Chapter 27 Student Reading Guide Bacteria and Archaea Overview
... Bacterial cell walls contain __________________, a network of _____________ cross-linked by _________ Archaea contain polysaccharides and proteins but lack peptidoglycan Using the Gram stain, scientists classify many bacterial species into Gram-___________ and Gram-_________ __groups based on ...
... Bacterial cell walls contain __________________, a network of _____________ cross-linked by _________ Archaea contain polysaccharides and proteins but lack peptidoglycan Using the Gram stain, scientists classify many bacterial species into Gram-___________ and Gram-_________ __groups based on ...
12369 Demonstrate knowledge of bacterial genetics
... before they can report credits from assessment against unit standards or deliver courses of study leading to that assessment. Industry Training Organisations must be granted consent to assess against standards by NZQA before they can register credits from assessment against unit standards. Providers ...
... before they can report credits from assessment against unit standards or deliver courses of study leading to that assessment. Industry Training Organisations must be granted consent to assess against standards by NZQA before they can register credits from assessment against unit standards. Providers ...
Sources of microorganisms in food.
... porous vegetables and leafy vegetables. • Some plants produce natural antimicrobial metabolites that limit the presence of microorganisms. • Fruits and vegetables harbour microbes on their surfaces and microbe presence depends on their type, soil condition, water used and air quality. ...
... porous vegetables and leafy vegetables. • Some plants produce natural antimicrobial metabolites that limit the presence of microorganisms. • Fruits and vegetables harbour microbes on their surfaces and microbe presence depends on their type, soil condition, water used and air quality. ...
Bacterial Cell Wall and Differential Staining
... Image: Bonding structure peptidoglycan, Mouagip; Other Image Source Unknown ...
... Image: Bonding structure peptidoglycan, Mouagip; Other Image Source Unknown ...
Photoautotrophs
... Prokaryotes – Bacteria and Archea No membrane bound organelles Asexual reproduction by binary fusion Large surface area to volume ratio Single celled or colonial ...
... Prokaryotes – Bacteria and Archea No membrane bound organelles Asexual reproduction by binary fusion Large surface area to volume ratio Single celled or colonial ...
Lesson Overview
... To truly understand genetics, scientists realized they had to discover the chemical nature of the gene. If the molecule that carries genetic information could be identified, it might be possible to understand how genes control the inherited characteristics of living things. The discovery of the chem ...
... To truly understand genetics, scientists realized they had to discover the chemical nature of the gene. If the molecule that carries genetic information could be identified, it might be possible to understand how genes control the inherited characteristics of living things. The discovery of the chem ...
Outcomes and evidence requirements
... before they can report credits from assessment against unit standards or deliver courses of study leading to that assessment. Industry Training Organisations must be granted consent to assess against standards by NZQA before they can register credits from assessment against unit standards. Providers ...
... before they can report credits from assessment against unit standards or deliver courses of study leading to that assessment. Industry Training Organisations must be granted consent to assess against standards by NZQA before they can register credits from assessment against unit standards. Providers ...
assignment 1
... bacteria. As harmful bacteria is present on everything which we use in our daily life like on food, clothes and on many more things. Some bacteria have natural resistant to some antibacterial but some bacteria is of that kind whose solution till now is not present, but in both cases detection of pre ...
... bacteria. As harmful bacteria is present on everything which we use in our daily life like on food, clothes and on many more things. Some bacteria have natural resistant to some antibacterial but some bacteria is of that kind whose solution till now is not present, but in both cases detection of pre ...
National University of Life and Environmental Sciences of Ukraine
... unicellular organisms, all the life processes are performed in a single cell. Regardless of the complexity of an organism, the cell is the true, basic unit of life. All living organisms have the capacity to respond to, and often alter, their environment. They are capable of autonomous movement, alth ...
... unicellular organisms, all the life processes are performed in a single cell. Regardless of the complexity of an organism, the cell is the true, basic unit of life. All living organisms have the capacity to respond to, and often alter, their environment. They are capable of autonomous movement, alth ...
ABSTRACT: Introduction: Most humans have their hands colonized
... Most humans have their hands colonized with Staphylococcus epidermidis, and sometimes with Staphylococcus aureus, which is an important opportunistic human pathogen. In addition, human hands can be also contaminated with other opportunistic and primary microbial pathogens during our daily activities ...
... Most humans have their hands colonized with Staphylococcus epidermidis, and sometimes with Staphylococcus aureus, which is an important opportunistic human pathogen. In addition, human hands can be also contaminated with other opportunistic and primary microbial pathogens during our daily activities ...
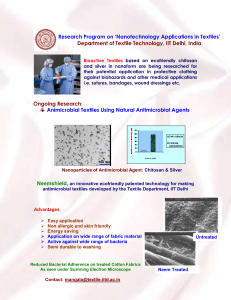
bioactive and functional textiles - Department of Textile Technology
... Research Program on ‘Nanotechnology Applications in Textiles’ Department of Textile Technology, IIT Delhi, India Bioactive Textiles based on ecofriendly chitosan and silver in nanoform are being researched for their potential application in protective clothing against biohazards and other medical ap ...
... Research Program on ‘Nanotechnology Applications in Textiles’ Department of Textile Technology, IIT Delhi, India Bioactive Textiles based on ecofriendly chitosan and silver in nanoform are being researched for their potential application in protective clothing against biohazards and other medical ap ...
