Endocrine System: How Hormones Control Bodily Functions
... Endocrine System: How Hormones Control Bodily Functions ...
... Endocrine System: How Hormones Control Bodily Functions ...
Chapter 9- Endocrine System
... – An unequal distribution of auxin, causes a tropism. Tropism: ...
... – An unequal distribution of auxin, causes a tropism. Tropism: ...
Endocrine System 2013-2014 with four embedded
... diffuse across cell membrane & enter cells bind to receptor proteins in cytoplasm & nucleus bind to DNA as transcription factors ...
... diffuse across cell membrane & enter cells bind to receptor proteins in cytoplasm & nucleus bind to DNA as transcription factors ...
Endocrine System booklet
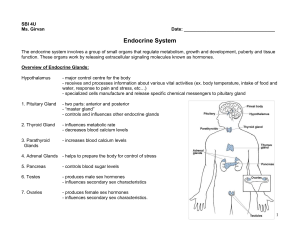
... Endocrine System The endocrine system involves a group of small organs that regulate metabolism, growth and development, puberty and tissue function. These organs work by releasing extracellular signaling molecules known as hormones. Overview of Endocrine Glands: Hypothalamus ...
... Endocrine System The endocrine system involves a group of small organs that regulate metabolism, growth and development, puberty and tissue function. These organs work by releasing extracellular signaling molecules known as hormones. Overview of Endocrine Glands: Hypothalamus ...
PITUITARY GLAND: POSTERIOR LOBE
... 1. Testosterone • cause growth and maturation of reproductive system • secondary sex characteristics; sperm production in adult • Hyposecretion = infertility ...
... 1. Testosterone • cause growth and maturation of reproductive system • secondary sex characteristics; sperm production in adult • Hyposecretion = infertility ...
Endocrine System
... neurotransmitters: transmit nerve impulses o between nerve cells o between nerve cells and muscles We will focus on hormones (& some neurotransmitters now and more later) ...
... neurotransmitters: transmit nerve impulses o between nerve cells o between nerve cells and muscles We will focus on hormones (& some neurotransmitters now and more later) ...
Endocrine System Quiz Quiz # 2 Fall 2008
... • A hormone that stimulates the secretion of another hormone is called a TROPIC hormone. • (Write the one-word anwer in the space provided on the answer sheet.) ...
... • A hormone that stimulates the secretion of another hormone is called a TROPIC hormone. • (Write the one-word anwer in the space provided on the answer sheet.) ...
Chapter 11
... How many hormones does it secrete? What function do most of them have in common? growth hormone GH: What is the function of GH? What factors influence growth besides GH? ...
... How many hormones does it secrete? What function do most of them have in common? growth hormone GH: What is the function of GH? What factors influence growth besides GH? ...
Answers to Mastering Concepts Questions
... 1. The hypothalamus controls secretions from the pituitary gland. Releasing hormones from the hypothalamus stimulate the secretion of pituitary hormones, and inhibiting hormones from the hypothalamus inhibit the secretion of anterior pituitary hormones. In addition, the hypothalamus secretes hormone ...
... 1. The hypothalamus controls secretions from the pituitary gland. Releasing hormones from the hypothalamus stimulate the secretion of pituitary hormones, and inhibiting hormones from the hypothalamus inhibit the secretion of anterior pituitary hormones. In addition, the hypothalamus secretes hormone ...
LECTURE OUTLINE
... 20.6 Other Endocrine Glands Testes and Ovaries The testes produce androgens, which are the male sex hormones. The female sex hormones, estrogen and progesterone, are produced by the ovaries. Thymus Gland The thymus gland secretes thymosins which aid in the differentiation of T lymphocytes. Pineal Gl ...
... 20.6 Other Endocrine Glands Testes and Ovaries The testes produce androgens, which are the male sex hormones. The female sex hormones, estrogen and progesterone, are produced by the ovaries. Thymus Gland The thymus gland secretes thymosins which aid in the differentiation of T lymphocytes. Pineal Gl ...
CHARACTERISTICS OF LIVING THINGS
... complex in the nucleus affects protein synthesis. The hormone-receptor complex bound to mitochondria increases production of ATP. Releasing and inhibiting hormones from hypothalamus target anterior pituitary, causing or inhibiting secretion of hormones. Hypothalamus produces ADH and oxytocin which a ...
... complex in the nucleus affects protein synthesis. The hormone-receptor complex bound to mitochondria increases production of ATP. Releasing and inhibiting hormones from hypothalamus target anterior pituitary, causing or inhibiting secretion of hormones. Hypothalamus produces ADH and oxytocin which a ...
No Slide Title
... FUNCTIONS OF THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM 1. It helps with the control and coordination of all activity of the body with the use of hormones -- it is like the Nervous System in this function except: Hormones take longer to produce an action, but action last longer -- help maintain Homeostasis primarily by ...
