Astronomy - Scioly.org
... e. They are 88 groups of stars with members of each constellation physically close together in space 3. What is the most likely Greek letter name of the second brightest star in the constellation Lyra? a. alpha Lyrae. b. beta Lyrae. c. gamma Lyrae. d. delta Lyrae. e. epsilon Lyrae 4. The apparent vi ...
... e. They are 88 groups of stars with members of each constellation physically close together in space 3. What is the most likely Greek letter name of the second brightest star in the constellation Lyra? a. alpha Lyrae. b. beta Lyrae. c. gamma Lyrae. d. delta Lyrae. e. epsilon Lyrae 4. The apparent vi ...
Burgess_final - University of Hertfordshire
... 348. Their atmospheres all show evidence of methane absorption which was used to select and identify these young objects. "There has been some controversy about identifying young, low mass brown dwarfs in this region. An object of a similar mass was discovered in 2002, but some groups have argued t ...
... 348. Their atmospheres all show evidence of methane absorption which was used to select and identify these young objects. "There has been some controversy about identifying young, low mass brown dwarfs in this region. An object of a similar mass was discovered in 2002, but some groups have argued t ...
Chapter 20 Notes (smaller PDF file)
... • As a low-mass star ages, convection occurs over a larger portion of its volume • This takes heavy elements formed in the star’s interior and distributes them throughout the star ...
... • As a low-mass star ages, convection occurs over a larger portion of its volume • This takes heavy elements formed in the star’s interior and distributes them throughout the star ...
Abundance of Elements
... lifetime on main sequence is longer than the age of universe the chemical evolution of the universe ...
... lifetime on main sequence is longer than the age of universe the chemical evolution of the universe ...
1b91: answers to problem sheet no 1
... Outline the main phenomena observed in the Sun during its most active phases. Determine the fraction of energy emitted per unit area by a sunspot of temperature 4500 K compared to the surrounding photosphere of temperature 5800 K. When the Sun is in an active phase, the phenomena that are seen are: ...
... Outline the main phenomena observed in the Sun during its most active phases. Determine the fraction of energy emitted per unit area by a sunspot of temperature 4500 K compared to the surrounding photosphere of temperature 5800 K. When the Sun is in an active phase, the phenomena that are seen are: ...
doc - Jnoodle
... from b = L / 4d2 ) we still need the surface area A. We assume that the star is shaped like a sphere so if we find its volume V = (4/3)r3 we can get the radius of the star r and then its surface A = 4r2 (Notice the conceptual difference between the surface area of a spherical radiation source and ...
... from b = L / 4d2 ) we still need the surface area A. We assume that the star is shaped like a sphere so if we find its volume V = (4/3)r3 we can get the radius of the star r and then its surface A = 4r2 (Notice the conceptual difference between the surface area of a spherical radiation source and ...
THE BIG BANG THEORY
... • Astronomers observe galaxies are all red shifted from Earth – What does this say about the galaxies in relation to Earth? • Therefore, all galaxies are moving away from earth • Therefore, the universe is expanding ...
... • Astronomers observe galaxies are all red shifted from Earth – What does this say about the galaxies in relation to Earth? • Therefore, all galaxies are moving away from earth • Therefore, the universe is expanding ...
Are the Signs of the Zodiac Wrong? Is Ophiuchus
... defined by the stars within chosen constellations along the ecliptic (the apparent annual path of the Sun) in Mesopotamia at the end of the Iron Age (around 500 BC). Though the Babylonians used stars and constellations for measurement, they were also using zones which start from the position of the ...
... defined by the stars within chosen constellations along the ecliptic (the apparent annual path of the Sun) in Mesopotamia at the end of the Iron Age (around 500 BC). Though the Babylonians used stars and constellations for measurement, they were also using zones which start from the position of the ...
N (North) Equator Latitude and Declination
... passing through the observer; it’s perpendicular to the line from the center of the earth, passing through the observer, and going out toward the zenith. The celestial equator is the plane which passes through the earth’s equator and extends out into space. The observed altitude of a star is its ang ...
