Earth in the Universe Answer each in your binder or notebook. Date
... Which statement about stars is not accurate? A. A small group of stars is called a galaxy. B. Stars consist mainly of hydrogen and helium. C. Types of stars include red giants, super giants, and dwarf stars. D. Constellations of stars are found in different places in the sky. ...
... Which statement about stars is not accurate? A. A small group of stars is called a galaxy. B. Stars consist mainly of hydrogen and helium. C. Types of stars include red giants, super giants, and dwarf stars. D. Constellations of stars are found in different places in the sky. ...
CAREERS IN ASTRONOMY: GRADUATE SCHOOL AND TEACHING
... Small upright radio receivers – about 1.5m high (known as the sparse aperture array) which will operate at low frequencies. What will the SKA be used for? Radio Astronomers will use the SKA to understand how stars and galaxies formed and how they evolved over time; what the so called “Dark matter” i ...
... Small upright radio receivers – about 1.5m high (known as the sparse aperture array) which will operate at low frequencies. What will the SKA be used for? Radio Astronomers will use the SKA to understand how stars and galaxies formed and how they evolved over time; what the so called “Dark matter” i ...
PH507lecnote07_mcp2
... few of the many hundred different species and their emission (absorption) frequency. ...
... few of the many hundred different species and their emission (absorption) frequency. ...
Newton`s laws of motion and gravity
... troughs = wavelength How many peaks or troughs pass by you per second? = frequency ...
... troughs = wavelength How many peaks or troughs pass by you per second? = frequency ...
Slide 1
... (a very short, woefully incomplete list) 1) How else do we know the brightnesses of stars? (how bright is a Cepheid, tests of stellar evolution code, distance to LMC, distance ladder…) 2) We’d like a volume limited sample of stars (in the largest possible volume (Sun’s nearest neighbors are well hid ...
... (a very short, woefully incomplete list) 1) How else do we know the brightnesses of stars? (how bright is a Cepheid, tests of stellar evolution code, distance to LMC, distance ladder…) 2) We’d like a volume limited sample of stars (in the largest possible volume (Sun’s nearest neighbors are well hid ...
Word
... isotropic to one of our ant-astronomers. In each direction within the 2-d surface of the balloon, he/she will see the same general appearance of the Universe (our 2-d ant-astronomers are not allowed to even think of the third dimension, let alone look in that direction!). Furthermore, that view of t ...
... isotropic to one of our ant-astronomers. In each direction within the 2-d surface of the balloon, he/she will see the same general appearance of the Universe (our 2-d ant-astronomers are not allowed to even think of the third dimension, let alone look in that direction!). Furthermore, that view of t ...
- EPJ Web of Conferences
... significant numbers in the Milky Way. The dSph are indeed small galaxies, formed over long times with low rates of star formation. Most of the stars in the Milky Way halo however seem to have formed quickly, at higher star formation rate, in gas mixed efficiently on kpc scales. The overwhelming majo ...
... significant numbers in the Milky Way. The dSph are indeed small galaxies, formed over long times with low rates of star formation. Most of the stars in the Milky Way halo however seem to have formed quickly, at higher star formation rate, in gas mixed efficiently on kpc scales. The overwhelming majo ...
b) How to Create Large Disks despite Major Mergers
... II. What we Learn a) The Creation of a Bulgeless Disk Galaxy with a Dark Matter “Core” b) How to Create Large Disks despite Major Mergers ...
... II. What we Learn a) The Creation of a Bulgeless Disk Galaxy with a Dark Matter “Core” b) How to Create Large Disks despite Major Mergers ...
IOSR Journal of Applied Physics (IOSR-JAP) e-ISSN: 2278-4861.
... then, the distribution of galaxy shapes has been frozen, an indication that smash-ups and mergers have become relatively uncommon. This is a good story, but is it true? Galaxy mergers, black hole activity and star formation all decline with time, and very likely they are related in some way. But ast ...
... then, the distribution of galaxy shapes has been frozen, an indication that smash-ups and mergers have become relatively uncommon. This is a good story, but is it true? Galaxy mergers, black hole activity and star formation all decline with time, and very likely they are related in some way. But ast ...
