Cosmic future of nuclear and particle physics
... One of the most striking discoveries in astronomy was observation of pulsars − objects emitting radiowave pulses with a period of milliseconds to seconds. Later, it was understood that pulsars are, in fact, neutron stars, composed of densely packed neutrons. They can be considered as gigantic nuclei ...
... One of the most striking discoveries in astronomy was observation of pulsars − objects emitting radiowave pulses with a period of milliseconds to seconds. Later, it was understood that pulsars are, in fact, neutron stars, composed of densely packed neutrons. They can be considered as gigantic nuclei ...
PPT - ALFALFA survey
... Schneider (2000). It was a drift-scan survey taken in a series of declination strips with the Arecibo 305-m telescope. The velocity limit of the ADBS is 8000 km/s (it is volume limited!). The full ADBS sample includes 265 galaxies over ~420 sq. deg. • Since it is a “blind” HI survey, it does not suf ...
... Schneider (2000). It was a drift-scan survey taken in a series of declination strips with the Arecibo 305-m telescope. The velocity limit of the ADBS is 8000 km/s (it is volume limited!). The full ADBS sample includes 265 galaxies over ~420 sq. deg. • Since it is a “blind” HI survey, it does not suf ...
File
... This presentation was initially developed for the “Modeling the Universe” educator workshop by the Universe Education Forum and our NASA mission partners. For additional information and activities related to the themes of this presentation, please visit the “Modeling the Universe” web site: http://w ...
... This presentation was initially developed for the “Modeling the Universe” educator workshop by the Universe Education Forum and our NASA mission partners. For additional information and activities related to the themes of this presentation, please visit the “Modeling the Universe” web site: http://w ...
1 Is the Binding Energy of Galaxies related to their Core
... It is by now well established that most large galaxies (spiral, elliptical, etc.) host a supermassive black hole in their centre [1]. Again AGN’s, quasars, etc. are powered by the gravitational energy of matter accreting on to these central supermassive black holes [2]. These black hole masses are t ...
... It is by now well established that most large galaxies (spiral, elliptical, etc.) host a supermassive black hole in their centre [1]. Again AGN’s, quasars, etc. are powered by the gravitational energy of matter accreting on to these central supermassive black holes [2]. These black hole masses are t ...
The Big Bang
... • The universe had a specific beginning (night sky is dark; Hubble’s Law; approximate age = 1/H0) • The universe is expanding (Hubble’s Law) • The universe has evolved/changed over time • Initially, the universe was extremely hot, dense, and opaque • Cosmic objects (such as stars) should have a chem ...
... • The universe had a specific beginning (night sky is dark; Hubble’s Law; approximate age = 1/H0) • The universe is expanding (Hubble’s Law) • The universe has evolved/changed over time • Initially, the universe was extremely hot, dense, and opaque • Cosmic objects (such as stars) should have a chem ...
Astrophysics
... a. (2 pts) Write or derive an equation for hydrostatic equilibrium in a form that is suitable for the interior of the sun, i.e., express dP/dr in terms of G, m, ρ, and r, where m is the mass interior to radius r and ρ is the mass density. b. (1 pt) Rewrite the equation with m as the independent vari ...
... a. (2 pts) Write or derive an equation for hydrostatic equilibrium in a form that is suitable for the interior of the sun, i.e., express dP/dr in terms of G, m, ρ, and r, where m is the mass interior to radius r and ρ is the mass density. b. (1 pt) Rewrite the equation with m as the independent vari ...
Galaxies – Island universes
... the first billion years or so after the Big Bang • Many have later infalling matter which has been pulled on by nearby mass and thus doesn’t fall straight in. It settles into a rotating disk, arranging itself into a flat, roughly circularly orbiting plane of material • This material gradually conden ...
... the first billion years or so after the Big Bang • Many have later infalling matter which has been pulled on by nearby mass and thus doesn’t fall straight in. It settles into a rotating disk, arranging itself into a flat, roughly circularly orbiting plane of material • This material gradually conden ...
