The Star of Bethlehem: a Type Ia/Ic Supernova in the Andromeda
... there was a conjunction of Mars with the Sun. On this date, Venus was in Aries, and located at its rising almost exactly below M31 and only about 20 degrees in azimuth north of east at Babylon. Venus on that day rose shortly after dawn, and had magnitude −4.2, so it would be visible after sunrise. O ...
... there was a conjunction of Mars with the Sun. On this date, Venus was in Aries, and located at its rising almost exactly below M31 and only about 20 degrees in azimuth north of east at Babylon. Venus on that day rose shortly after dawn, and had magnitude −4.2, so it would be visible after sunrise. O ...
Celestial Sphere Lab
... ideas they proposed have since proven to be incorrect. Some of the concepts they developed are still useful today though. One of the more useful ideas proposed by the ancient Greeks is the idea of a celestial sphere. We now know that the Earth’s rotation causes the stars to appear to move around us ...
... ideas they proposed have since proven to be incorrect. Some of the concepts they developed are still useful today though. One of the more useful ideas proposed by the ancient Greeks is the idea of a celestial sphere. We now know that the Earth’s rotation causes the stars to appear to move around us ...
galctr
... --How did such apparently young stars come to be found in an environment where SF is so difficult? --Same, but more extreme version of question for He I emission-line stars at 0.1 -0.5 pc from ctr. --Would need n > 1014 cm-3 at R=0.01 pc; n> 108 cm-3 at R=0.1 pc to form in situ given strong tidal gr ...
... --How did such apparently young stars come to be found in an environment where SF is so difficult? --Same, but more extreme version of question for He I emission-line stars at 0.1 -0.5 pc from ctr. --Would need n > 1014 cm-3 at R=0.01 pc; n> 108 cm-3 at R=0.1 pc to form in situ given strong tidal gr ...
September 2016
... its orbit around Earth; this is where the unit of time we call the month was derived from. The Moon takes 27.32 days to complete one orbit which is called a Sidereal Month. However, because Earth is also moving around the Sun, the Moon actually travels further and takes slightly longer to complete i ...
... its orbit around Earth; this is where the unit of time we call the month was derived from. The Moon takes 27.32 days to complete one orbit which is called a Sidereal Month. However, because Earth is also moving around the Sun, the Moon actually travels further and takes slightly longer to complete i ...
Starbursts – from 30 Doradus to Lyman
... the recently discovered SCUBA galaxies, as well as from Lyman-break galaxies through luminous compact blue galaxies, perhaps down to dwarf ellipticals. It appears that the frequency of starbursts was larger at high redshifts (although of similar duration as in the local universe), yet there does not ...
... the recently discovered SCUBA galaxies, as well as from Lyman-break galaxies through luminous compact blue galaxies, perhaps down to dwarf ellipticals. It appears that the frequency of starbursts was larger at high redshifts (although of similar duration as in the local universe), yet there does not ...
Brightness + Magnitude of Stars
... A. Apparent or Relative Brightness-(cont.) *** As distance to Star Decreases brightness Increases (Inverse Relationship) *** As Luminosity of Star increases brightness Increases (Direct Relationship) B. Apparent Magnitude A number assigned to a celestial object that is a measure of its relative br ...
... A. Apparent or Relative Brightness-(cont.) *** As distance to Star Decreases brightness Increases (Inverse Relationship) *** As Luminosity of Star increases brightness Increases (Direct Relationship) B. Apparent Magnitude A number assigned to a celestial object that is a measure of its relative br ...
Classifying the Stars
... Stars give off different amounts of light depending on their size and temperature. ...
... Stars give off different amounts of light depending on their size and temperature. ...
PH607lec10-4gal2
... S0 galaxies can have bars – a bar can persist in the absence of gas Bar patterns are not static, they rotate with a pattern speed, but unlike spiral arms they are not density waves. Stars in the bar stay in the bar. The bar rotates as a unit in a rigidly rotating disk. The asymmetric gravitational f ...
... S0 galaxies can have bars – a bar can persist in the absence of gas Bar patterns are not static, they rotate with a pattern speed, but unlike spiral arms they are not density waves. Stars in the bar stay in the bar. The bar rotates as a unit in a rigidly rotating disk. The asymmetric gravitational f ...
