Cold galaxies at low and high z
... the distances between galaxies will increase at an ever-accelerating rate, but the horizon will remain fixed at more or less its current size, 13 billion light yrs eventually, after 100 billion years, our Galaxy will have merged with Andromeda and our other neighbours in the Local Group into a singl ...
... the distances between galaxies will increase at an ever-accelerating rate, but the horizon will remain fixed at more or less its current size, 13 billion light yrs eventually, after 100 billion years, our Galaxy will have merged with Andromeda and our other neighbours in the Local Group into a singl ...
FREE Sample Here
... 2) Briefly explain what we mean by the statement "The farther away we look in distance, the further back we look in time." Answer: It means that when we look at a distant object, we see it as it was some time in the past, rather than as it is now. This is because the light we see has taken time to t ...
... 2) Briefly explain what we mean by the statement "The farther away we look in distance, the further back we look in time." Answer: It means that when we look at a distant object, we see it as it was some time in the past, rather than as it is now. This is because the light we see has taken time to t ...
Unit 44: Astronomy
... learners to develop a detailed case study of one feature from the list provided. It is important for learners to fully appreciate the health and safety aspects of astronomical observations and all other practical activities which will be carried out in learning outcome 2. Experimental work on telesc ...
... learners to develop a detailed case study of one feature from the list provided. It is important for learners to fully appreciate the health and safety aspects of astronomical observations and all other practical activities which will be carried out in learning outcome 2. Experimental work on telesc ...
Multi-Object Adaptive Optics and Multi
... AO. The existing MOAO and MCAO design studies should be reviewed. This report is a summary of the issues related to these two approaches, including an understanding of the potential risks, technical challenges, limitations, advantages and room for improvement with each of these approaches. 1. Introd ...
... AO. The existing MOAO and MCAO design studies should be reviewed. This report is a summary of the issues related to these two approaches, including an understanding of the potential risks, technical challenges, limitations, advantages and room for improvement with each of these approaches. 1. Introd ...
The Cook Memorial Library
... Star Clusters are particularly pretty, usually bright and easy to see. Note that some deep sky objects, even those on the DeepMap 600, are very faint, and will take a while to find and see. A few are very dim, but may seem to appear like magic when you look at them “out of the corner of your eye”. T ...
... Star Clusters are particularly pretty, usually bright and easy to see. Note that some deep sky objects, even those on the DeepMap 600, are very faint, and will take a while to find and see. A few are very dim, but may seem to appear like magic when you look at them “out of the corner of your eye”. T ...
Galaxies
... understanding of gas cooling, star formation, and feedback. We know that our current prescriptions for these processes are vastly oversimplified, but hope to learn about how these processes operate – when averaged over entire galaxies – by comparison to observations. Because the overall process is s ...
... understanding of gas cooling, star formation, and feedback. We know that our current prescriptions for these processes are vastly oversimplified, but hope to learn about how these processes operate – when averaged over entire galaxies – by comparison to observations. Because the overall process is s ...
THE PRIMORDIAL HELIUM ABUNDANCE Manuel Peimbert
... representative of the whole star, and consequently that they had cosmological implications, and concluded that this was not the case. Searle & Sargent (17) obtained for Y values of 0.29 ± 0.05 and 0.25 ± 0.05 respectively, for I Zwicky 18 and II Zwicky 40 two irregular galaxies with: a low content o ...
... representative of the whole star, and consequently that they had cosmological implications, and concluded that this was not the case. Searle & Sargent (17) obtained for Y values of 0.29 ± 0.05 and 0.25 ± 0.05 respectively, for I Zwicky 18 and II Zwicky 40 two irregular galaxies with: a low content o ...
Stars Of Orion Essay Research Paper 01
... Initially looking at the Orion Nebula in the top image, is just like looking at a single point of light against a dark background. Only under the magnification of a telescope can you see that point, is actually a mass of gaseous cloud, which contains four very bright prominent stars, named the Trape ...
... Initially looking at the Orion Nebula in the top image, is just like looking at a single point of light against a dark background. Only under the magnification of a telescope can you see that point, is actually a mass of gaseous cloud, which contains four very bright prominent stars, named the Trape ...
dark matter. - Gordon State College
... Hubble’s Law • Hubble’s Measure of Distance – Hubble could deduce the distance of a star from the Earth by comparing its luminosity (energy) and brightness. – The brightness of light obeys an inverse square law. (An object twice as far away will appear one quarter as bright) © 2012 Pearson Educatio ...