... FUNCTIONS OF THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM 1. It helps with the control and coordination of all activity of the body with the use of hormones -- it is like the Nervous System in this function except: Hormones take longer to produce an action, but action last longer -- help maintain Homeostasis primarily by ...
Endocrine System
... Hypoglycemia can occur if levels become too low, can be cured with direct injection of glucose or with eating something high in sugar. This is why diabetics often have candy. ...
... Hypoglycemia can occur if levels become too low, can be cured with direct injection of glucose or with eating something high in sugar. This is why diabetics often have candy. ...
Endocrine system I
... adrenal cortex (cortisol and aldosterone), ovaries (estrogen and progesterone), testes (testosterone), placenta (estrogen and progesterone) ...
... adrenal cortex (cortisol and aldosterone), ovaries (estrogen and progesterone), testes (testosterone), placenta (estrogen and progesterone) ...
Endocrine System
... What is a hormone? How and where do hormones send messages? What is the difference between ‘steroid hormones’ and ‘nonsteroid hormones’? How does the hypothalamus connect the nervous system with the endocrine system? For each of the following hormones, you should know in what gland they are produced ...
... What is a hormone? How and where do hormones send messages? What is the difference between ‘steroid hormones’ and ‘nonsteroid hormones’? How does the hypothalamus connect the nervous system with the endocrine system? For each of the following hormones, you should know in what gland they are produced ...
Thyronim - Taj Pharmaceuticals
... and is formed by the coupling of one molecule of DIT with one molecule of monoiodotyrosine (MIT). Both hormones are stored in the thyroid colloid as thyroglobulin and released into the circulation. The major source of T3 has been shown to be peripheral deiodination of T4. T3 is bound less firmly tha ...
... and is formed by the coupling of one molecule of DIT with one molecule of monoiodotyrosine (MIT). Both hormones are stored in the thyroid colloid as thyroglobulin and released into the circulation. The major source of T3 has been shown to be peripheral deiodination of T4. T3 is bound less firmly tha ...
The Endocrine System
... Highly dependent on the hypothalamus and the autonomic nervous system Secretes the hormones epinephrine (adrenaline) Pancreas: Largest gland in the endocrine system: Lies behind the stomach Attached to the first part of the small intestine Secrete two hormones: o Glucagons Raises blood ...
... Highly dependent on the hypothalamus and the autonomic nervous system Secretes the hormones epinephrine (adrenaline) Pancreas: Largest gland in the endocrine system: Lies behind the stomach Attached to the first part of the small intestine Secrete two hormones: o Glucagons Raises blood ...
Endocrine System Jeopardy Round 1
... a decrease in the amount of thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) as a result of negative feedback. ...
... a decrease in the amount of thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) as a result of negative feedback. ...
Endocrine System
... • Mineralocorticoids. Salt & water balance. • Glucocorticoids. Regulate glucose levels. ...
... • Mineralocorticoids. Salt & water balance. • Glucocorticoids. Regulate glucose levels. ...
Ch 45 Test Questions
... e. nonsteroid hormones bind to cytoplasmic receptors; steroid hormones bind to plasma membrane receptors 18. The primary reason steroid hormones usually act slowly is that ________. a. acting via a signal transduction pathway makes for slower responses than interacting directly with a cell's DNA b. ...
... e. nonsteroid hormones bind to cytoplasmic receptors; steroid hormones bind to plasma membrane receptors 18. The primary reason steroid hormones usually act slowly is that ________. a. acting via a signal transduction pathway makes for slower responses than interacting directly with a cell's DNA b. ...
Natural Hormone Replacement Therapy
... Dangers of Oral Estrogen Replacement First-pass effect on the liverIGF-1, SHBG, CRP, clotting factors blood clots, strokes, heart attacks in the first year Smokers have greater risk of clots EE increases clotting much more than estradiol, Premarin® Transdermal estradiol has none of these eff ...
... Dangers of Oral Estrogen Replacement First-pass effect on the liverIGF-1, SHBG, CRP, clotting factors blood clots, strokes, heart attacks in the first year Smokers have greater risk of clots EE increases clotting much more than estradiol, Premarin® Transdermal estradiol has none of these eff ...
Nervous co-ordination gives control. Endocrine co
... - All hormones produced are steroids formed from cholesterol - glucocorticoids: for glucose metabolism mineralcorticoids: for mineral metabolism, e.g. aldosterone regulates water retention by controlling the distribution of Na and other minerals 26.5.2 The Adrenal Medulla - two hormones: adrenaline ...
... - All hormones produced are steroids formed from cholesterol - glucocorticoids: for glucose metabolism mineralcorticoids: for mineral metabolism, e.g. aldosterone regulates water retention by controlling the distribution of Na and other minerals 26.5.2 The Adrenal Medulla - two hormones: adrenaline ...