... passing through the observer; it’s perpendicular to the line from the center of the earth, passing through the observer, and going out toward the zenith. The celestial equator is the plane which passes through the earth’s equator and extends out into space. The observed altitude of a star is its ang ...
3-color photometry of stellar cluster - Kiepenheuer
... and from the sky are more severe near horizon. Due to the wavelenght dependant scattering cross-section, blue is affected the most followed by green and red (Weigert and Wendker, 1989). Lastly the observatory at Schauinsland is surrounded thees by which helps with straylight from the cities but rest ...
... and from the sky are more severe near horizon. Due to the wavelenght dependant scattering cross-section, blue is affected the most followed by green and red (Weigert and Wendker, 1989). Lastly the observatory at Schauinsland is surrounded thees by which helps with straylight from the cities but rest ...
Lab 6
... Astronomers, including Edwin Hubble, began to use the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram as a powerful tool to determine stellar properties. Initially, the method of standard candles for individual stars was applied to whole clusters within the Milky Way; this method relies on the inverse-square law you sa ...
... Astronomers, including Edwin Hubble, began to use the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram as a powerful tool to determine stellar properties. Initially, the method of standard candles for individual stars was applied to whole clusters within the Milky Way; this method relies on the inverse-square law you sa ...
Document
... Use scientific notation and astronomical units (AU, light year) to compare distances. Place astronomic objects (planets, moons, stars, solar systems, star clusters, galaxies) in relative size and distance order. Understand that the sun is a medium-sized star located near the edge of a disc-sha ...
... Use scientific notation and astronomical units (AU, light year) to compare distances. Place astronomic objects (planets, moons, stars, solar systems, star clusters, galaxies) in relative size and distance order. Understand that the sun is a medium-sized star located near the edge of a disc-sha ...
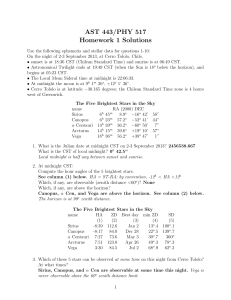
AST 443/PHY 517 Homework 1 Solutions
... 4. Which of these 5 stars is closest to the moon? What is the angular distance? Sirius, at about 44.3 degrees 5. The sidereal time at midnight advances by 3m 56s each day. What are the best days to observe these targets? See column (3) above. 6. What is the minimum zenith distance for each star? Se ...
... 4. Which of these 5 stars is closest to the moon? What is the angular distance? Sirius, at about 44.3 degrees 5. The sidereal time at midnight advances by 3m 56s each day. What are the best days to observe these targets? See column (3) above. 6. What is the minimum zenith distance for each star? Se ...
Motions in the Sky
... meridian one month (30 days) later? A. 8:30 pm Stars rise 4 minutes earlier each day, B. 10:14 pm so Sirius will rise 120 minutes earlier C. 10:26 pm after one month has passed. ...
... meridian one month (30 days) later? A. 8:30 pm Stars rise 4 minutes earlier each day, B. 10:14 pm so Sirius will rise 120 minutes earlier C. 10:26 pm after one month has passed. ...
Lecture 10: Stellar Evolution
... Role of Mass • A star’s mass determines its entire life story because it determines its core temperature • High-mass stars with >8MSun have short lives, eventually becoming hot enough to make iron, and end in supernova explosions • Low-mass stars with <2MSun have long lives, never become hot e ...
... Role of Mass • A star’s mass determines its entire life story because it determines its core temperature • High-mass stars with >8MSun have short lives, eventually becoming hot enough to make iron, and end in supernova explosions • Low-mass stars with <2MSun have long lives, never become hot e ...
center of mass
... 20. In a given volume of space the Red Dwarf (or lower main sequence) stars are the most abundant, however, on many H-R diagrams very few of these stars are plotted. Why? a. Photographic film and CCDs both have low sensitivity to lowenergy red photons. b. They are so very distant that parallax angle ...
