Document
... own DNA. The DNA in the nucleus does not instruct the cell to make mitochondria or chloroplasts. The endosymbiosis theory proposes that some early prokaryotes evolved internal cell membranes which eventually led to the development of primitive eukaryotic cells. ...
... own DNA. The DNA in the nucleus does not instruct the cell to make mitochondria or chloroplasts. The endosymbiosis theory proposes that some early prokaryotes evolved internal cell membranes which eventually led to the development of primitive eukaryotic cells. ...
Cell Organelle Function Review Interactive
... the cell membrane that contains organelles to carry out specific jobs and found in all cells. Transport highway surrounded by ribosomes where protein synthesis occurs. ...
... the cell membrane that contains organelles to carry out specific jobs and found in all cells. Transport highway surrounded by ribosomes where protein synthesis occurs. ...
CP Bio PPT\Ch.7 - Cells\Sec 3
... The concentration of a solution is defined as the a. volume of solute in a given mass of solution. b. mass of solute in a given volume of solution. c. mass of solution in a given volume of solute. ...
... The concentration of a solution is defined as the a. volume of solute in a given mass of solution. b. mass of solute in a given volume of solution. c. mass of solution in a given volume of solute. ...
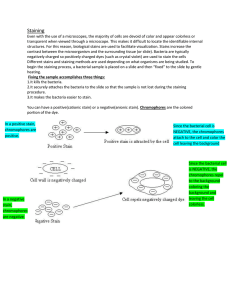
Gram Stain
... Some bacterial stains are simple, meaning only one type of stain is used. Simple stains are typically easy to perform and provide basic information about morphology. However, simple stains can't typically identify the type of bacteria in the sample. Differential stains are often used to identify bac ...
... Some bacterial stains are simple, meaning only one type of stain is used. Simple stains are typically easy to perform and provide basic information about morphology. However, simple stains can't typically identify the type of bacteria in the sample. Differential stains are often used to identify bac ...
Cells and Organisation
... Distance P to Q on the diagram is the diameter of the cell. This distance was measured on three cells using a microscope. The results were as follows: cell 1: 63 micrometres cell 2: 78 micrometres cell 3: 69 micrometres Calculate the average diameter of these cells. Show clearly how you work out you ...
... Distance P to Q on the diagram is the diameter of the cell. This distance was measured on three cells using a microscope. The results were as follows: cell 1: 63 micrometres cell 2: 78 micrometres cell 3: 69 micrometres Calculate the average diameter of these cells. Show clearly how you work out you ...
chapter 7 section 3 notes
... Cell membranes have proteins that act as carriers, or channels, making it easy for certain molecules to cross. Molecules that cannot directly diffuse across the membrane pass through special protein channels in a process known as facilitated diffusion. ...
... Cell membranes have proteins that act as carriers, or channels, making it easy for certain molecules to cross. Molecules that cannot directly diffuse across the membrane pass through special protein channels in a process known as facilitated diffusion. ...
Syllabus for Medical Cell Biology
... principles, focusing on cells, but also applying modern physics, chemistry and test biology the experimental method. It deals with the structure and functions or the interaction of cell components by using different approaches, namely at the whole cell, subcellular and molecular levels, it is concer ...
... principles, focusing on cells, but also applying modern physics, chemistry and test biology the experimental method. It deals with the structure and functions or the interaction of cell components by using different approaches, namely at the whole cell, subcellular and molecular levels, it is concer ...
fundamentals-of-human-physiology-4th-edition-lauralee
... Cellular respiration refers collectively to the intracellular reactions in which energy-rich molecules are broken down to form ATP, using O2 and producing CO2 in the process. Oxidative phosphorylation refers to the process by which ATP is synthesized using the energy released by electrons as they ar ...
... Cellular respiration refers collectively to the intracellular reactions in which energy-rich molecules are broken down to form ATP, using O2 and producing CO2 in the process. Oxidative phosphorylation refers to the process by which ATP is synthesized using the energy released by electrons as they ar ...
Plant Cell Walls: Basics of Structure, Chemistry, Accessibility and the
... D-mannopyranose and D-glucopyranose units. Hemicelluloses are amorphous, branched, single-chain polysaccharides and are not particularly recalcitrant to conversion. Hemicellulose chains are thought to interact with more than one cellulose fibril so that they form non-covalent cross-links between cel ...
... D-mannopyranose and D-glucopyranose units. Hemicelluloses are amorphous, branched, single-chain polysaccharides and are not particularly recalcitrant to conversion. Hemicellulose chains are thought to interact with more than one cellulose fibril so that they form non-covalent cross-links between cel ...
3-3, 3-4, 3-5 membrane, diff, trans
... There are other molecules embedded in the membrane. The fluid mosaic model describes the membrane. cell membrane ...
... There are other molecules embedded in the membrane. The fluid mosaic model describes the membrane. cell membrane ...
EMBO Workshop on Cell Size Regulation
... Suckjoon Jun - Deconstructing cell size control into physiological modules in bacteria Petra Levin – Fat makes bacteria fatter: Flux through lipid synthesis links bacterial size to nutrient availability Short talk – Leigh Harris - Relative rates of surface and volume synthesis set bacterial ce ...
... Suckjoon Jun - Deconstructing cell size control into physiological modules in bacteria Petra Levin – Fat makes bacteria fatter: Flux through lipid synthesis links bacterial size to nutrient availability Short talk – Leigh Harris - Relative rates of surface and volume synthesis set bacterial ce ...
