes – Thylakoids, membranous sacs, stacked to form a granum – Str ...
... • Chloroplasts contain the green pigment chlorophyll, as well as enzymes and other molecules that function in photosynthesis • Chloroplasts are found in leaves and other green organs of plants and in algae • Chloroplast structure includes – Thylakoids, membranous sacs, stacked to form a granum – Str ...
BIO201 Lecture 5
... endomembrane system – membranes inside and around a eukaryotic cell, related through direct contact or by transfer of membranous ...
... endomembrane system – membranes inside and around a eukaryotic cell, related through direct contact or by transfer of membranous ...
Cell Organelle Web Quest
... Objective: Upon completion of this activity, you should be able to describe the cell and identify its parts (organelles). You should also be able to distinguish between plant and animal cells. PART I https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=URUJD5NEXC8 Watch the video “Biology: Cell Structure.” Turn on subti ...
... Objective: Upon completion of this activity, you should be able to describe the cell and identify its parts (organelles). You should also be able to distinguish between plant and animal cells. PART I https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=URUJD5NEXC8 Watch the video “Biology: Cell Structure.” Turn on subti ...
Chapter 5
... • Isosmotic regulation involves keeping cells isotonic with their environment – Marine organisms adjust internal concentration to match sea water – Terrestrial animals circulate isotonic fluid ...
... • Isosmotic regulation involves keeping cells isotonic with their environment – Marine organisms adjust internal concentration to match sea water – Terrestrial animals circulate isotonic fluid ...
BSCI 124: LECTURE 2
... • Each cell is functionally independent – it can live on its own under the right conditions – Uses sugars to get energy and stay alive – Contains all necessary info to replicate produce a multicellular organism – Can make a whole plant from a single cell! ...
... • Each cell is functionally independent – it can live on its own under the right conditions – Uses sugars to get energy and stay alive – Contains all necessary info to replicate produce a multicellular organism – Can make a whole plant from a single cell! ...
Active Transport
... • Movement from low concentration to high concentration – moving up the hill ...
... • Movement from low concentration to high concentration – moving up the hill ...
Flow Cytometry - Austin Community College
... and eosinophils produce a great deal of side scatter due to their cytoplasmic granules. ...
... and eosinophils produce a great deal of side scatter due to their cytoplasmic granules. ...
Cell biology topics
... function). The significance of 'Detoxification'. How is a protein produced in the interior of the reticulum, what happens there? Translocators. 4. 2. The significance and possible ways of protein molecule signalling. The role of protein conformation. Chaperones (heat-shock proteins). Proteasomes. 4. ...
... function). The significance of 'Detoxification'. How is a protein produced in the interior of the reticulum, what happens there? Translocators. 4. 2. The significance and possible ways of protein molecule signalling. The role of protein conformation. Chaperones (heat-shock proteins). Proteasomes. 4. ...
Chapter 9
... Protist – a single or many celled organism that lies in moist or wet surroundings Eukaryotic Plant like Animal like Fungus like Some contain chlorophyll Some do not have chlorophyll ...
... Protist – a single or many celled organism that lies in moist or wet surroundings Eukaryotic Plant like Animal like Fungus like Some contain chlorophyll Some do not have chlorophyll ...
down the concentration gradient
... • What will happen to a cell that is too hypotonic? – The cell will burst! ...
... • What will happen to a cell that is too hypotonic? – The cell will burst! ...
BI 112 VITAL VOCAB #2 Be sure to review the SCIENTIFIC
... PARTS OF THE CELL – Know the FUNCTION of each of these parts, what it’s basic structure is (made of membrane, etc), what types of organisms it is found in (prokaryote vs animal vs plant), and be able to identify it on a picture of a cell. 1. Cell membrane 2. Cell wall 3. Cytoplasm 4. Nucleus, nuclea ...
... PARTS OF THE CELL – Know the FUNCTION of each of these parts, what it’s basic structure is (made of membrane, etc), what types of organisms it is found in (prokaryote vs animal vs plant), and be able to identify it on a picture of a cell. 1. Cell membrane 2. Cell wall 3. Cytoplasm 4. Nucleus, nuclea ...
Ch. 2-2: The Organelles of the Cell ER, Golgi Complex, Lysosomes
... 1. Organelles are very _________ in size and can only be observed with a __________. 2. They each have a specific ___________and are found throughout the ____________. 3. ___________ takes part in nearly every cell _______________. 4. What makes these proteins? ________________ 5. RIbosomes do not h ...
... 1. Organelles are very _________ in size and can only be observed with a __________. 2. They each have a specific ___________and are found throughout the ____________. 3. ___________ takes part in nearly every cell _______________. 4. What makes these proteins? ________________ 5. RIbosomes do not h ...
Cell Theory and Cell Structure
... A series of flattened sacs where newly made fats and proteins from the E.R. are repackaged and shipped to the plasma membrane. (Lysosomes are Golgi-derived vesicles, ...
