5X_Measuring_galaxy_redshifts
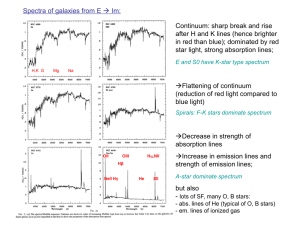
... Emission-line galaxies have wonderfully sharp spectral features that give precise redshifts. Again the correlation technique can be used, but with an emission-line template. ...
... Emission-line galaxies have wonderfully sharp spectral features that give precise redshifts. Again the correlation technique can be used, but with an emission-line template. ...
of the star. - Colyton High School
... magnitude (or luminosity) versus surface temperature (not core temperature). Notice most of the stars are in the main sequence, yet some are in white dwarf, super red giant or other stages. 13) Which named star shown on the H-R diagrams is a white dwarf and which is a super giant? Why are they given ...
... magnitude (or luminosity) versus surface temperature (not core temperature). Notice most of the stars are in the main sequence, yet some are in white dwarf, super red giant or other stages. 13) Which named star shown on the H-R diagrams is a white dwarf and which is a super giant? Why are they given ...
Lecture 42
... collapse, as is occurring in the Great Nebula in Orion. Such clouds may have dimensions in excess of 106 AU and masses greater than 106 MO (solar masses). Gravity will tend to make such clouds collapse upon themselves, but is resisted by magnetic, rotational, and thermal forces. Collapse of a part o ...
... collapse, as is occurring in the Great Nebula in Orion. Such clouds may have dimensions in excess of 106 AU and masses greater than 106 MO (solar masses). Gravity will tend to make such clouds collapse upon themselves, but is resisted by magnetic, rotational, and thermal forces. Collapse of a part o ...
Take Home #1 Complete the following on your own paper. Do not
... B. it proved that not everything revolved around the earth C. we discovered geological activity on another world D. it proved that astronomy was a useful science 11) In the 1600's Copernicus and Galileo believed that the earth and other planets orbited the sun. Why were their ideas not accepted at f ...
... B. it proved that not everything revolved around the earth C. we discovered geological activity on another world D. it proved that astronomy was a useful science 11) In the 1600's Copernicus and Galileo believed that the earth and other planets orbited the sun. Why were their ideas not accepted at f ...
Take Home #1 Complete the following on your own paper. Do not
... B. it proved that not everything revolved around the earth C. we discovered geological activity on another world D. it proved that astronomy was a useful science 11) In the 1600's Copernicus and Galileo believed that the earth and other planets orbited the sun. Why were their ideas not accepted at f ...
... B. it proved that not everything revolved around the earth C. we discovered geological activity on another world D. it proved that astronomy was a useful science 11) In the 1600's Copernicus and Galileo believed that the earth and other planets orbited the sun. Why were their ideas not accepted at f ...
Astronomy ANSWER KEY KEEP SECURE
... 16. Expressed in solar masses, a type 1a supernova will occur when the left hand star reaches what mass? 1.4 solar masses 17. Expressed in kg, and in scientific notation, a type 1a supernova will occur when the left hand star reaches what mass? 2.864 X 1030kg 18. This point at which a type 1a supern ...
... 16. Expressed in solar masses, a type 1a supernova will occur when the left hand star reaches what mass? 1.4 solar masses 17. Expressed in kg, and in scientific notation, a type 1a supernova will occur when the left hand star reaches what mass? 2.864 X 1030kg 18. This point at which a type 1a supern ...
What color are stars?
... – semidetached binary(material can flow across along a path called the Roche lobe) – contact binary (the two stars share a common envelope of material) ...
... – semidetached binary(material can flow across along a path called the Roche lobe) – contact binary (the two stars share a common envelope of material) ...
10.1 The Solar Neighborhood Barnard`s Star
... The darkened curve is called the Main Sequence, as this is where most stars are. Also indicated is the white dwarf region; these stars are hot but not very luminous, as they are quite small. ...
... The darkened curve is called the Main Sequence, as this is where most stars are. Also indicated is the white dwarf region; these stars are hot but not very luminous, as they are quite small. ...
4. Survey Observations
... earlier for the same star to be on your meridian – each month, you must observe 2 hours earlier for the same star to be on you meridian (a given RA is on your meridian 2 hours earlier each month) • Thus, the airmass of a star changes through the year as the star becomes easier or harder to observe • ...
... earlier for the same star to be on your meridian – each month, you must observe 2 hours earlier for the same star to be on you meridian (a given RA is on your meridian 2 hours earlier each month) • Thus, the airmass of a star changes through the year as the star becomes easier or harder to observe • ...
Absolute magnitude
... 2. m of star C is 12, m of star D is 2: How many times brighter is star D than star C? (Or, equally stated, how many times dimmer is star C than star D?) a) 10 ...
... 2. m of star C is 12, m of star D is 2: How many times brighter is star D than star C? (Or, equally stated, how many times dimmer is star C than star D?) a) 10 ...
the rest of the univ..
... Spectra and photometric data have been obtained for 5145 Pholus. Its albedo is very low (less than 0.1). Its spectra indicates the presence of organic compounds, which are often very dark (e.g. the nucleus of Comet Halley). Some believe that Triton, Pluto and its moon Charon are merely the largest e ...
... Spectra and photometric data have been obtained for 5145 Pholus. Its albedo is very low (less than 0.1). Its spectra indicates the presence of organic compounds, which are often very dark (e.g. the nucleus of Comet Halley). Some believe that Triton, Pluto and its moon Charon are merely the largest e ...
Chapter 16 - Astronomy
... 2. The abundance of heavy elements decreases by a factor of 0.8 for each thousand parsecs from the center of the Galactic disk. 3. Most Population I stars are found in the Galactic disk. Most globular clusters are made of Population II stars. 4. 70% of known globular clusters in the Milky Way have a ...
... 2. The abundance of heavy elements decreases by a factor of 0.8 for each thousand parsecs from the center of the Galactic disk. 3. Most Population I stars are found in the Galactic disk. Most globular clusters are made of Population II stars. 4. 70% of known globular clusters in the Milky Way have a ...
Ursa Major

Ursa Major /ˈɜrsə ˈmeɪdʒər/ (also known as the Great Bear and Charles' Wain) is a constellation in the northern celestial hemisphere. One of the 48 constellations listed by Ptolemy (second century AD), it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. It can be visible throughout the year in most of the northern hemisphere. Its name, Latin for ""the greater (or larger) she-bear"", stands as a reference to and in direct contrast with Ursa Minor, ""the smaller she-bear"", with which it is frequently associated in mythology and amateur astronomy. The constellation's most recognizable asterism, a group of seven relatively bright stars commonly known as the ""Big Dipper"", ""the Wagon"" or ""the Plough"" (among others), both mimicks the shape of the lesser bear (the ""Little Dipper"") and is commonly used as a navigational pointer towards the current northern pole star, Polaris in Ursa Minor. The Big Dipper and the constellation as a whole have mythological significance in numerous world cultures, usually as a symbol of the north.The third largest constellation in the sky, Ursa Major is home to many deep-sky objects including seven Messier objects, four other NGC objects and I Zwicky 18, the youngest known galaxy in the visible universe.