Project topics
... 1. Equipment and instruments that explore the universe (telescopes, satellites, probes, rockets, shuttles etc.). 2. Electromagnetic spectrum and its importance in astronomy. 3. Spectroscopes and the spectrums of stars. Include information about a spectroscope, spectrums of different gases, the Doppl ...
... 1. Equipment and instruments that explore the universe (telescopes, satellites, probes, rockets, shuttles etc.). 2. Electromagnetic spectrum and its importance in astronomy. 3. Spectroscopes and the spectrums of stars. Include information about a spectroscope, spectrums of different gases, the Doppl ...
Astronomy 101 Section 4
... A quasar (it’s the “star” on the right) - pretty boring until you get close. But not too close! ...
... A quasar (it’s the “star” on the right) - pretty boring until you get close. But not too close! ...
Lecture 1 Coordinate Systems - Department of Physics & Astronomy
... Type IA Supernovae •Explosion of white dwarf in a binary system ...
... Type IA Supernovae •Explosion of white dwarf in a binary system ...
Math Primer - UMass Amherst
... You can say the distance to Boston in miles (or km) instead of inches (or cm)! Translating to useful units is a very handy skill. The key to changing units is remembering to replace a unit by something equivalent ...
... You can say the distance to Boston in miles (or km) instead of inches (or cm)! Translating to useful units is a very handy skill. The key to changing units is remembering to replace a unit by something equivalent ...
ITB - In the Beginning
... from the city. It wasn't radiation from our galaxy or extraterrestrial radio sources. It wasn't even the pigeons living in the big, horn-shaped antenna. They kicked them out and swept out all their droppings. The source remained the same through four seasons, so it couldn't have come from the solar ...
... from the city. It wasn't radiation from our galaxy or extraterrestrial radio sources. It wasn't even the pigeons living in the big, horn-shaped antenna. They kicked them out and swept out all their droppings. The source remained the same through four seasons, so it couldn't have come from the solar ...
Before people could understand the history of the universe, they had
... - applied his equations to Kepler's observations (it fit almost perfectly) • The conclusions were indisputable: Copernicus had been right all along (actually Aristarchus had been!) ...
... - applied his equations to Kepler's observations (it fit almost perfectly) • The conclusions were indisputable: Copernicus had been right all along (actually Aristarchus had been!) ...
Deep Space and Solar System
... • One light year is how far light travels in one year (based on distance NOT time) • We see all night stars as they were when the light we see left each star ...
... • One light year is how far light travels in one year (based on distance NOT time) • We see all night stars as they were when the light we see left each star ...
Then another Big Bang will occur and the
... If stars were 10 times closer (~2 trillion miles), a nearby ...
... If stars were 10 times closer (~2 trillion miles), a nearby ...
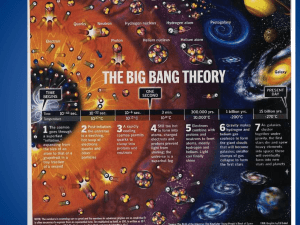
The Big Bang Theory:
... Origin of the Universe • The universe began about 13.77 billion years ago. • The Big Bang Theory states that, in the beginning, the universe was all in one place. • All of its matter and energy were squished into an infinitely small point, a singularity. ...
... Origin of the Universe • The universe began about 13.77 billion years ago. • The Big Bang Theory states that, in the beginning, the universe was all in one place. • All of its matter and energy were squished into an infinitely small point, a singularity. ...
The Components and Origin of the Universe
... 2. at first, the universe was hot (10 32 C) and energy went rushing out in all directions energy became cooled enough to become matter 3. matter then cooled enough to form protons, electrons and neutrons (subatomic particles) 4. subatomic particles combined to form mostly hydrogen but some helium n ...
... 2. at first, the universe was hot (10 32 C) and energy went rushing out in all directions energy became cooled enough to become matter 3. matter then cooled enough to form protons, electrons and neutrons (subatomic particles) 4. subatomic particles combined to form mostly hydrogen but some helium n ...
Gravitational mass
... We can use this to estimate the age of the universe: Assume that the universe a galaxy at distance d from has been moving away from us since the start of the universe and calculate how long that has been. ...
... We can use this to estimate the age of the universe: Assume that the universe a galaxy at distance d from has been moving away from us since the start of the universe and calculate how long that has been. ...
Integrative Studies 410 Our Place in the Universe
... voids • Reflect structure of the universe close to the Big Bang • Largest known structure: the Great Wall (70 Mpc 200 Mpc!) ...
