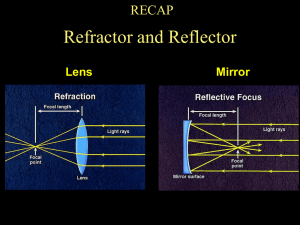
PHYSICS – Astrophysics Section I
... This formula requires either the distance (in parsecs) or the parallax angle (in arc seconds) to work. Shouldn’t be hard. Discuss the limitations of trigonometric parallax measurements Trigonometric parallax, although useful, has several limitations on its usefulness in finding distances to other st ...
... This formula requires either the distance (in parsecs) or the parallax angle (in arc seconds) to work. Shouldn’t be hard. Discuss the limitations of trigonometric parallax measurements Trigonometric parallax, although useful, has several limitations on its usefulness in finding distances to other st ...
7.4 Evolution on the Main-Sequence Main-sequence (m
... Main-sequence (m-s) stars evolve on the nuclear time-scale which is very slow in contrast to the Kelvin-Helmholtz time-scale which governs the length of the pre-main-sequence phase. For the Sun, the contraction time to the m-s τK−H ∼ 30 × 106 yr and τm−s ∼ 1010 yr. For a 9 M star, the corresponding ...
... Main-sequence (m-s) stars evolve on the nuclear time-scale which is very slow in contrast to the Kelvin-Helmholtz time-scale which governs the length of the pre-main-sequence phase. For the Sun, the contraction time to the m-s τK−H ∼ 30 × 106 yr and τm−s ∼ 1010 yr. For a 9 M star, the corresponding ...
r*=13.6 km MPA1 EOS
... Comptonized emission from the one visible hot spot and makes use of the Oblate Schwarzschild approximation for ray-tracing. We include a scattered light contribution, which accounts for flux scattered off an equatorial accretion disk to the observer including time delays in the scattered light. We g ...
... Comptonized emission from the one visible hot spot and makes use of the Oblate Schwarzschild approximation for ray-tracing. We include a scattered light contribution, which accounts for flux scattered off an equatorial accretion disk to the observer including time delays in the scattered light. We g ...
How Bright is that star?
... Relates luminosity, temperature and Radius of a star. The luminosity/meter² (l), is determined by the temperature (T) of that area ) l = σT⁴ (σ is a constant which if T is in °K, l comes out in Watts) Surface area is determined by radius(R): A = 4πR² So the total Lumnosity of star becomes L = 4πR²σT ...
... Relates luminosity, temperature and Radius of a star. The luminosity/meter² (l), is determined by the temperature (T) of that area ) l = σT⁴ (σ is a constant which if T is in °K, l comes out in Watts) Surface area is determined by radius(R): A = 4πR² So the total Lumnosity of star becomes L = 4πR²σT ...
Inquiry Activity - Ball State University
... zoom by the moving car. Just like the far off tree which appears to move much slower than the hitchhiker next to the road, the very far off stars appear to move slower than the nearby planets. Therefore over time it appears as though the planets are moving against the back ground of the stars. (Note ...
... zoom by the moving car. Just like the far off tree which appears to move much slower than the hitchhiker next to the road, the very far off stars appear to move slower than the nearby planets. Therefore over time it appears as though the planets are moving against the back ground of the stars. (Note ...
光學望遠鏡
... Observational astronomy is a division of the astronomical science that is concerned with getting data, in contrast with theoretical astrophysics, which is mainly concerned with finding out the measurable implications of physical models. It is the practice of observing celestial objects by using tele ...
... Observational astronomy is a division of the astronomical science that is concerned with getting data, in contrast with theoretical astrophysics, which is mainly concerned with finding out the measurable implications of physical models. It is the practice of observing celestial objects by using tele ...
Elliptical galaxies
... A simple pair that can be used to represent the profile of elliptical galaxies, is: ...
... A simple pair that can be used to represent the profile of elliptical galaxies, is: ...
how to precisely measure astronomic periods of time
... the Pleiades. The artist, however, painted four stars in a row. When we take the map of the night sky and place it over the painting (Figure 2), we can see that the artist indeed might have meant the Orion belt1 . In Section 2, we will see how it may have been possible to determine the length of yea ...
... the Pleiades. The artist, however, painted four stars in a row. When we take the map of the night sky and place it over the painting (Figure 2), we can see that the artist indeed might have meant the Orion belt1 . In Section 2, we will see how it may have been possible to determine the length of yea ...
Galaxy Sorting
... galaxies contain mostly old stars, with very little gas and dust found between stars. Since new stars form from clouds of interstellar gas and dust, elliptical galaxies lack the raw ingredients to make new stars. Spiral galaxies, on the other hand, have a mix of young and old stars. Interstellar ...
