The Stars education kit - Student activities 5-10
... South Celestial Pole using hand-spans and finger width measurements as accurately as you can. 3. Discuss how accurate the measurements are. Compare measurements with other students. Who had the closest value to the tabulated value? Find out ...
... South Celestial Pole using hand-spans and finger width measurements as accurately as you can. 3. Discuss how accurate the measurements are. Compare measurements with other students. Who had the closest value to the tabulated value? Find out ...
chapter 7
... Note: These are apparent magnitudes because they are an attempt to measure brightness as seen from Earth. Furthermore, they are apparent visual magnitudes, since the human eye only detects or is sensitive to a limited portion of all the radiations emitted by an object. This portion is called the vi ...
... Note: These are apparent magnitudes because they are an attempt to measure brightness as seen from Earth. Furthermore, they are apparent visual magnitudes, since the human eye only detects or is sensitive to a limited portion of all the radiations emitted by an object. This portion is called the vi ...
1.2.43The stellar populations of the Milky Way
... stellar populations can now be defined in terms of the age, metal content, and location of the stars. While this work has been extremely profitable in developing an understanding of the nature of the stars and the origins of the populations, the proliferation of alternative definitions of population ...
... stellar populations can now be defined in terms of the age, metal content, and location of the stars. While this work has been extremely profitable in developing an understanding of the nature of the stars and the origins of the populations, the proliferation of alternative definitions of population ...
3rd EXAM VERSION A key - Department of Physics and Astronomy
... A. a galaxy with streams of stars arching out from one region, as if from an explosion B. *a galaxy with an unusually large number of newborn and young stars C. a galaxy that is still in the process of formation from the intergalactic medium and is undergoing its first episode of star formation D. a ...
... A. a galaxy with streams of stars arching out from one region, as if from an explosion B. *a galaxy with an unusually large number of newborn and young stars C. a galaxy that is still in the process of formation from the intergalactic medium and is undergoing its first episode of star formation D. a ...
What is Astronomy?
... Procedure: (NOTE: Use standard S.I. Units…meters for distances and seconds for time.) 1. Find a place where you have a clear view of the sunset* on a beach or one of the Great Lakes. The water should be calm the day you perform your measurements. Approximate the height of the waves on the ocean in ...
... Procedure: (NOTE: Use standard S.I. Units…meters for distances and seconds for time.) 1. Find a place where you have a clear view of the sunset* on a beach or one of the Great Lakes. The water should be calm the day you perform your measurements. Approximate the height of the waves on the ocean in ...
Spiral galaxies: Spiral galaxies: Inclination Spiral galaxies: Internal
... • In denser regions of the ISM, collisions between atoms become frequent enough to form molecules. • The most common molecule is H2, but since H2 is a symmetric molecule, it has no rotational quantum transitions. It is therefore extremely difficult to detect. • As a tracer of H2, astronomers usually ...
... • In denser regions of the ISM, collisions between atoms become frequent enough to form molecules. • The most common molecule is H2, but since H2 is a symmetric molecule, it has no rotational quantum transitions. It is therefore extremely difficult to detect. • As a tracer of H2, astronomers usually ...
young science communicator`s competition
... SHAPLEY: Well, we all know that the familiar band of stars across the sky which we call the Milky Way is in fact a disk shaped galaxy, filled with millions of stars, of which our sun is one. I propose that the Milky Way is ten times larger than previously thought [gasp from the audience] and as such ...
... SHAPLEY: Well, we all know that the familiar band of stars across the sky which we call the Milky Way is in fact a disk shaped galaxy, filled with millions of stars, of which our sun is one. I propose that the Milky Way is ten times larger than previously thought [gasp from the audience] and as such ...
Supermassive black holes
... A galaxy with a disk and prominent bulge but with no obvious spiral arms. Although they can have dust, they have little gas and do not have much star formation and are mostly older stars ...
... A galaxy with a disk and prominent bulge but with no obvious spiral arms. Although they can have dust, they have little gas and do not have much star formation and are mostly older stars ...
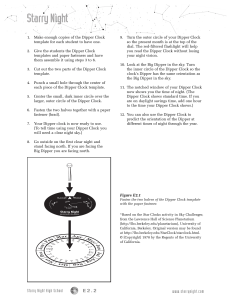
The Big Dipper Clock Astronomy Lesson
... has shifted our view of the constellations by a small amount. Each star rises four minutes earlier every day. This includes the stars of the Big Dipper. Over the course of an entire year, the stars and the Big Dipper advance by a complete circle. They come back to the point where they started one ye ...