AST 207 Test 3 23 November 2009
... a. (1 pt.) At the present time, does the value of Hubble’s constant depend on the galaxy in which the observations are made? (2 pts.) Explain your reasoning. b. Simplicio erroneously believes that everything in the universe is expanding according to Hubble’s Law. At an earlier time, everything did o ...
... a. (1 pt.) At the present time, does the value of Hubble’s constant depend on the galaxy in which the observations are made? (2 pts.) Explain your reasoning. b. Simplicio erroneously believes that everything in the universe is expanding according to Hubble’s Law. At an earlier time, everything did o ...
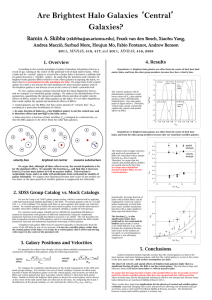
Ramin A. Skibba - Southern California Center for Galaxy Evolution
... We use the Yang et al. (2007) galaxy group catalog, which is constructed by applying a DM halo-based group-finding algorithm to the SDSS. We include galaxies with mr=-18 and 0.01 < z < 0.20, yielding 7234 groups with three or more galaxies that satisfy our selection criteria. We exclude groups in wh ...
... We use the Yang et al. (2007) galaxy group catalog, which is constructed by applying a DM halo-based group-finding algorithm to the SDSS. We include galaxies with mr=-18 and 0.01 < z < 0.20, yielding 7234 groups with three or more galaxies that satisfy our selection criteria. We exclude groups in wh ...
SCIN 293-PL-New Course
... Topic Mastery: Describe the steps in the life of a 1 solar mass stars and contrast them with the steps in the life of a 10 solar mass star. Also focus on the differences in the fusion processes of low vs. high mass stars. ...
... Topic Mastery: Describe the steps in the life of a 1 solar mass stars and contrast them with the steps in the life of a 10 solar mass star. Also focus on the differences in the fusion processes of low vs. high mass stars. ...
Conference Summary Richard Ellis (Caltech) ITALIA
... The complex gas flows into a dark matter halo with a forming disk galaxy at a redshift z=3. R=temperature, G=metals and B=density. (Agertz, Teyssier & Moore 2009). One can clearly distinguish the cold pristine gas streams in blue connecting directly onto the edge of the disk, the shock heated gas i ...
... The complex gas flows into a dark matter halo with a forming disk galaxy at a redshift z=3. R=temperature, G=metals and B=density. (Agertz, Teyssier & Moore 2009). One can clearly distinguish the cold pristine gas streams in blue connecting directly onto the edge of the disk, the shock heated gas i ...
the world after the revolution: physics in the
... First of all, by the time the Tomonaga-SchwingerFeynman theory came out, it was already clear that, besides the traditional forces of electromagnetism and gravity, there were two more: weak force, responsible for the existence of radioactivity; and strong force, which holds together the components ( ...
... First of all, by the time the Tomonaga-SchwingerFeynman theory came out, it was already clear that, besides the traditional forces of electromagnetism and gravity, there were two more: weak force, responsible for the existence of radioactivity; and strong force, which holds together the components ( ...
First Light for May, 2001 - South Bay Astronomical Society
... motion towards or away from Earth. Thus, the Wobble method provides for a wider range of planetary systems. If both methods can be used on a exo-system, the size and mass of the planets can be determined. Given these two methods, it’s not entirely surprising that many of the earliest exo-planets dis ...
... motion towards or away from Earth. Thus, the Wobble method provides for a wider range of planetary systems. If both methods can be used on a exo-system, the size and mass of the planets can be determined. Given these two methods, it’s not entirely surprising that many of the earliest exo-planets dis ...