... galaxies contain mostly old stars, with very little gas and dust found between stars. Since new stars form from clouds of interstellar gas and dust, elliptical galaxies lack the raw ingredients to make new stars. Spiral galaxies, on the other hand, have a mix of young and old stars. Interstellar ...
Astronomy 12 - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... E. Estimate Main-Sequence Life of Sun. Estimate the main-sequence lifetime of the Sun: i.e., how long the Sun will burn hydrogen into helium in its core. Assume that the Sun was initially entirely composed of hydrogen, and that the Sun's current mass was its mass before main-sequence burning. You wi ...
... E. Estimate Main-Sequence Life of Sun. Estimate the main-sequence lifetime of the Sun: i.e., how long the Sun will burn hydrogen into helium in its core. Assume that the Sun was initially entirely composed of hydrogen, and that the Sun's current mass was its mass before main-sequence burning. You wi ...
Linking Asteroids and Meteorites through Reflectance
... • Not hot enough to emit significant amounts of light • Since the time required for a white dwarf to reach this state is calculated to be longer than the current age of the universe of 13.7 billion years, no black dwarfs are expected to exist in the universe yet ...
... • Not hot enough to emit significant amounts of light • Since the time required for a white dwarf to reach this state is calculated to be longer than the current age of the universe of 13.7 billion years, no black dwarfs are expected to exist in the universe yet ...
Summary: Modes of Star Formation
... It has also become clear in recent years that the Galactic halo contains moving streams that are the debris of disrupted halo systems or satellite galaxies. A large fraction of the halo could belong to a relatively small number of streams created by the disruption of a relatively small number of sat ...
... It has also become clear in recent years that the Galactic halo contains moving streams that are the debris of disrupted halo systems or satellite galaxies. A large fraction of the halo could belong to a relatively small number of streams created by the disruption of a relatively small number of sat ...
Lec09_ch11_lifecycleofstars
... • An H-R census of the Globular cluster stars reveals the age of the cluster – since the globular cluster stars are gravitationally bound close together, they are the same distance from us • use apparent magnitude ...
... • An H-R census of the Globular cluster stars reveals the age of the cluster – since the globular cluster stars are gravitationally bound close together, they are the same distance from us • use apparent magnitude ...
PowerPoint
... TMT can resolve source and lens star Average relative proper motion of lens and source star: μ=6±4mas/yr Resolution: •1.2x2.2μm/8.2m= 66mas (~80mass in VLT/NACO and Keck AO) •1.2x2.2μm/30m=18mass ...
... TMT can resolve source and lens star Average relative proper motion of lens and source star: μ=6±4mas/yr Resolution: •1.2x2.2μm/8.2m= 66mas (~80mass in VLT/NACO and Keck AO) •1.2x2.2μm/30m=18mass ...
27B Star Life Cycle and the HR Diagram
... all of the known stars were put on their graph, several obvious groups became apparent. By examining the differences in these groups, later astronomers were able to realize that the groups were best described as stars in different periods in their life cycle, rather than completely different types o ...
... all of the known stars were put on their graph, several obvious groups became apparent. By examining the differences in these groups, later astronomers were able to realize that the groups were best described as stars in different periods in their life cycle, rather than completely different types o ...
Jupiter - Midland ISD
... Jupiter has storms that grow up to cover up thousands of km in hours. Last up to hundreds of years It has clouds made up of ammonia crystals that can be seen as bands of yellow, brown and white. Clouds are located in the tropopouse and are arranged into bands of different latitudes. The Gr ...
... Jupiter has storms that grow up to cover up thousands of km in hours. Last up to hundreds of years It has clouds made up of ammonia crystals that can be seen as bands of yellow, brown and white. Clouds are located in the tropopouse and are arranged into bands of different latitudes. The Gr ...
Ursa Major

Ursa Major /ˈɜrsə ˈmeɪdʒər/ (also known as the Great Bear and Charles' Wain) is a constellation in the northern celestial hemisphere. One of the 48 constellations listed by Ptolemy (second century AD), it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. It can be visible throughout the year in most of the northern hemisphere. Its name, Latin for ""the greater (or larger) she-bear"", stands as a reference to and in direct contrast with Ursa Minor, ""the smaller she-bear"", with which it is frequently associated in mythology and amateur astronomy. The constellation's most recognizable asterism, a group of seven relatively bright stars commonly known as the ""Big Dipper"", ""the Wagon"" or ""the Plough"" (among others), both mimicks the shape of the lesser bear (the ""Little Dipper"") and is commonly used as a navigational pointer towards the current northern pole star, Polaris in Ursa Minor. The Big Dipper and the constellation as a whole have mythological significance in numerous world cultures, usually as a symbol of the north.The third largest constellation in the sky, Ursa Major is home to many deep-sky objects including seven Messier objects, four other NGC objects and I Zwicky 18, the youngest known galaxy in the visible universe.