Module II
... Bacterial spores are something very different from fungal spores Bacterial spores can only be killed by very high temperatures (sterilizer) Bacteria that are able to form spores are called spore-forming bacteria (e.g. the causative organisms of anthrax, gas gangrene and tetanus) • Some bacteria can ...
... Bacterial spores are something very different from fungal spores Bacterial spores can only be killed by very high temperatures (sterilizer) Bacteria that are able to form spores are called spore-forming bacteria (e.g. the causative organisms of anthrax, gas gangrene and tetanus) • Some bacteria can ...
module 10 study guide
... 9. Why can dehydrated food be stored for a long time without worry of it being contaminated by bacteria? _________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ 10. Why did people salt meat be ...
... 9. Why can dehydrated food be stored for a long time without worry of it being contaminated by bacteria? _________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ 10. Why did people salt meat be ...
Genus
... (coccus), and spiral-shaped (spirillum). • Bacterial Toxins-- Bacteria can cause disease by releasing toxins, which damage their host. • Biowarfare-- Biowarfare is the deliberate exposure of people to biological toxins or pathogens such as bacteria or viruses. • Fighting Bacteria --Bacterial disease ...
... (coccus), and spiral-shaped (spirillum). • Bacterial Toxins-- Bacteria can cause disease by releasing toxins, which damage their host. • Biowarfare-- Biowarfare is the deliberate exposure of people to biological toxins or pathogens such as bacteria or viruses. • Fighting Bacteria --Bacterial disease ...
citrate & oxidase test
... in pH to change the medium from its initial green color to deep blue. ...
... in pH to change the medium from its initial green color to deep blue. ...
chapter05
... 5.3 Using Heat to Destroy Microorganisms and Viruses Moist heat Boiling kills most bacteria and viruses Pasteurization is effective for many food-borne ...
... 5.3 Using Heat to Destroy Microorganisms and Viruses Moist heat Boiling kills most bacteria and viruses Pasteurization is effective for many food-borne ...
Escherichia coli is a bacterium, which inhabits the intestinal tract of
... catheterized patients. •K. pneumoniae is second only to E. coli as a urinary tract pathogen. Klebsiella infections are encountered far more often now than in the past. ...
... catheterized patients. •K. pneumoniae is second only to E. coli as a urinary tract pathogen. Klebsiella infections are encountered far more often now than in the past. ...
Wet Mount Proficiency Test 2009B Critique
... called pseudohyphae because they lack true branching as seen with mold like fungi. The side walls are parallel to each other which is an important characteristic that helps separate pseudohyphae from artifact whose side walls vary in width. Small oval structures called blastoconidia are often seen a ...
... called pseudohyphae because they lack true branching as seen with mold like fungi. The side walls are parallel to each other which is an important characteristic that helps separate pseudohyphae from artifact whose side walls vary in width. Small oval structures called blastoconidia are often seen a ...
Chapter 16 Innate Immunity: Nonspecific Defenses of the Host
... microorganisms from settling on the eyes. Saliva produce by salivary glands dilutes microorganism, wash them away from teeths and mucous membranes of the mouth Nose hairs filters inhaled microorganisms Cillia in the lower respiratory tract help propels out toward the throat (ciliary escalator) micro ...
... microorganisms from settling on the eyes. Saliva produce by salivary glands dilutes microorganism, wash them away from teeths and mucous membranes of the mouth Nose hairs filters inhaled microorganisms Cillia in the lower respiratory tract help propels out toward the throat (ciliary escalator) micro ...
Slide 1
... • Many are unicellular, sometimes cells are organized in filaments or clumps, and others are complex with only a portion of their life cycle being microscopic. • Most can carry out life processes independently from other cells, others are highly parasitic. • They often require specialized techniques ...
... • Many are unicellular, sometimes cells are organized in filaments or clumps, and others are complex with only a portion of their life cycle being microscopic. • Most can carry out life processes independently from other cells, others are highly parasitic. • They often require specialized techniques ...
Cell Structure and Function Chapter 3
... Vegetative cells transform into endospores when multiple nutrients are limited. Dehydrated, metabolically inactive Longevity verges on immortality, 250 million years Resistant to extreme conditions such as heat, radiation, chemicals Resistant to ordinary cleaning methods and boiling Pressurized stea ...
... Vegetative cells transform into endospores when multiple nutrients are limited. Dehydrated, metabolically inactive Longevity verges on immortality, 250 million years Resistant to extreme conditions such as heat, radiation, chemicals Resistant to ordinary cleaning methods and boiling Pressurized stea ...
Eubacteria and Archaebacteria
... or reproduction at temperatures of -15 °C or lower for extended periods Radioresistant Organisms resistant to high levels of ionizing radiation, most commonly ultraviolet radiation, but also including organisms capable of resisting nuclear radiation Thermophile An organism that can thrive at tempera ...
... or reproduction at temperatures of -15 °C or lower for extended periods Radioresistant Organisms resistant to high levels of ionizing radiation, most commonly ultraviolet radiation, but also including organisms capable of resisting nuclear radiation Thermophile An organism that can thrive at tempera ...
Chapter 4 Supplement
... encephalopathy (BSE). It is a progressive neurologic disorder of cattle that results from infection by an unconventional transmissible agent. The most accepted theory is that the agent is a modified form of an abnormal cell surface component known as a prion protein. As of November, 2005, only two B ...
... encephalopathy (BSE). It is a progressive neurologic disorder of cattle that results from infection by an unconventional transmissible agent. The most accepted theory is that the agent is a modified form of an abnormal cell surface component known as a prion protein. As of November, 2005, only two B ...