6 Viruses and Other Acellular Infectious Agents
... B. Bacterial and archaeal viruses are usually cultivated in broth or agar cultures of suitable host cells; broth cultures are usually clear, while areas of localized destruction (plaques) form in bacterial lawns on agar plates C. Embryonated eggs have long been used to culture animal viruses D. In t ...
... B. Bacterial and archaeal viruses are usually cultivated in broth or agar cultures of suitable host cells; broth cultures are usually clear, while areas of localized destruction (plaques) form in bacterial lawns on agar plates C. Embryonated eggs have long been used to culture animal viruses D. In t ...
1. dia - Figshare
... role in the speciation and evolution of many strains. It also has particular significance for the risk assessment of plants that have been genetically modified for disease resistance by incorporating viral sequences into plant genomes. In the world of RNA viruses the source of recombination during r ...
... role in the speciation and evolution of many strains. It also has particular significance for the risk assessment of plants that have been genetically modified for disease resistance by incorporating viral sequences into plant genomes. In the world of RNA viruses the source of recombination during r ...
Making an Animal Virus in Vitro
... the simplest of the plant viruses (the simplest of all viruses?) 3. cDNA clones are available for RNA genomes 4. Natural expression vectors, since structural genes are under control of separate and strong, “subgenomic”, promoter 5. Purified viruses can be disassembled by detergent into intact nucleo ...
... the simplest of the plant viruses (the simplest of all viruses?) 3. cDNA clones are available for RNA genomes 4. Natural expression vectors, since structural genes are under control of separate and strong, “subgenomic”, promoter 5. Purified viruses can be disassembled by detergent into intact nucleo ...
File
... Lysogenic: Attach to a host, enters, viral DNA becomes part of host cell’s chromosome (provirus formation), onset of disease at lytic cycle. 7. What is a prion? How can they cause diseases? Prion-protein, no DNA or RNA, harmful when it changes molecular shape. 8. Briefly describe 3 ways viruses are ...
... Lysogenic: Attach to a host, enters, viral DNA becomes part of host cell’s chromosome (provirus formation), onset of disease at lytic cycle. 7. What is a prion? How can they cause diseases? Prion-protein, no DNA or RNA, harmful when it changes molecular shape. 8. Briefly describe 3 ways viruses are ...
Viruses Living or Not
... Determined by a lock-and-key fit between the virus and the receptor (proteins) on the surface of a host cell. ...
... Determined by a lock-and-key fit between the virus and the receptor (proteins) on the surface of a host cell. ...
Virus Structure Lecture PowerPoint
... • The SPO Virtual Classrooms offer many educational resources, including practice test questions, review questions, lecture PowerPoints, video tutorials, sample assignments and course syllabi. New materials are continually being developed, so check back frequently, or follow us on Facebook (Science ...
... • The SPO Virtual Classrooms offer many educational resources, including practice test questions, review questions, lecture PowerPoints, video tutorials, sample assignments and course syllabi. New materials are continually being developed, so check back frequently, or follow us on Facebook (Science ...
Viruses, viroids, prions
... • All life forms are parasitized by specific virus • Virus that is not in host cell = virion – Metabolically inert – No respiratory or biosynthetic function ...
... • All life forms are parasitized by specific virus • Virus that is not in host cell = virion – Metabolically inert – No respiratory or biosynthetic function ...
Chapter 8
... 3. Signs are variable and range anywhere from lameness to paralysis and coma. 4. Humans can get West Nile from infected mosquitoes. RHINOPNEUMONITIS 1. Caused by a type of equine herpes virus. 2. Majority of adult horses are infected with this virus from natural exposure. 3. Fever, mucous discharge, ...
... 3. Signs are variable and range anywhere from lameness to paralysis and coma. 4. Humans can get West Nile from infected mosquitoes. RHINOPNEUMONITIS 1. Caused by a type of equine herpes virus. 2. Majority of adult horses are infected with this virus from natural exposure. 3. Fever, mucous discharge, ...
Bacteria vs. Virus KWL and Article
... Definition: Bacteria is plural for Bacterium. A bacterium is a microbe (a microscopic single cell organism) that can be found virtually anywhere. They are in air, the soil, and water, and in and on plants and animals. Function: There are good and bad bacteria. They have useful functions like: making ...
... Definition: Bacteria is plural for Bacterium. A bacterium is a microbe (a microscopic single cell organism) that can be found virtually anywhere. They are in air, the soil, and water, and in and on plants and animals. Function: There are good and bad bacteria. They have useful functions like: making ...
Paracytology and virology 2nd stage Germs: Viruses, Bacteria, and
... diseases, and should they be treated differently? Because viruses, bacteria, and fungi cause many well-known diseases, it is common to confuse them, but they are as different as a mouse and an elephant. A look at the size, structure, reproduction, hosts, and diseases caused by each will shed يفصلs ...
... diseases, and should they be treated differently? Because viruses, bacteria, and fungi cause many well-known diseases, it is common to confuse them, but they are as different as a mouse and an elephant. A look at the size, structure, reproduction, hosts, and diseases caused by each will shed يفصلs ...
Biological hazards
... of the host body. Helicobacter pylori is able to survive in the acidic environment of the human stomach by producing the enzyme urease. Colonization of the stomach lining by this bacterium can lead to Gastric ulcer and cancer. The virulence of various strains of Helicobacter pylori tends to correlat ...
... of the host body. Helicobacter pylori is able to survive in the acidic environment of the human stomach by producing the enzyme urease. Colonization of the stomach lining by this bacterium can lead to Gastric ulcer and cancer. The virulence of various strains of Helicobacter pylori tends to correlat ...