... 20. In a given volume of space the Red Dwarf (or lower main sequence) stars are the most abundant, however, on many H-R diagrams very few of these stars are plotted. Why? a. Photographic film and CCDs both have low sensitivity to lowenergy red photons. b. They are so very distant that parallax angle ...
Chapter 27 Quasars, Active Galaxies, and Gamma
... • Early radio telescopes found radio emission from stars, nebulae, and some galaxies. • There were also point-like, or star-like, radio sources which varied rapidly these are the `quasi-stellar’ radio sources or quasars. • In visible light quasars appear as points, like stars. ...
... • Early radio telescopes found radio emission from stars, nebulae, and some galaxies. • There were also point-like, or star-like, radio sources which varied rapidly these are the `quasi-stellar’ radio sources or quasars. • In visible light quasars appear as points, like stars. ...
Chapter 09
... 20. In a given volume of space the Red Dwarf (or lower main sequence) stars are the most abundant, however, on many H-R diagrams very few of these stars are plotted. Why? a. Photographic film and CCDs both have low sensitivity to lowenergy red photons. b. They are so very distant that parallax angle ...
... 20. In a given volume of space the Red Dwarf (or lower main sequence) stars are the most abundant, however, on many H-R diagrams very few of these stars are plotted. Why? a. Photographic film and CCDs both have low sensitivity to lowenergy red photons. b. They are so very distant that parallax angle ...
File - Mr. Gray`s Class
... "wiggle" or because the planet gets in front of the star as it orbits and cuts down its light just a bit. One of the most profound discoveries of modern astronomy is that stars do not last forever. Over the millions and billions of years, stars are born from the raw material of space, shine steadily ...
... "wiggle" or because the planet gets in front of the star as it orbits and cuts down its light just a bit. One of the most profound discoveries of modern astronomy is that stars do not last forever. Over the millions and billions of years, stars are born from the raw material of space, shine steadily ...
Sky Watcher - Boise Astronomical Society
... bolts, with the loud CRACKs and rumbles of surround-sound thunder following close behind. But don’t. Lightning is dangerous. Stay inside. Each year there are around 25 million lightning flashes in the United States. That’s a lot of chances to be a lightning victim. Although most people who are struc ...
... bolts, with the loud CRACKs and rumbles of surround-sound thunder following close behind. But don’t. Lightning is dangerous. Stay inside. Each year there are around 25 million lightning flashes in the United States. That’s a lot of chances to be a lightning victim. Although most people who are struc ...
Stars - CBSD.org
... night sky were “first order magnitude” stars. • As they got dimmer, he classified them as “second magnitude,” “third magnitude,” and so on… • He got up to magnitude 6, after which stars are too dim to be seen without a telescope. • So, a star’s apparent magnitude is essentially its brightness. – The ...
... night sky were “first order magnitude” stars. • As they got dimmer, he classified them as “second magnitude,” “third magnitude,” and so on… • He got up to magnitude 6, after which stars are too dim to be seen without a telescope. • So, a star’s apparent magnitude is essentially its brightness. – The ...
Ursa Major

Ursa Major /ˈɜrsə ˈmeɪdʒər/ (also known as the Great Bear and Charles' Wain) is a constellation in the northern celestial hemisphere. One of the 48 constellations listed by Ptolemy (second century AD), it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. It can be visible throughout the year in most of the northern hemisphere. Its name, Latin for ""the greater (or larger) she-bear"", stands as a reference to and in direct contrast with Ursa Minor, ""the smaller she-bear"", with which it is frequently associated in mythology and amateur astronomy. The constellation's most recognizable asterism, a group of seven relatively bright stars commonly known as the ""Big Dipper"", ""the Wagon"" or ""the Plough"" (among others), both mimicks the shape of the lesser bear (the ""Little Dipper"") and is commonly used as a navigational pointer towards the current northern pole star, Polaris in Ursa Minor. The Big Dipper and the constellation as a whole have mythological significance in numerous world cultures, usually as a symbol of the north.The third largest constellation in the sky, Ursa Major is home to many deep-sky objects including seven Messier objects, four other NGC objects and I Zwicky 18, the youngest known galaxy in the visible universe.