... voids • Reflect structure of the universe close to the Big Bang • Largest known structure: the Great Wall (70 Mpc 200 Mpc!) ...
Hypothesis vs. Theory ~The Big Bang
... entity came to be, based on a number of logical assumptions. ...
... entity came to be, based on a number of logical assumptions. ...
24.1 The Study of Light
... As the dough rises, raisins that were farther apart travel a greater distance in the same time as those that were closer together. Like galaxies in an expanding universe, the distant raisins move away from one another more rapidly than those that are near one another. ...
... As the dough rises, raisins that were farther apart travel a greater distance in the same time as those that were closer together. Like galaxies in an expanding universe, the distant raisins move away from one another more rapidly than those that are near one another. ...
The Big Bang Theory - Red Hook Central Schools
... a violent expansion – All matter and space were created from a single point of pure energy in an instant ...
... a violent expansion – All matter and space were created from a single point of pure energy in an instant ...
Stars, Galaxies, and the Universe
... Galaxies • Scientist study distant galaxies because it takes a long time for light to travel through space and to learn what early galaxies looked like. • Edwin Hubble has identified three major types of galaxies: – Spiral (our Milky way) – Elliptical – Irregular ...
... Galaxies • Scientist study distant galaxies because it takes a long time for light to travel through space and to learn what early galaxies looked like. • Edwin Hubble has identified three major types of galaxies: – Spiral (our Milky way) – Elliptical – Irregular ...
AST101_lect_25
... universe is not infinite in space universe is not infinite in time universe is infinite, but evolves – It may not be in equilibrium – It may not have had stars in the past ...
... universe is not infinite in space universe is not infinite in time universe is infinite, but evolves – It may not be in equilibrium – It may not have had stars in the past ...
AST101 Lecture 25 Why is the Night Sky Dark?
... universe is not infinite in space universe is not infinite in time universe is infinite, but evolves – It may not be in equilibrium – It may not have had stars in the past ...
... universe is not infinite in space universe is not infinite in time universe is infinite, but evolves – It may not be in equilibrium – It may not have had stars in the past ...
notes_chapter1 - Auburn University
... In 1929, Hubble recognized this as a Doppler shift. He concluded that galaxies were moving away rapidly. No galaxies were found to be moving toward Earth. ...
... In 1929, Hubble recognized this as a Doppler shift. He concluded that galaxies were moving away rapidly. No galaxies were found to be moving toward Earth. ...
Not a limitation
... What’s next? • Galaxies don’t seem to be slowing down (so Big Crunch is doubtful, or we’re still in a period of expansion) • Open universe: idea that not enough matter to keep it all together, and things keep expanding (like molecules from open jar) • Closed universe: idea that enough mass to pull ...
... What’s next? • Galaxies don’t seem to be slowing down (so Big Crunch is doubtful, or we’re still in a period of expansion) • Open universe: idea that not enough matter to keep it all together, and things keep expanding (like molecules from open jar) • Closed universe: idea that enough mass to pull ...
Document
... Every direction you point ends on a tree Therefore, every direction is tree-bark brown ...
... Every direction you point ends on a tree Therefore, every direction is tree-bark brown ...
PODSTAWY FIZYKI ŚRODOWISKA
... The anthropic principle • The weak anthropic principle states that the universe must be compatible with our existence. • The strong anthropic principle states that the universe is such as it is because its purpose is to create life. Example • Existence of life (as we know it) strongly depends on the ...
... The anthropic principle • The weak anthropic principle states that the universe must be compatible with our existence. • The strong anthropic principle states that the universe is such as it is because its purpose is to create life. Example • Existence of life (as we know it) strongly depends on the ...
The Universe: “Beyond the Big Bang” Video Questions
... 2. What is a major problem with the Big Bang theory? It doesn’t explain everything. 3. The Big Bang theory only deals with the aftermath. 4. What is the sun mostly made of? Hydrogen, mostly (and Helium) 5. What is the surface temperature of the Sun? 10,000° F 6. When did our Solar System form? 4.5 b ...
... 2. What is a major problem with the Big Bang theory? It doesn’t explain everything. 3. The Big Bang theory only deals with the aftermath. 4. What is the sun mostly made of? Hydrogen, mostly (and Helium) 5. What is the surface temperature of the Sun? 10,000° F 6. When did our Solar System form? 4.5 b ...