Word Notes - Eric Hamber Secondary
... 3. What are the 2 phases of an action potential, and how are they brought about? What is the refractory period and why is it important? (p. 320 -321) 4. Discuss the structures involved and steps that occur for an impulse to move from 1 nerve cell to another. (p. 322 – 323) 5. What is a Neurotransmit ...
... 3. What are the 2 phases of an action potential, and how are they brought about? What is the refractory period and why is it important? (p. 320 -321) 4. Discuss the structures involved and steps that occur for an impulse to move from 1 nerve cell to another. (p. 322 – 323) 5. What is a Neurotransmit ...
Endocrine System
... Pancreas The pancreas also has an exocrine function. Where are these products released? Describe the overlapping homeostatic mechanisms involving insulin and glucagon. ...
... Pancreas The pancreas also has an exocrine function. Where are these products released? Describe the overlapping homeostatic mechanisms involving insulin and glucagon. ...
Chapter 47
... Prostaglandins are modified fatty acids that have a wide range of activities. Lungs, liver, digestive tract and reproductive organs release prostaglandins. Affect cells in their immediate vicinity. Mimic cyclic AMP and interact with other hormones that regulate many metabolic activities. ...
... Prostaglandins are modified fatty acids that have a wide range of activities. Lungs, liver, digestive tract and reproductive organs release prostaglandins. Affect cells in their immediate vicinity. Mimic cyclic AMP and interact with other hormones that regulate many metabolic activities. ...
Anatomy and Physiology Unit 9 Review Sheet
... released into the blood to be transported to target tissues. Nervous control only works on a small area or target tissues, whereas endocrine control can be widespread because it uses the bloodstream and only a small amount of hormone is needed. 3. What are hormones? Describe the different types, act ...
... released into the blood to be transported to target tissues. Nervous control only works on a small area or target tissues, whereas endocrine control can be widespread because it uses the bloodstream and only a small amount of hormone is needed. 3. What are hormones? Describe the different types, act ...
File
... The pituitary gland is not bigger than a pea and located at the base of the brain just beneath the hypothalamus. It is considered the most important part of the endocrine system. It's often called the "master gland" because it makes hormones that control several other endocrine glands. The pituitary ...
... The pituitary gland is not bigger than a pea and located at the base of the brain just beneath the hypothalamus. It is considered the most important part of the endocrine system. It's often called the "master gland" because it makes hormones that control several other endocrine glands. The pituitary ...
Endocrine System
... response to stimulation by the sympathetic nervous system Some endocrine cells are not under direct control of ...
... response to stimulation by the sympathetic nervous system Some endocrine cells are not under direct control of ...
Definition Hormone - Home - KSU Faculty Member websites
... Endocrinology A group of cells that secrete substances called hormones that affect the rest of the cells of the body. Glands function in an orderly fashion with the nervous system, which plays an important role in the secretion of certain hormones . ...
... Endocrinology A group of cells that secrete substances called hormones that affect the rest of the cells of the body. Glands function in an orderly fashion with the nervous system, which plays an important role in the secretion of certain hormones . ...
Anatomy and Physiology Unit 9 Review Sheet
... released into the blood to be transported to target tissues. Nervous control only works on a small area or target tissues, whereas endocrine control can be widespread because it uses the bloodstream and only a small amount of hormone is needed. 3. What are hormones? Describe the different types, act ...
... released into the blood to be transported to target tissues. Nervous control only works on a small area or target tissues, whereas endocrine control can be widespread because it uses the bloodstream and only a small amount of hormone is needed. 3. What are hormones? Describe the different types, act ...
notes - Belle Vernon Area School District
... Which type of feedback is used to control blood sugar levels? ...
... Which type of feedback is used to control blood sugar levels? ...
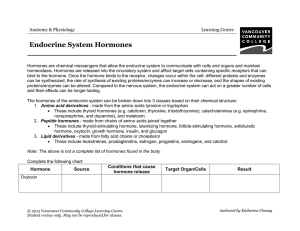
Endocrine System Hormones - VCC Library
... Hormones are chemical messengers that allow the endocrine system to communicate with cells and organs and maintain homeostasis. Hormones are released into the circulatory system and affect target cells containing specific receptors that can bind to the hormone. Once the hormone binds to the receptor ...
... Hormones are chemical messengers that allow the endocrine system to communicate with cells and organs and maintain homeostasis. Hormones are released into the circulatory system and affect target cells containing specific receptors that can bind to the hormone. Once the hormone binds to the receptor ...