... has shifted our view of the constellations by a small amount. Each star rises four minutes earlier every day. This includes the stars of the Big Dipper. Over the course of an entire year, the stars and the Big Dipper advance by a complete circle. They come back to the point where they started one ye ...
Hubble’s Law & Black Holes at a Galaxy’s Center
... The Andromeda galaxy is coming toward us, not moving away. Simplicio: That must be a mistake. 4. Sagredo explains: The reason is a. Part of the Big Bang went the wrong way. b. Andromeda is a little galaxy. c. Over time, the gravitational force between Andromeda & the Milky Way has slowed and reverse ...
... The Andromeda galaxy is coming toward us, not moving away. Simplicio: That must be a mistake. 4. Sagredo explains: The reason is a. Part of the Big Bang went the wrong way. b. Andromeda is a little galaxy. c. Over time, the gravitational force between Andromeda & the Milky Way has slowed and reverse ...
29-4 - Fremont Peak Observatory
... 14° 48.4’. R Lep is a “Carbon Star,” and as such it is a long period variable star. It is often called “Hind’s Crimson Star” because of its colour. British astronomer J. R. Hind first observed the star in 1845. Hind reported that the star appeared “like a drop of blood on a black field.” R Lep varie ...
... 14° 48.4’. R Lep is a “Carbon Star,” and as such it is a long period variable star. It is often called “Hind’s Crimson Star” because of its colour. British astronomer J. R. Hind first observed the star in 1845. Hind reported that the star appeared “like a drop of blood on a black field.” R Lep varie ...
Volume 2 (Issue 7), July 2013
... located with the naked eye, resembling a star of 6th magnitude. It is easy to find with binoculars, even from urban areas. Its identity can be confirmed by watching its movements from night to night. At oppositions, which occur a year and four days apart, a magnification of 500times will show Uranus ...
... located with the naked eye, resembling a star of 6th magnitude. It is easy to find with binoculars, even from urban areas. Its identity can be confirmed by watching its movements from night to night. At oppositions, which occur a year and four days apart, a magnification of 500times will show Uranus ...
Astronomy Final Study Guide - With Answers!!– Name: **This will be
... 3. Where do our space shuttles currently go when they get launched into space? Our space shuttles, although only one shuttle launch is left, go to the International Space Station to do research and tests. 4. List out the electromagnetic spectrum using energy levels from highest to lowest (or lowest ...
... 3. Where do our space shuttles currently go when they get launched into space? Our space shuttles, although only one shuttle launch is left, go to the International Space Station to do research and tests. 4. List out the electromagnetic spectrum using energy levels from highest to lowest (or lowest ...
Chapter 19 Star Formation
... At stage 6, the core reaches 10 million K, and nuclear fusion begins. The protostar has become a star. The star continues to contract and increase in temperature until it is in equilibrium: Internal pressure force outward, balancing the inward force of gravity, at every layer of the star’s interior. ...
... At stage 6, the core reaches 10 million K, and nuclear fusion begins. The protostar has become a star. The star continues to contract and increase in temperature until it is in equilibrium: Internal pressure force outward, balancing the inward force of gravity, at every layer of the star’s interior. ...
Ursa Major

Ursa Major /ˈɜrsə ˈmeɪdʒər/ (also known as the Great Bear and Charles' Wain) is a constellation in the northern celestial hemisphere. One of the 48 constellations listed by Ptolemy (second century AD), it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. It can be visible throughout the year in most of the northern hemisphere. Its name, Latin for ""the greater (or larger) she-bear"", stands as a reference to and in direct contrast with Ursa Minor, ""the smaller she-bear"", with which it is frequently associated in mythology and amateur astronomy. The constellation's most recognizable asterism, a group of seven relatively bright stars commonly known as the ""Big Dipper"", ""the Wagon"" or ""the Plough"" (among others), both mimicks the shape of the lesser bear (the ""Little Dipper"") and is commonly used as a navigational pointer towards the current northern pole star, Polaris in Ursa Minor. The Big Dipper and the constellation as a whole have mythological significance in numerous world cultures, usually as a symbol of the north.The third largest constellation in the sky, Ursa Major is home to many deep-sky objects including seven Messier objects, four other NGC objects and I Zwicky 18, the youngest known galaxy in the visible universe.