ANTARES - National Optical Astronomy Observatory
... different algorithms used to determine the credible region. The total area is greater than 600 square degrees while follow-up images on the ground generally have a field-of-view of less than one square degree. Figure from Abbott et al. (2016b). will be annotated in the alert. Such galaxy catalogs do ...
... different algorithms used to determine the credible region. The total area is greater than 600 square degrees while follow-up images on the ground generally have a field-of-view of less than one square degree. Figure from Abbott et al. (2016b). will be annotated in the alert. Such galaxy catalogs do ...
How far away are the Stars?
... The Distance to the Stars! • Angular Separation is not enough! • We want to know the answer to the ‘age old question’: How far away are the stars? ...
... The Distance to the Stars! • Angular Separation is not enough! • We want to know the answer to the ‘age old question’: How far away are the stars? ...
Li-cai Deng
... position and velocity, with much higher accuracy information for each star. Many surveys currently in progress will provide multi-color imaging of the sky. However, there is a great need for spectroscopic surveys of millions of stars. Twenty years ago, when the idea for the SDSS was born, large scal ...
... position and velocity, with much higher accuracy information for each star. Many surveys currently in progress will provide multi-color imaging of the sky. However, there is a great need for spectroscopic surveys of millions of stars. Twenty years ago, when the idea for the SDSS was born, large scal ...
Chapter 12 - Indiana State University
... – The system is still used today and units of measurement are called apparent magnitudes to emphasize how bright a star looks to an observer ...
... – The system is still used today and units of measurement are called apparent magnitudes to emphasize how bright a star looks to an observer ...
Exoplanet Discoveries and the Fermi Paradox
... their lives, they migrate to the giant or supergiant phase, then to white dwarfs, neutron stars, or black holes. Our sun is a G2 star on the main sequence, brighter and more massive than about 90% of all stars. Astronomers classify stars according to their intrinsic brightness and temperature into c ...
... their lives, they migrate to the giant or supergiant phase, then to white dwarfs, neutron stars, or black holes. Our sun is a G2 star on the main sequence, brighter and more massive than about 90% of all stars. Astronomers classify stars according to their intrinsic brightness and temperature into c ...
Astronomy and Space Science
... • Motion planets around epicycle centers and epicycle centers around the Earth are uniform circular motions. • Note: the centers of epicycles for Mercury and Venus always align with the Sun, which explains their maximum elongations (29° and 48°). • Ptolemy (90-168 CE) modified this model to be quant ...
... • Motion planets around epicycle centers and epicycle centers around the Earth are uniform circular motions. • Note: the centers of epicycles for Mercury and Venus always align with the Sun, which explains their maximum elongations (29° and 48°). • Ptolemy (90-168 CE) modified this model to be quant ...
It is now recognized that the vast majority of ellipticals are of
... • Only a few E galaxies actually have flat luminosity profiles at small radii; instead, the profiles rise inward to the last measured point. • Cores may exhibit unusual kinematics; for example, about a quarter of all elliptical galaxies have cores which appear to counter-rotate with respect to the r ...
... • Only a few E galaxies actually have flat luminosity profiles at small radii; instead, the profiles rise inward to the last measured point. • Cores may exhibit unusual kinematics; for example, about a quarter of all elliptical galaxies have cores which appear to counter-rotate with respect to the r ...
E3 – Stellar distances
... • At distances greater than Mpc, neither parallax nor spectroscopic parallax can be relied upon to measure the distance to a star. • When we observe another galaxy, all of the stars in that galaxy are approximately the same distance away from the earth. What we really need is a light source of known ...
... • At distances greater than Mpc, neither parallax nor spectroscopic parallax can be relied upon to measure the distance to a star. • When we observe another galaxy, all of the stars in that galaxy are approximately the same distance away from the earth. What we really need is a light source of known ...
Project 4: The HR diagram. Open clusters
... stars do not fall randomly on the graph; rather they are confined to specific regions. This tells you that there is some physical relationship between the luminosity and temperature of a star. From the figure, one sees that most stars fall along a diagonal strip from high temperature, high lumi ...
... stars do not fall randomly on the graph; rather they are confined to specific regions. This tells you that there is some physical relationship between the luminosity and temperature of a star. From the figure, one sees that most stars fall along a diagonal strip from high temperature, high lumi ...
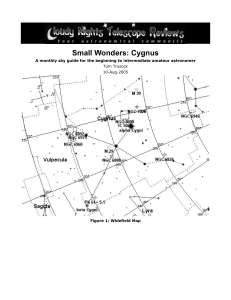
Small Wonders: Cygnus
... Another possible origin for the celestial bird, lies with Cycnus, Poseidon’s son. Abandoned by his parents and raised by a swan, Cycnus was eventually turned into one by Poseidon after he was killed by Achilles. (Do these ancient Greek / Roman myths remind anyone else of today’s soap operas?) In any ...
