A Tour of the Radio Universe
... cosmic explosions (gamma-ray bursts, X-ray flashes, and some types of supernovae) have the same amount of total energy and therefore share a common origin. Image credit The final stop on any tour of the radio universe is the cosmic microwave background radiation (CMBR), which is thermal radiation fr ...
... cosmic explosions (gamma-ray bursts, X-ray flashes, and some types of supernovae) have the same amount of total energy and therefore share a common origin. Image credit The final stop on any tour of the radio universe is the cosmic microwave background radiation (CMBR), which is thermal radiation fr ...
Eye in the sky - Academy of Science of South Africa
... blurring is corrected for (and many large telescopes are starting to have this capability, called adaptive optics), the distance to distinguish those headlights would be close to 10 000 km for SALT. So far the discussion has been centred on images a telescope takes, but in fact the great majority of ...
... blurring is corrected for (and many large telescopes are starting to have this capability, called adaptive optics), the distance to distinguish those headlights would be close to 10 000 km for SALT. So far the discussion has been centred on images a telescope takes, but in fact the great majority of ...
Astronomy Exam Notes.docx
... d. the photoelectric effect can be create vacuum energy 19. the light from distant galaxies is redshifted because a. they are moving through space b. the wavelengths are stretched by the expansion of space c. their lookback times are less d. the stars in them are older at these lookback times 20. th ...
... d. the photoelectric effect can be create vacuum energy 19. the light from distant galaxies is redshifted because a. they are moving through space b. the wavelengths are stretched by the expansion of space c. their lookback times are less d. the stars in them are older at these lookback times 20. th ...
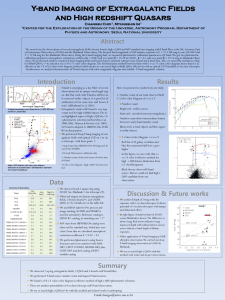
Y-band Imaging of Extragalatic Fields and High redshift
... We carried out the observations of several extragalactic fields, brown dwarfs, high-z QSO and A0V standard star imaging with Y-band filter at the Mt. Lemmon Opti cal Astronomy Observatory (LOAO) and the Maidanak Observatory. The deepest limit magnitude of 260 minutes exposure is Y = 21.5 AB mag in c ...
... We carried out the observations of several extragalactic fields, brown dwarfs, high-z QSO and A0V standard star imaging with Y-band filter at the Mt. Lemmon Opti cal Astronomy Observatory (LOAO) and the Maidanak Observatory. The deepest limit magnitude of 260 minutes exposure is Y = 21.5 AB mag in c ...
Galileo Galilei From The Starry Messenger (1610) and The Assayer
... prominences, deep valleys, and chasms. Again, it seems to me a matter of no small importance to have ended the dispute about the Milky Way by making its nature manifest to the very senses as well as to the intellect. Similarly it will be a pleasant and elegant thing to demonstrate that the nature of ...
... prominences, deep valleys, and chasms. Again, it seems to me a matter of no small importance to have ended the dispute about the Milky Way by making its nature manifest to the very senses as well as to the intellect. Similarly it will be a pleasant and elegant thing to demonstrate that the nature of ...
Chapter 16 - "The Universe"
... – After millions of years of helium fusion reactions the core gradually is converted to a carbon core, with two shells, one of helium fusion reactions and one of hydrogen fusion reactions • This results in a great release of energy and the star reverts back to a red giant one more time. • As the ou ...
... – After millions of years of helium fusion reactions the core gradually is converted to a carbon core, with two shells, one of helium fusion reactions and one of hydrogen fusion reactions • This results in a great release of energy and the star reverts back to a red giant one more time. • As the ou ...
File - Science with Mrs. Schmidt
... _____ 10. A continuous spectrum is a spectrum that shows a. some of the colors. b. some of the colors and some black lines. c. all the colors. d. all the colors and some black lines. _____ 11. What instrument breaks a star’s light into a spectrum? a. a continuous spectrum b. a telescope c. a spectro ...
... _____ 10. A continuous spectrum is a spectrum that shows a. some of the colors. b. some of the colors and some black lines. c. all the colors. d. all the colors and some black lines. _____ 11. What instrument breaks a star’s light into a spectrum? a. a continuous spectrum b. a telescope c. a spectro ...
Wednesday, April 17 - Otterbein University
... Where Stars come from: the Interstellar Medium • Gas – Single atoms and molecules – Mostly hydrogen (90%), 9% helium; deficient in heavier elements ...
... Where Stars come from: the Interstellar Medium • Gas – Single atoms and molecules – Mostly hydrogen (90%), 9% helium; deficient in heavier elements ...
Starburst Galaxies Under the Microscope: High
... evolution of galaxies that are by definition transient, and during which they convert a significant fraction of their gas reservoirs into stars. During a starburst phase a galaxy thus evolves rapidly in stellar, gas, dust and metal content, colour, luminosity and morphology. Starburst galaxies also ...
... evolution of galaxies that are by definition transient, and during which they convert a significant fraction of their gas reservoirs into stars. During a starburst phase a galaxy thus evolves rapidly in stellar, gas, dust and metal content, colour, luminosity and morphology. Starburst galaxies also ...
VLT identifications in the Chandra/XMM
... has covered this field to moderate depths in several bands (Arnouts et al. 2001; Vandame et al. 2001). The EIS data have been obtained using the Wide Field Imager (WFI) on the ESOMPG 2.2 meter telescope at La Silla. Figure 3 shows Chandra X-ray contours in a selected area of the CDFS superposed on a ...
