Cellular Transport Vocabulary Words
... 1. Passive Transport- General transport mechanism that requires no energy expenditure by the cell, molecules move with the concentration gradient…… molecules move from an area of high concentration to an area of lower concentration (energy that moves the molecules is provided by Brownian Movement)…… ...
... 1. Passive Transport- General transport mechanism that requires no energy expenditure by the cell, molecules move with the concentration gradient…… molecules move from an area of high concentration to an area of lower concentration (energy that moves the molecules is provided by Brownian Movement)…… ...
Mitosis PPT - Roslyn School
... The cell then enters the “S” or Synthesis stage. During this stage of Interphase DNA replication occurs and the chromosomes make identical copies of themselves. ...
... The cell then enters the “S” or Synthesis stage. During this stage of Interphase DNA replication occurs and the chromosomes make identical copies of themselves. ...
Name
... 7. Observe the cells of the Elodea leaf. Each cell should look like a brick that is part of a large brick wall. Each individual “brick” is one cell. The outer covering of the plant cell is the cell wall. The cell wall surrounds the cell membrane in a plant cell. It is stiff and rigid and provides su ...
... 7. Observe the cells of the Elodea leaf. Each cell should look like a brick that is part of a large brick wall. Each individual “brick” is one cell. The outer covering of the plant cell is the cell wall. The cell wall surrounds the cell membrane in a plant cell. It is stiff and rigid and provides su ...
Cell-Pre-test
... Cells break food into smaller parts, releasing energy. Cells have electricity in the nucleus that travels to the rest of the cell. Cells create energy because they are able to move. The sun sends food through space that turns into energy. ...
... Cells break food into smaller parts, releasing energy. Cells have electricity in the nucleus that travels to the rest of the cell. Cells create energy because they are able to move. The sun sends food through space that turns into energy. ...
Most living things are made up of cells. Cells are the building blocks
... – contains membrane-bound structures called organelles which have specific functions. For example, organelles called mitochondria are responsible for respiration. • A cell membrane. This is a partially permeable membrane enclosing the cytoplasm. The cell membrane: – forms the boundary of the cell – ...
... – contains membrane-bound structures called organelles which have specific functions. For example, organelles called mitochondria are responsible for respiration. • A cell membrane. This is a partially permeable membrane enclosing the cytoplasm. The cell membrane: – forms the boundary of the cell – ...
Cellular Activities
... Made of two layers of phospholipids Has protein ‘gates’ that pass materials in and out. ...
... Made of two layers of phospholipids Has protein ‘gates’ that pass materials in and out. ...
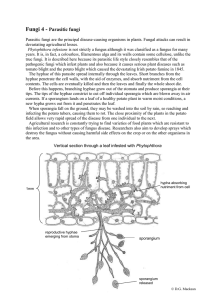
Parasitic fungi - Biology Resources
... Parasitic fungi are the principal disease-causing organisms in plants. Fungal attacks can result in devastating agricultural losses. Phytophthora infestans is not strictly a fungus although it was classified as a fungus for many years. It is, in fact, a colourless, filamentous alga and its walls con ...
... Parasitic fungi are the principal disease-causing organisms in plants. Fungal attacks can result in devastating agricultural losses. Phytophthora infestans is not strictly a fungus although it was classified as a fungus for many years. It is, in fact, a colourless, filamentous alga and its walls con ...
Answer Key: What do I need to know for the test
... 4. Diffusion is the movement of materials (ions, molecules, gases) from an area of high conc. to low conc. Some examples of diffusion are: burning toast, perfume sprayed, food coloring added to water, baggie experiment (starch and iodine) ...
... 4. Diffusion is the movement of materials (ions, molecules, gases) from an area of high conc. to low conc. Some examples of diffusion are: burning toast, perfume sprayed, food coloring added to water, baggie experiment (starch and iodine) ...
CELL CITY INTRODUCTION! Floating around in the cytoplasm are
... 1. The nucleus is a large, round/oval structure usually located near the center of the cell. It is the control center for all the activities of the cell. a. What company or place does the nucleus resemble in a Cell City? ______________________________________________________________________________ ...
... 1. The nucleus is a large, round/oval structure usually located near the center of the cell. It is the control center for all the activities of the cell. a. What company or place does the nucleus resemble in a Cell City? ______________________________________________________________________________ ...
Cell Defense Build a membrane: The membrane of the cell is
... The membrane of the cell is selectively permeable meaning that only some substances are allowed to enter and leave the cell. The membrane is organized into a lipid bilayer. Each layer is made up of macromolecules called phospholipids (a phosphate head and 2 fatty acid tails). The heads are hydroph ...
... The membrane of the cell is selectively permeable meaning that only some substances are allowed to enter and leave the cell. The membrane is organized into a lipid bilayer. Each layer is made up of macromolecules called phospholipids (a phosphate head and 2 fatty acid tails). The heads are hydroph ...
Cell Defense App Guide Sheet Build a membrane: Diffusion
... selectively permeable meaning that only some substances are allowed to enter and leave the cell. The membrane is organized into a lipid bilayer. Each layer is made up of macromolecules called phospholipids (a phosphate head and 2 fatty acid tails). ...
... selectively permeable meaning that only some substances are allowed to enter and leave the cell. The membrane is organized into a lipid bilayer. Each layer is made up of macromolecules called phospholipids (a phosphate head and 2 fatty acid tails). ...
Cells and Their Organelles
... spherical body in the center of the cell. The nucleus controls many of the functions of the cell. It contains DNA assembled into chromosomes, which provides the instructions necessary for the production of other cell components and for the reproduction of life. The nucleus is surrounded by the nucle ...
... spherical body in the center of the cell. The nucleus controls many of the functions of the cell. It contains DNA assembled into chromosomes, which provides the instructions necessary for the production of other cell components and for the reproduction of life. The nucleus is surrounded by the nucle ...