... Hubble’s Law • Hubble’s Measure of Distance – Hubble could deduce the distance of a star from the Earth by comparing its luminosity (energy) and brightness. – The brightness of light obeys an inverse square law. (An object twice as far away will appear one quarter as bright) © 2012 Pearson Educatio ...
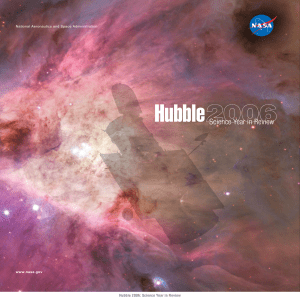
Hubble 2006: Science Year in Review
... This book is a joint project of NASA Goddard Space Flight Center and the Space Telescope Science Institute under contract NAS5-26555. The Space Telescope Science Institute is operated by the Association of Universities for Research in Astronomy, Inc., in cooperation with the European Space Agency a ...
... This book is a joint project of NASA Goddard Space Flight Center and the Space Telescope Science Institute under contract NAS5-26555. The Space Telescope Science Institute is operated by the Association of Universities for Research in Astronomy, Inc., in cooperation with the European Space Agency a ...
Galaxies
... b. the barred spiral galaxies. c. the dwarf elliptical galaxies. d. the irregular galaxies. e. the giant elliptical galaxies. We should expect galaxies to collide fairly often because a. they are large with respect to their separation distances. b. galaxies contain large amounts of neutral hydrogen. ...
... b. the barred spiral galaxies. c. the dwarf elliptical galaxies. d. the irregular galaxies. e. the giant elliptical galaxies. We should expect galaxies to collide fairly often because a. they are large with respect to their separation distances. b. galaxies contain large amounts of neutral hydrogen. ...
Xiao Yang Xia
... decreases with the central black hole mass. This shows that the tight correlation between the stellar mass and the central black hole mass is preserved in massive starbursts during violent mergers. (3) Similar to IR QSOs at low redshift, the optically selected QSOs detected at mm band at high redshi ...
... decreases with the central black hole mass. This shows that the tight correlation between the stellar mass and the central black hole mass is preserved in massive starbursts during violent mergers. (3) Similar to IR QSOs at low redshift, the optically selected QSOs detected at mm band at high redshi ...
pkt 14 Astrophysics
... centre of mass. For each star, the other is its companion star. A large percentage of stars are part of systems with at least two stars. Binary star systems are very important in astrophysics, because observing their mutual orbits allows their mass to be determined. The masses of many single stars c ...
... centre of mass. For each star, the other is its companion star. A large percentage of stars are part of systems with at least two stars. Binary star systems are very important in astrophysics, because observing their mutual orbits allows their mass to be determined. The masses of many single stars c ...
Neistein_dekel60
... The history of one galaxy We follow all the particles, and check which got heated/cooled/SF/accreted ...
... The history of one galaxy We follow all the particles, and check which got heated/cooled/SF/accreted ...
Hubble Deep Field

The Hubble Deep Field (HDF) is an image of a small region in the constellation Ursa Major, constructed from a series of observations by the Hubble Space Telescope. It covers an area 2.5 arcminutes across, about one 24-millionth of the whole sky, which is equivalent in angular size to a 65 mm tennis ball at a distance of 100 metres. The image was assembled from 342 separate exposures taken with the Space Telescope's Wide Field and Planetary Camera 2 over ten consecutive days between December 18 and December 28, 1995.The field is so small that only a few foreground stars in the Milky Way lie within it; thus, almost all of the 3,000 objects in the image are galaxies, some of which are among the youngest and most distant known. By revealing such large numbers of very young galaxies, the HDF has become a landmark image in the study of the early universe, with the associated scientific paper having received over 900 citations by the end of 2014.Three years after the HDF observations were taken, a region in the south celestial hemisphere was imaged in a similar way and named the Hubble Deep Field South. The similarities between the two regions strengthened the belief that the universe is uniform over large scales and that the Earth occupies a typical region in the Universe (the cosmological principle). A wider but shallower survey was also made as part of the Great Observatories Origins Deep Survey. In 2004 a deeper image, known as the Hubble Ultra-Deep Field (HUDF), was constructed from a few months of light exposure. The HUDF image was at the time the most sensitive astronomical image ever made at visible wavelengths, and it remained so until the Hubble Extreme Deep Field (XDF) was released in 2012.