... has covered this field to moderate depths in several bands (Arnouts et al. 2001; Vandame et al. 2001). The EIS data have been obtained using the Wide Field Imager (WFI) on the ESOMPG 2.2 meter telescope at La Silla. Figure 3 shows Chandra X-ray contours in a selected area of the CDFS superposed on a ...
December 2007 Clear Skies Newsletter PDF
... A study of ancient galaxies led astronomers to a goldmine of black holes, a discovery that more than doubles the number found in the early universe. "We had seen the tip of the iceberg. Now, we can see the iceberg itself," says Dr Mark Dickinson, with the US National Optical Astronomy Observatory in ...
... A study of ancient galaxies led astronomers to a goldmine of black holes, a discovery that more than doubles the number found in the early universe. "We had seen the tip of the iceberg. Now, we can see the iceberg itself," says Dr Mark Dickinson, with the US National Optical Astronomy Observatory in ...
Intro
... less light to reach a threshold response than do the rods. Thereafter, the rods require less light. The point at which the rods become more sensitive is called the rod-cone break. It is after this break where you can start to really see detail well in the dark. ...
... less light to reach a threshold response than do the rods. Thereafter, the rods require less light. The point at which the rods become more sensitive is called the rod-cone break. It is after this break where you can start to really see detail well in the dark. ...
Instructor`s Guide
... • All motion is relative to whatever frame of reference is chosen, for there is no motionless frame from which to judge all motion. • In empty space, all electromagnetic waves move at the same speed — the “speed of light.” • Because the light seen from almost all distant galaxies has longer wavel ...
... • All motion is relative to whatever frame of reference is chosen, for there is no motionless frame from which to judge all motion. • In empty space, all electromagnetic waves move at the same speed — the “speed of light.” • Because the light seen from almost all distant galaxies has longer wavel ...
Take our Astronomy Test
... 1. How was it first determined that Earth was a sphere and who (what culture) did this? 2. What did Eratosthenes do? 3. What is a geocentric model? 4. What are the contributions of Ptolemy? 5. What was the contribution of Copernicus? 6. What is a heliocentric model? 7. How does the heliocentric mode ...
... 1. How was it first determined that Earth was a sphere and who (what culture) did this? 2. What did Eratosthenes do? 3. What is a geocentric model? 4. What are the contributions of Ptolemy? 5. What was the contribution of Copernicus? 6. What is a heliocentric model? 7. How does the heliocentric mode ...
Sample final exam
... 19. On page 184, the text states “Understand the fact that we [the Milky Way] are moving toward M31 and that the Large Magellenic Cloud [LMC] is moving toward us.” First, explain what we observe about these galaxies (M31, the LMC) that shows they are moving in the directions the text states. I thoug ...
... 19. On page 184, the text states “Understand the fact that we [the Milky Way] are moving toward M31 and that the Large Magellenic Cloud [LMC] is moving toward us.” First, explain what we observe about these galaxies (M31, the LMC) that shows they are moving in the directions the text states. I thoug ...
Lab Writeup
... eyepiece of our refractor telescopes. At least two eyepieces will be used. The first will have a fairly large field of view. The second will have higher magnification, and has a scale which allows you to fairly accurately measure small angles. The focal length of the Orion 80 “short tube” refractor ...
... eyepiece of our refractor telescopes. At least two eyepieces will be used. The first will have a fairly large field of view. The second will have higher magnification, and has a scale which allows you to fairly accurately measure small angles. The focal length of the Orion 80 “short tube” refractor ...
Stars
... b. their temperature. c. their age. d. their size. ______ 18. Stars are now classified by a. their elements. b. their temperature. c. their age. d. their size. ______ 19. Class O stars, the hottest stars, are a. yellow. b. orange. c. red. d. blue. 20. Early astronomers called the brightest stars in ...
... b. their temperature. c. their age. d. their size. ______ 18. Stars are now classified by a. their elements. b. their temperature. c. their age. d. their size. ______ 19. Class O stars, the hottest stars, are a. yellow. b. orange. c. red. d. blue. 20. Early astronomers called the brightest stars in ...
Hubble Deep Field

The Hubble Deep Field (HDF) is an image of a small region in the constellation Ursa Major, constructed from a series of observations by the Hubble Space Telescope. It covers an area 2.5 arcminutes across, about one 24-millionth of the whole sky, which is equivalent in angular size to a 65 mm tennis ball at a distance of 100 metres. The image was assembled from 342 separate exposures taken with the Space Telescope's Wide Field and Planetary Camera 2 over ten consecutive days between December 18 and December 28, 1995.The field is so small that only a few foreground stars in the Milky Way lie within it; thus, almost all of the 3,000 objects in the image are galaxies, some of which are among the youngest and most distant known. By revealing such large numbers of very young galaxies, the HDF has become a landmark image in the study of the early universe, with the associated scientific paper having received over 900 citations by the end of 2014.Three years after the HDF observations were taken, a region in the south celestial hemisphere was imaged in a similar way and named the Hubble Deep Field South. The similarities between the two regions strengthened the belief that the universe is uniform over large scales and that the Earth occupies a typical region in the Universe (the cosmological principle). A wider but shallower survey was also made as part of the Great Observatories Origins Deep Survey. In 2004 a deeper image, known as the Hubble Ultra-Deep Field (HUDF), was constructed from a few months of light exposure. The HUDF image was at the time the most sensitive astronomical image ever made at visible wavelengths, and it remained so until the Hubble Extreme Deep Field (XDF) was released in 2012.