Viruses and Public Health
... though they aren’t cells, they still need a genetic blueprint so they can reproduce. Viruses may have ds DNA, ss DNA, ds RNA, or ssRNA, depending on the virus. ...
... though they aren’t cells, they still need a genetic blueprint so they can reproduce. Viruses may have ds DNA, ss DNA, ds RNA, or ssRNA, depending on the virus. ...
IRRN 1984 9 (6) - James Litsinger
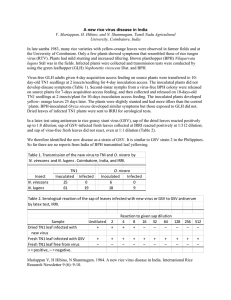
... yellow- orange leaves 25 days later. The plants were slightly stunted and had more tillers than the control `plants. BPH-inoculated Oryza nivara developed similar symptoms but those exposed to GLH did not. Dried leaves of infected TN1 plants were sent to IRRI for serological tests. In a latex test u ...
... yellow- orange leaves 25 days later. The plants were slightly stunted and had more tillers than the control `plants. BPH-inoculated Oryza nivara developed similar symptoms but those exposed to GLH did not. Dried leaves of infected TN1 plants were sent to IRRI for serological tests. In a latex test u ...
BIOL260Exam2 review
... induces tumors? How do viruses induce tumors in animal cells? 22. Understand how genetic re-assortment contributes to new strain of the influenza virus. What is the structure of the influenza virus? What is the role of the H and N spikes? What is meant by the terms antigenic drift and antigenic shif ...
... induces tumors? How do viruses induce tumors in animal cells? 22. Understand how genetic re-assortment contributes to new strain of the influenza virus. What is the structure of the influenza virus? What is the role of the H and N spikes? What is meant by the terms antigenic drift and antigenic shif ...
HIV Worksheet A Lead-in 1 Do you know what the letters
... Step 2 - The viral RNA and core proteins are released into the cytoplasm where reverse transcriptase converts the viral RNA to DNA. Step 3 - Viral DNA, now doublestranded is transported into the nucleus and the nuclear membrane. In the nucleus, the enzyme called integrase fuses it with the host cell ...
... Step 2 - The viral RNA and core proteins are released into the cytoplasm where reverse transcriptase converts the viral RNA to DNA. Step 3 - Viral DNA, now doublestranded is transported into the nucleus and the nuclear membrane. In the nucleus, the enzyme called integrase fuses it with the host cell ...
Viruses and Bacteria
... They cannot reproduce without a host cell. The virus will inject a material into the host cell to take over all it's functions. The cell will eventually reproduce, but reproduces the virus not its original reproductions. ...
... They cannot reproduce without a host cell. The virus will inject a material into the host cell to take over all it's functions. The cell will eventually reproduce, but reproduces the virus not its original reproductions. ...
Bacteria / Virus ppt
... and sometimes lipids • MUST enter living cells in order to reproduce • Very small • Range from a few to 100s of genes ...
... and sometimes lipids • MUST enter living cells in order to reproduce • Very small • Range from a few to 100s of genes ...
Hello Mighty Achievers
... parts: a protein coat that protects the virus and an inner core made of genetic material. Capsid: the protein shell that surround a virus In addition to the capsid, some viruses also have protective coating called an envelope. This envelope may be covered with spikes. Note: A virus uses these spikes ...
... parts: a protein coat that protects the virus and an inner core made of genetic material. Capsid: the protein shell that surround a virus In addition to the capsid, some viruses also have protective coating called an envelope. This envelope may be covered with spikes. Note: A virus uses these spikes ...
IMMUNE RESPONSE TO INFECTIOUS DISEASE
... Induction of Type I Interferons: The double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) of the virus induces the expression of the interferons by the infected cell. The bound IFN’s will activate the JAK/STAT pathway responsible for the synthesis of ...
... Induction of Type I Interferons: The double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) of the virus induces the expression of the interferons by the infected cell. The bound IFN’s will activate the JAK/STAT pathway responsible for the synthesis of ...
BioHnrs TEST TOPICS: Intro to Cells (4.1
... 2. Explain how viruses were discovered and the hypotheses regarding their evolution. 3. Explain how viruses can differ and identify what they all have in common. 4. Describe how the human immune system functions to prevent repeat viral infections. 5. Explain what a vaccine is and provide a historica ...
... 2. Explain how viruses were discovered and the hypotheses regarding their evolution. 3. Explain how viruses can differ and identify what they all have in common. 4. Describe how the human immune system functions to prevent repeat viral infections. 5. Explain what a vaccine is and provide a historica ...
Virus quantification

Virus quantification involves counting the number of viruses in a specific volume to determine the virus concentration. It is utilized in both research and development (R&D) in commercial and academic laboratories as well as production situations where the quantity of virus at various steps is an important variable. For example, the production of viral vaccines, recombinant proteins using viral vectors and viral antigens all require virus quantification to continually adapt and monitor the process in order to optimize production yields and respond to ever changing demands and applications. Examples of specific instances where known viruses need to be quantified include clone screening, multiplicity of infection (MOI) optimization and adaptation of methods to cell culture. This page discusses various techniques currently used to quantify viruses in liquid samples. These methods are separated into two categories, traditional vs. modern methods. Traditional methods are industry-standard methods that have been used for decades but are generally slow and labor-intensive. Modern methods are relatively new commercially available products and kits that greatly reduce quantification time. This is not meant to be an exhaustive review of all potential methods, but rather a representative cross-section of traditional methods and new, commercially available methods. While other published methods may exist for virus quantification, non-commercial methods are not discussed here.