A n A n c i e n... How Astronomers Know the Vast Scale of Cosmic Time
... Over a hundred of these stars are now known to have planets, just the way the Sun does. Some stars show evidence of being much older than the Sun, and some are just gathering together from the raw material of the galaxy. One of the nicest things about the universe is that it sends its information to ...
... Over a hundred of these stars are now known to have planets, just the way the Sun does. Some stars show evidence of being much older than the Sun, and some are just gathering together from the raw material of the galaxy. One of the nicest things about the universe is that it sends its information to ...
Starbursts – from 30 Doradus to Lyman
... our UV spectroscopic capability, while HST’s gyros (used for attitude control) are not expected to last more than a few years. A robotic repair mission is currently under design, but many are sceptical that this will be realized rapidly enough to avert disaster for our community. ...
... our UV spectroscopic capability, while HST’s gyros (used for attitude control) are not expected to last more than a few years. A robotic repair mission is currently under design, but many are sceptical that this will be realized rapidly enough to avert disaster for our community. ...
Interacting Galaxies
... universe, 1 out of every 20 gas-rich disk galaxies, like our Milky Way galaxy, is in the act of colliding. Galaxy mergers were much more common in the past, however, when the expanding universe was smaller. For example, in a class of galaxies called ultraluminous infrared galaxies, which have quasar ...
... universe, 1 out of every 20 gas-rich disk galaxies, like our Milky Way galaxy, is in the act of colliding. Galaxy mergers were much more common in the past, however, when the expanding universe was smaller. For example, in a class of galaxies called ultraluminous infrared galaxies, which have quasar ...
Powerpoint slides
... If this movie does not appear on the screen, please download the sixth animation down on this page: http://wmap.gsfc.nasa.gov/m_or/mr_media2.html caption: “See how the structure of the Universe evolved from WMAP's "baby picture" of the Big Bang through the clumping and ignition of matter (which cau ...
... If this movie does not appear on the screen, please download the sixth animation down on this page: http://wmap.gsfc.nasa.gov/m_or/mr_media2.html caption: “See how the structure of the Universe evolved from WMAP's "baby picture" of the Big Bang through the clumping and ignition of matter (which cau ...
Equation of State of Dense Matter and the Upper Mass Limit for
... compression modulus, etc. , because the small rv 16 MeV net binding energy per nucleon results from near cancellation of large quantities, each of natural scale I Ge V. Thus, the fit is a very sensitive one. Extrapolation of theories of nuclear matter to supranuclear densities has had Iittle empiric ...
... compression modulus, etc. , because the small rv 16 MeV net binding energy per nucleon results from near cancellation of large quantities, each of natural scale I Ge V. Thus, the fit is a very sensitive one. Extrapolation of theories of nuclear matter to supranuclear densities has had Iittle empiric ...
Lambda-CDM model

The ΛCDM (Lambda cold dark matter) or Lambda-CDM model is a parametrization of the Big Bang cosmological model in which the universe contains a cosmological constant, denoted by Lambda (Greek Λ), associated with dark energy, and cold dark matter (abbreviated CDM). It is frequently referred to as the standard model of Big Bang cosmology, because it is the simplest model that provides a reasonably good account of the following properties of the cosmos: the existence and structure of the cosmic microwave background the large-scale structure in the distribution of galaxies the abundances of hydrogen (including deuterium), helium, and lithium the accelerating expansion of the universe observed in the light from distant galaxies and supernovaeThe model assumes that general relativity is the correct theory of gravity on cosmological scales.It emerged in the late 1990s as a concordance cosmology, after a period of time when disparate observed properties of the universe appeared mutually inconsistent, and there was no consensus on the makeup of the energy density of the universe.The ΛCDM model can be extended by adding cosmological inflation, quintessence and other elements that are current areas of speculation and research in cosmology.Some alternative models challenge the assumptions of the ΛCDM model. Examples of these are modified Newtonian dynamics, modified gravity and theories of large-scale variations in the matter density of the universe.