Answers The Universe Year 10 Science Chapter 6
... 13.8 billion years ago and massively expanded. The universe expanded faster than the speed of light within the first few tiny fractions of a second and has continued to expand. 2 Phase 1 The inflation phase of a very early universe where extremely intense energy expands spacetime. Phase 2 The coo ...
... 13.8 billion years ago and massively expanded. The universe expanded faster than the speed of light within the first few tiny fractions of a second and has continued to expand. 2 Phase 1 The inflation phase of a very early universe where extremely intense energy expands spacetime. Phase 2 The coo ...
April 2015 - Southern Astronomical Society
... dark matter does not slow down when it collides with itself. This is significant as it shows the ghostly substance interacts with itself less than previously thought, narrowing down the options of what this invisible material might be. Dark matter does not reflect or absorb light. But its presence c ...
... dark matter does not slow down when it collides with itself. This is significant as it shows the ghostly substance interacts with itself less than previously thought, narrowing down the options of what this invisible material might be. Dark matter does not reflect or absorb light. But its presence c ...
Dark Sky Scotland - Constellation Project
... Scottish contributions to astronomy. On a clear night, some of the stars that we can see are up to 2,000 Light Years away. But measuring accurately the distance to stars and other distant objects still remains a problem for astronomers. In the 1990s, many stellar distances were radically updated bas ...
... Scottish contributions to astronomy. On a clear night, some of the stars that we can see are up to 2,000 Light Years away. But measuring accurately the distance to stars and other distant objects still remains a problem for astronomers. In the 1990s, many stellar distances were radically updated bas ...
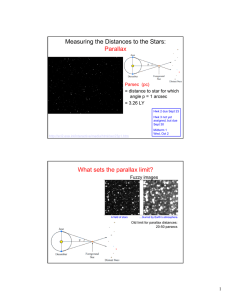
Measuring the Distances to the Stars: Parallax What sets the parallax limit?
... MW Rotation Curve • In principle, for stars, clusters, etc: ...
... MW Rotation Curve • In principle, for stars, clusters, etc: ...
22 pm - Starmap
... Using binoculars, preferably with a tripod, will considerably enhance your star gazing experience. Many deep sky objects like galaxies and clusters will be within reach. Jupiter satellites and Saturn’s rings will also be visible. A spectacular experience for beginners in astronomy... Avoid the night ...
... Using binoculars, preferably with a tripod, will considerably enhance your star gazing experience. Many deep sky objects like galaxies and clusters will be within reach. Jupiter satellites and Saturn’s rings will also be visible. A spectacular experience for beginners in astronomy... Avoid the night ...
Cosmology, galaxies, stars and the sun
... form it into a disk with a hot, condensed object called a protostar. •Once the protostar becomes hot ...
... form it into a disk with a hot, condensed object called a protostar. •Once the protostar becomes hot ...
Hubble Deep Field

The Hubble Deep Field (HDF) is an image of a small region in the constellation Ursa Major, constructed from a series of observations by the Hubble Space Telescope. It covers an area 2.5 arcminutes across, about one 24-millionth of the whole sky, which is equivalent in angular size to a 65 mm tennis ball at a distance of 100 metres. The image was assembled from 342 separate exposures taken with the Space Telescope's Wide Field and Planetary Camera 2 over ten consecutive days between December 18 and December 28, 1995.The field is so small that only a few foreground stars in the Milky Way lie within it; thus, almost all of the 3,000 objects in the image are galaxies, some of which are among the youngest and most distant known. By revealing such large numbers of very young galaxies, the HDF has become a landmark image in the study of the early universe, with the associated scientific paper having received over 900 citations by the end of 2014.Three years after the HDF observations were taken, a region in the south celestial hemisphere was imaged in a similar way and named the Hubble Deep Field South. The similarities between the two regions strengthened the belief that the universe is uniform over large scales and that the Earth occupies a typical region in the Universe (the cosmological principle). A wider but shallower survey was also made as part of the Great Observatories Origins Deep Survey. In 2004 a deeper image, known as the Hubble Ultra-Deep Field (HUDF), was constructed from a few months of light exposure. The HUDF image was at the time the most sensitive astronomical image ever made at visible wavelengths, and it remained so until the Hubble Extreme Deep Field (XDF) was released in 2012.