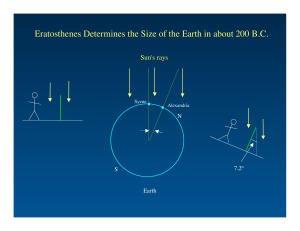
DTU_9e_ch15
... largest of its day. The improved resolution it provided over other telescopes was similar to the improvement that the Hubble Space Telescope provided over Earthbound optical instruments. ...
... largest of its day. The improved resolution it provided over other telescopes was similar to the improvement that the Hubble Space Telescope provided over Earthbound optical instruments. ...
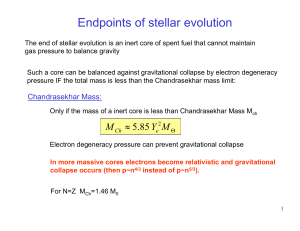
Mass and composition determine most of the properties of a star
... Our sun in 5 billion years will be 2000 times brighter and ...
... Our sun in 5 billion years will be 2000 times brighter and ...
Star Light, Star Bright
... each of the 40 hands-on activities at this grade level. 1. Ask, Why does a streetlight just 10 meters away from us appear brighter to us than the full Moon or any stars in the night sky? (Even though the streetlight is less intense in brightness than the full Moon or stars, it is closer to us, so it ...
... each of the 40 hands-on activities at this grade level. 1. Ask, Why does a streetlight just 10 meters away from us appear brighter to us than the full Moon or any stars in the night sky? (Even though the streetlight is less intense in brightness than the full Moon or stars, it is closer to us, so it ...
Is the Sun a Star? - Classroom Websites
... The probe is primarily designed for students in upper elementary grades or middle school, although it can be used with students in high school as well, both to learn abour students' current thinking and to spark conversation as an introduction to a unit on stars. If students aren't sure what is mean ...
... The probe is primarily designed for students in upper elementary grades or middle school, although it can be used with students in high school as well, both to learn abour students' current thinking and to spark conversation as an introduction to a unit on stars. If students aren't sure what is mean ...
Sun - Cobb Learning
... 6. The apparent visual magnitude of star A is 2 and the apparent visual magnitude of star B is 1. Based on this information which statement below must be true? a. Star A emits more light than star B. b. Star B emits more light than star A. c. Star A is closer than star B. d. Star B is closer than st ...
... 6. The apparent visual magnitude of star A is 2 and the apparent visual magnitude of star B is 1. Based on this information which statement below must be true? a. Star A emits more light than star B. b. Star B emits more light than star A. c. Star A is closer than star B. d. Star B is closer than st ...
1 Epiphany 2014 Following Stars Fr. Frank Schuster In preparation
... was cool. He ranks at number 92 with about 9 million followers. This made me kind of wonder where Pope Francis ranks. So, I scrolled down, and down, and down. Somewhere past Mike Tyson, and Kelly Osbourne I finally found our beloved Pope. He is ranked at number 377 with 3 ½ million followers. I thou ...
... was cool. He ranks at number 92 with about 9 million followers. This made me kind of wonder where Pope Francis ranks. So, I scrolled down, and down, and down. Somewhere past Mike Tyson, and Kelly Osbourne I finally found our beloved Pope. He is ranked at number 377 with 3 ½ million followers. I thou ...
Ursa Major

Ursa Major /ˈɜrsə ˈmeɪdʒər/ (also known as the Great Bear and Charles' Wain) is a constellation in the northern celestial hemisphere. One of the 48 constellations listed by Ptolemy (second century AD), it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. It can be visible throughout the year in most of the northern hemisphere. Its name, Latin for ""the greater (or larger) she-bear"", stands as a reference to and in direct contrast with Ursa Minor, ""the smaller she-bear"", with which it is frequently associated in mythology and amateur astronomy. The constellation's most recognizable asterism, a group of seven relatively bright stars commonly known as the ""Big Dipper"", ""the Wagon"" or ""the Plough"" (among others), both mimicks the shape of the lesser bear (the ""Little Dipper"") and is commonly used as a navigational pointer towards the current northern pole star, Polaris in Ursa Minor. The Big Dipper and the constellation as a whole have mythological significance in numerous world cultures, usually as a symbol of the north.The third largest constellation in the sky, Ursa Major is home to many deep-sky objects including seven Messier objects, four other NGC objects and I Zwicky 18, the youngest known galaxy in the visible universe.