... A series of flattened sacs where newly made fats and proteins from the E.R. are repackaged and shipped to the plasma membrane. (Lysosomes are Golgi-derived vesicles, ...
Cell structure
... Structure: Vacuoles are membrane bound containers filled with water and other molecules. They may contain solids which have been engulfed. Their shape and size depend on the needs of the cell. Function: The function and significance of vacuoles depends on the type of cell and include: isolating mate ...
... Structure: Vacuoles are membrane bound containers filled with water and other molecules. They may contain solids which have been engulfed. Their shape and size depend on the needs of the cell. Function: The function and significance of vacuoles depends on the type of cell and include: isolating mate ...
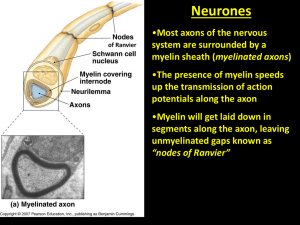
Myelin Sheaths Plant Hormone Intro
... • The part of a shoot sensitive to light is the tip. • The part of the shoot which responds to the stimulus is the part just below the tip. • These two parts of the shoot must be communicating with one another by means hormones. • Plant hormones are chemical that affect the activities of particular ...
... • The part of a shoot sensitive to light is the tip. • The part of the shoot which responds to the stimulus is the part just below the tip. • These two parts of the shoot must be communicating with one another by means hormones. • Plant hormones are chemical that affect the activities of particular ...
Gram positive cell wall
... to enter the cell while keeping toxins and waste products out. The plasma membrane is a double phospholipid membrane, or a lipid bilayer, with the nonpolar hydrophobic tails pointing toward the inside of the membrane and the polar hydrophilic heads forming the inner and outer surfaces of the membran ...
... to enter the cell while keeping toxins and waste products out. The plasma membrane is a double phospholipid membrane, or a lipid bilayer, with the nonpolar hydrophobic tails pointing toward the inside of the membrane and the polar hydrophilic heads forming the inner and outer surfaces of the membran ...
Lecture 8, Feb 5 - web.biosci.utexas.edu
... Nearly all kinds of cells (prokaryotic and eukaryotic) have a coating external to the plasma of membrane. Depending on the kind of cell and its location, this coating may be used to: - shield the cell from physical and/or chemical agents in its environment, ...
... Nearly all kinds of cells (prokaryotic and eukaryotic) have a coating external to the plasma of membrane. Depending on the kind of cell and its location, this coating may be used to: - shield the cell from physical and/or chemical agents in its environment, ...
Cytoplasmic streaming

Cytoplasmic streaming, also called protoplasmic streaming and cyclosis, is the directed flow of cytosol (the liquid component of the cytoplasm) and organelles around large fungal and plant cells through the mediation of actin. This movement aids in the delivery of organelles, nutrients, metabolites, genetic information, and other materials to all parts of the cell. Cytoplasmic streaming occurs along actin filaments in the cytoskeleton of the cell.Cytoplasmic streaming was first discovered in the 1830s. The scientific breakthrough assisted scientists in developing an understanding of the different roles of cells and how they function as the basic operating systems of life.This process occurs through the operation of motor proteins called myosins.These proteins use energy of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) to act as a molecular motor, which slides along actin filaments. This works in a manner that tows the organelles and other cytoplasmic contents in the same direction. Myosin proteins consist of two conjoined proteins. If one protein remains attached to the substrate, the substance acted upon by the protein, such as a microfilament, has the ability to move organelles through the cytoplasm.The green alga genus Chara and other genera in the Division Charophyta, such as Coleochaete, are thought to be the closest relatives of land plants. These haploid organisms contain some of the largest plant cells on earth, a single cell of which can reach up to 10 cm in length. The large size of these cells demands an efficient means to distribute resources, which is enabled via cytoplasmic streaming.Cytoplasmic streaming is strongly dependent upon intracellular pH and temperature. It has been observed that the effect of temperature on cytoplasmic streaming created linear variance and dependence at different high temperatures in comparison to low temperatures. This process is complicated, with temperature alterations in the system increasing its efficiency, with other factors such as the transport of ions across the membrane being simultaneously affected. This is due to cells homeostasis depending upon active transport which may be affected at some critical temperatures.In plant cells, chloroplasts may be moved around with the stream, possibly to a position of optimum light absorption for photosynthesis. The rate of motion is usually affected by light exposure, temperature, and pH levels.In reference to pH, because actin and myosin are both proteins, strong dependence on pH is expected. The optimal pH at which cytoplasmic streaming is highest, is achieved at neutral pH and decreases at both low and high pH.The flow of cytoplasm may be stopped by:Adding Lugol's iodine solutionAdding Cytochalasin D (dissolved in dimethyl sulfoxide)↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