Cell Membranes Practice Test
... A cell with a 75% salt concentration is placed in a hypotonic solution. Which of the following is true? The solution is 25% water. b) The solution is 80% salt. c) Water moves into the cell. d) The cell starts to shrink. a) ...
... A cell with a 75% salt concentration is placed in a hypotonic solution. Which of the following is true? The solution is 25% water. b) The solution is 80% salt. c) Water moves into the cell. d) The cell starts to shrink. a) ...
intro.phys.psu.edu
... "How Do Mobile Phones Work?| Explore | Physics.org." How Do Mobile Phones Work?| Explore | Physics.org. N.p., n.d. ...
... "How Do Mobile Phones Work?| Explore | Physics.org." How Do Mobile Phones Work?| Explore | Physics.org. N.p., n.d. ...
(Gram +ve) bacteria
... Fig. 7.4 The prokaryotic cell is much simpler in structure, lacking a nucleus and the other membrane-enclosed organelles of the eukaryotic cell. ...
... Fig. 7.4 The prokaryotic cell is much simpler in structure, lacking a nucleus and the other membrane-enclosed organelles of the eukaryotic cell. ...
Exam #1 Review
... a battery). When the protons are allowed to flow back through a protein into the cell, the reserve energy can be harnessed to make ATP!! In prokaryotes, this battery-like energy can also be used to power other cellular processes (e.g. flagella rotation and certain transport systems). 5. The cell wal ...
... a battery). When the protons are allowed to flow back through a protein into the cell, the reserve energy can be harnessed to make ATP!! In prokaryotes, this battery-like energy can also be used to power other cellular processes (e.g. flagella rotation and certain transport systems). 5. The cell wal ...
lesson-7-cytoskeleton
... A series of protein fibres keep the cells shape stable by providing a internal framework (cytoskeleton) ...
... A series of protein fibres keep the cells shape stable by providing a internal framework (cytoskeleton) ...
Cell
... or place does the cell membrane resemble in a Cell City? ii)Why do you think so? i) _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ ii) _____________________________________________________________ __________________________ ...
... or place does the cell membrane resemble in a Cell City? ii)Why do you think so? i) _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ ii) _____________________________________________________________ __________________________ ...
Chapter 6 Guided Notes
... Almost all eukaryotic cells have mitochondria. ○ The number of mitochondria is correlated with __________________________________________. ○ Mitochondria have a smooth outer membrane and a convoluted inner membrane with infoldings called ___________________________. ○ The inner membrane encloses the ...
... Almost all eukaryotic cells have mitochondria. ○ The number of mitochondria is correlated with __________________________________________. ○ Mitochondria have a smooth outer membrane and a convoluted inner membrane with infoldings called ___________________________. ○ The inner membrane encloses the ...
lab quiz 4 study guide sp 2015
... 1. Know the Domain, Kingdom and cellular characteristics (structure/organelles) of: a. Amoeba (including how they eat and move) see my ppt notes i. Domain: Eukarya; Kingdom: Protista; a single-celled protozoan (animal-like protist) ii. Cellular structure/organelles: remember no cell wall; there is a ...
... 1. Know the Domain, Kingdom and cellular characteristics (structure/organelles) of: a. Amoeba (including how they eat and move) see my ppt notes i. Domain: Eukarya; Kingdom: Protista; a single-celled protozoan (animal-like protist) ii. Cellular structure/organelles: remember no cell wall; there is a ...
Directions Cell City Introduction
... 2. Road System – Allows for movement throughout the city. 3. City Hall – Controls all the activities of the city. 4. City Planning Office – A place in the city hall where plans are made for the construction of the city. 5. Construction Company – Builds structures and buildings for the city. 6. Deliv ...
... 2. Road System – Allows for movement throughout the city. 3. City Hall – Controls all the activities of the city. 4. City Planning Office – A place in the city hall where plans are made for the construction of the city. 5. Construction Company – Builds structures and buildings for the city. 6. Deliv ...
Commercial uses of cells
... • Give the word equations for aerobic and anaerobic respiration in yeast. • Describe the role of carbon dioxide in bread making • Write a simple word equation to summarise the process of malting in barley grains about to be used in the brewing of beer. • Copy the following sentences choosing the cor ...
... • Give the word equations for aerobic and anaerobic respiration in yeast. • Describe the role of carbon dioxide in bread making • Write a simple word equation to summarise the process of malting in barley grains about to be used in the brewing of beer. • Copy the following sentences choosing the cor ...
biology 30 human anatomy fall 1995 - AVC Online
... ____________________________ microscopy visualizes internal cellular components due to refractive differences. ...
... ____________________________ microscopy visualizes internal cellular components due to refractive differences. ...
Cell wall
The cell wall is a tough, flexible and sometimes rigid layer that surrounds some types of cells. It surrounds the cell membrane and provides these cells with structural support and protection. In addition, the cell wall acts as a filtering mechanism. A major function of the cell wall is to act as a pressure vessel, preventing over-expansion when water enters the cell. Cell walls are found in plants, fungi and prokaryotic cells but not in mycoplasmas.The composition of the cell wall varies between species and may depend on cell type and developmental stage. The primary cell wall of land plants is composed of the polysaccharides cellulose, hemicellulose and pectin. In bacteria, peptidoglycan forms the cell wall. Archaean cell walls have various compositions, and may be formed of glycoprotein S-layers, pseudopeptidoglycan, or polysaccharides. Fungi possess cell walls made of the glucosamine polymer chitin, and algae typically possess walls made of glycoproteins and polysaccharides. Unusually, diatoms have a cell wall composed of biogenic silica. Often, other accessory molecules are found anchored to the cell wall.