... Another possible origin for the celestial bird, lies with Cycnus, Poseidon’s son. Abandoned by his parents and raised by a swan, Cycnus was eventually turned into one by Poseidon after he was killed by Achilles. (Do these ancient Greek / Roman myths remind anyone else of today’s soap operas?) In any ...
colour
... . For spectroscopic eclipsing binaries i ∼ 90o; hence determination of M1 and M2 possible. About 100 good mass determinations; all main-sequence stars. • Summary of mass determinations: . Apart from main-sequence stars, reliable masses are known for 3 white dwarfs a few giants . Range of masses: 0.1 ...
... . For spectroscopic eclipsing binaries i ∼ 90o; hence determination of M1 and M2 possible. About 100 good mass determinations; all main-sequence stars. • Summary of mass determinations: . Apart from main-sequence stars, reliable masses are known for 3 white dwarfs a few giants . Range of masses: 0.1 ...
Chapter 12
... The Crab Nebula This supernova was recorded by Chinese astronomers in 1054 AD. It was BRIGHT! It was seen in daylight! ...
... The Crab Nebula This supernova was recorded by Chinese astronomers in 1054 AD. It was BRIGHT! It was seen in daylight! ...
STELLAR STRUCTURE AND EVOLUTION
... . For spectroscopic eclipsing binaries i ∼ 90o; hence determination of M1 and M2 possible. About 100 good mass determinations; all main-sequence stars. • Summary of mass determinations: . Apart from main-sequence stars, reliable masses are known for 3 white dwarfs a few giants . Range of masses: 0.1 ...
... . For spectroscopic eclipsing binaries i ∼ 90o; hence determination of M1 and M2 possible. About 100 good mass determinations; all main-sequence stars. • Summary of mass determinations: . Apart from main-sequence stars, reliable masses are known for 3 white dwarfs a few giants . Range of masses: 0.1 ...
Goal: To understand how we know distances to
... brightness (the rotation gives an indication of mass which therefore would affect brightness). • The rotation is found using the Doppler shifts of the 21 cm line of Hydrogen. • You can also use bright objects such as very massive stars, novae, and some supernova. • There is also some who think the s ...
... brightness (the rotation gives an indication of mass which therefore would affect brightness). • The rotation is found using the Doppler shifts of the 21 cm line of Hydrogen. • You can also use bright objects such as very massive stars, novae, and some supernova. • There is also some who think the s ...
18. Formation of Stars.
... begin. At this point, the star enters onto the Main Sequence of the H-R diagram for the first time. For a star like the Sun, it will remain on the Main Sequence for about 10 billion yrs. • While on the Main Sequence, stars are in pressure equilibrium. That is, there is a balance between the force ...
... begin. At this point, the star enters onto the Main Sequence of the H-R diagram for the first time. For a star like the Sun, it will remain on the Main Sequence for about 10 billion yrs. • While on the Main Sequence, stars are in pressure equilibrium. That is, there is a balance between the force ...
What are the Spectral Lines? - University of Texas Astronomy Home
... - real knowledge only due to hard facts, e.g., laboratory science, measurements • claimed ...
... - real knowledge only due to hard facts, e.g., laboratory science, measurements • claimed ...
Star in a Box
... The stars Vega and Sirius are brighter than the Sun, and also hotter. Where would you put them? Where would you mark the Sun on the plot? ...
... The stars Vega and Sirius are brighter than the Sun, and also hotter. Where would you put them? Where would you mark the Sun on the plot? ...
Ursa Major

Ursa Major /ˈɜrsə ˈmeɪdʒər/ (also known as the Great Bear and Charles' Wain) is a constellation in the northern celestial hemisphere. One of the 48 constellations listed by Ptolemy (second century AD), it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. It can be visible throughout the year in most of the northern hemisphere. Its name, Latin for ""the greater (or larger) she-bear"", stands as a reference to and in direct contrast with Ursa Minor, ""the smaller she-bear"", with which it is frequently associated in mythology and amateur astronomy. The constellation's most recognizable asterism, a group of seven relatively bright stars commonly known as the ""Big Dipper"", ""the Wagon"" or ""the Plough"" (among others), both mimicks the shape of the lesser bear (the ""Little Dipper"") and is commonly used as a navigational pointer towards the current northern pole star, Polaris in Ursa Minor. The Big Dipper and the constellation as a whole have mythological significance in numerous world cultures, usually as a symbol of the north.The third largest constellation in the sky, Ursa Major is home to many deep-sky objects including seven Messier objects, four other NGC objects and I Zwicky 18, the youngest known galaxy in the visible universe.