Vacuole metabolites
... herbivore, then the two chemicals can react forming toxic chemicals (e.g. in garlic, alliin and the enzyme alliinase are normally separated but form allicin if the vacuole is broken) useful for defensive purposes. ...
... herbivore, then the two chemicals can react forming toxic chemicals (e.g. in garlic, alliin and the enzyme alliinase are normally separated but form allicin if the vacuole is broken) useful for defensive purposes. ...
Prokaryotic
... seen 5. Prokaryotic—small, simple, no organelles are seen 6. Eukaryotic—unicellular, organelles present ...
... seen 5. Prokaryotic—small, simple, no organelles are seen 6. Eukaryotic—unicellular, organelles present ...
Unit 1 Notes
... cytoplasm, ribosomes and mitochondria. They are however not green – they don’t photosynthesise and so don’t contain chloroplasts. Fungi need to feed on other organisms to obtain their energy source. Fungi are involved in decomposition - recycling nutrients from dead organisms back into the ecosystem ...
... cytoplasm, ribosomes and mitochondria. They are however not green – they don’t photosynthesise and so don’t contain chloroplasts. Fungi need to feed on other organisms to obtain their energy source. Fungi are involved in decomposition - recycling nutrients from dead organisms back into the ecosystem ...
Candida albicans Iff11, a Secreted Protein Required for Cell Wall
... wall is comprised of an inner layer consisting of glucans and chitin, which provide mechanical strength, and an outer layer enriched in mannoproteins (7, 15, 20, 26) that determine cell surface properties and play a vital role in the host-fungal interaction. The major class of cell surface mannoprot ...
... wall is comprised of an inner layer consisting of glucans and chitin, which provide mechanical strength, and an outer layer enriched in mannoproteins (7, 15, 20, 26) that determine cell surface properties and play a vital role in the host-fungal interaction. The major class of cell surface mannoprot ...
7-3 Cell Boundaries - River Dell Regional School District
... Endocytosis and Exocytosis Endocytosis is the process of taking material into the cell. ...
... Endocytosis and Exocytosis Endocytosis is the process of taking material into the cell. ...
Cell Membranes Osmosis and Diffusion
... • Salt is a solute, when it is concentrated inside or outside the cell, it will draw the water in its direction. This is also why you get thirsty after eating something salty. ...
... • Salt is a solute, when it is concentrated inside or outside the cell, it will draw the water in its direction. This is also why you get thirsty after eating something salty. ...
Plant hormones – Chapter 27
... Some seeds that require special environmental conditions to germinate, such as exposure to light or cold temperatures, will break dormancy if they are treated with gibberellins Gibberellins support the growth of cereal seedlings by stimulating the synthesis of digestive enzymes that mobilize sto ...
... Some seeds that require special environmental conditions to germinate, such as exposure to light or cold temperatures, will break dormancy if they are treated with gibberellins Gibberellins support the growth of cereal seedlings by stimulating the synthesis of digestive enzymes that mobilize sto ...
The Plant Kingdom
... The pistil consists of three parts: the stigma, style, and ovary. The stigma is the sticky part that traps and holds the pollen. The style is the tube-like structure that holds up the stigma. The ovary and the ovule are at the bottom of the style. ...
... The pistil consists of three parts: the stigma, style, and ovary. The stigma is the sticky part that traps and holds the pollen. The style is the tube-like structure that holds up the stigma. The ovary and the ovule are at the bottom of the style. ...
Sickle Cell Anemia
... 2. Why has natural selection NOT acted against the sickle cell allele in Africa by reduced its frequency in the African population? (In other words, why is this fatal allele so common in Africa?) The defective allele is common in central Africa because people who are heterozygous (Aa) for the sickle ...
... 2. Why has natural selection NOT acted against the sickle cell allele in Africa by reduced its frequency in the African population? (In other words, why is this fatal allele so common in Africa?) The defective allele is common in central Africa because people who are heterozygous (Aa) for the sickle ...
315-332
... exert some influence over the direction of plant growth. Light has been shown to exert control over the positioning of new cell walls in apical cells of fern gametophytes (Racusen, 2002) in such a way as to cause two dimensional growth. A plant will then exhibit an upward growth habit in addition to ...
... exert some influence over the direction of plant growth. Light has been shown to exert control over the positioning of new cell walls in apical cells of fern gametophytes (Racusen, 2002) in such a way as to cause two dimensional growth. A plant will then exhibit an upward growth habit in addition to ...
Cell wall
The cell wall is a tough, flexible and sometimes rigid layer that surrounds some types of cells. It surrounds the cell membrane and provides these cells with structural support and protection. In addition, the cell wall acts as a filtering mechanism. A major function of the cell wall is to act as a pressure vessel, preventing over-expansion when water enters the cell. Cell walls are found in plants, fungi and prokaryotic cells but not in mycoplasmas.The composition of the cell wall varies between species and may depend on cell type and developmental stage. The primary cell wall of land plants is composed of the polysaccharides cellulose, hemicellulose and pectin. In bacteria, peptidoglycan forms the cell wall. Archaean cell walls have various compositions, and may be formed of glycoprotein S-layers, pseudopeptidoglycan, or polysaccharides. Fungi possess cell walls made of the glucosamine polymer chitin, and algae typically possess walls made of glycoproteins and polysaccharides. Unusually, diatoms have a cell wall composed of biogenic silica. Often, other accessory molecules are found anchored to the cell wall.