The Endocrine System - FW Johnson Collegiate
... of the pancreas in dogs lead to what we now identify as symptoms of diabetes. Although this shed some light on the endocrine system, many glands produce more than one hormone, and levels of some hormones affect the level of other hormones. - To study hormones today, scientists inject radioactive tra ...
... of the pancreas in dogs lead to what we now identify as symptoms of diabetes. Although this shed some light on the endocrine system, many glands produce more than one hormone, and levels of some hormones affect the level of other hormones. - To study hormones today, scientists inject radioactive tra ...
58 XX Lecture Notes BLY 122 (O`Brien)
... V. How Do Hormones Act on Target Cells? (47.4) Fig 47.4 A. Steroid Hormones and Intracellular Receptors 1. Steroid hormones are small lipids that slip easily through cell membranes. 2. Receptors for steroid hormones are inside the cell. 3. The receptor has a DNA-binding domain. 4. The hormone binds ...
... V. How Do Hormones Act on Target Cells? (47.4) Fig 47.4 A. Steroid Hormones and Intracellular Receptors 1. Steroid hormones are small lipids that slip easily through cell membranes. 2. Receptors for steroid hormones are inside the cell. 3. The receptor has a DNA-binding domain. 4. The hormone binds ...
PowerPoint to accompany
... • The adrenal medulla consists of hormone-producing cells, called chromaffin cells, which surround large blood-filled sinuses. • Medullary secretions are epinephrine and norepinephrine (NE), which produce effects similar to sympathetic responses. • They are released under stress by direct innervatio ...
... • The adrenal medulla consists of hormone-producing cells, called chromaffin cells, which surround large blood-filled sinuses. • Medullary secretions are epinephrine and norepinephrine (NE), which produce effects similar to sympathetic responses. • They are released under stress by direct innervatio ...
Endocrinology of reproduction I (Lecture 6 and 7 combined)
... birth control (DES, Estradiol, Progesterone) estrous cycle regulation (PGF2) superovulation and embryo transplant (FSH,PMSG) – induction of parturition (oxytocin, dexamethazone) ...
... birth control (DES, Estradiol, Progesterone) estrous cycle regulation (PGF2) superovulation and embryo transplant (FSH,PMSG) – induction of parturition (oxytocin, dexamethazone) ...
You have completed this lesson regarding the Endocrine System of
... organ involved in the endocrine system, it only secretes two hormones. • Insulin & Glucagon are secreted by the Pancreas and aid in regulating the body’s blood sugar. ...
... organ involved in the endocrine system, it only secretes two hormones. • Insulin & Glucagon are secreted by the Pancreas and aid in regulating the body’s blood sugar. ...
endocrine glands - Catawba County Schools
... to enlargement of gland People with this disease consume large quantities of food but lose body fat and weight Most pronounced symptoms are enlargement of gland (GOITER) and bulging of eyeballs (EXOPHTHALMOS) Rx – total or partial removal of thyroid gland, drugs to reduce thyroxine, radiation ...
... to enlargement of gland People with this disease consume large quantities of food but lose body fat and weight Most pronounced symptoms are enlargement of gland (GOITER) and bulging of eyeballs (EXOPHTHALMOS) Rx – total or partial removal of thyroid gland, drugs to reduce thyroxine, radiation ...
Chapter 9 Vocab
... 16. Hormonal stimuli – when endocrine glands are forced into action by other hormones 17. Hormones – chemical substances that are secreted by endocrine cells into the extracellular fluids and regulate the me ...
... 16. Hormonal stimuli – when endocrine glands are forced into action by other hormones 17. Hormones – chemical substances that are secreted by endocrine cells into the extracellular fluids and regulate the me ...
chapt11answers
... ___Steroid_____ hormones are lipid-soluble and can pass through cell membranes. Their receptors are located in the target cell's __nucleus___. The hormone-receptor complex binds with the _DNA__ and activates specific __genes___ that, in turn, direct the synthesis of specific ___proteins__. __non-ste ...
... ___Steroid_____ hormones are lipid-soluble and can pass through cell membranes. Their receptors are located in the target cell's __nucleus___. The hormone-receptor complex binds with the _DNA__ and activates specific __genes___ that, in turn, direct the synthesis of specific ___proteins__. __non-ste ...
CHAPTER 18
... Endocrine Anatomy (cont.) • B. Thyroid and Parathyroid Glands – 1. Thyroid - controlled by TSH • a. Thyroxine (T3/T4) – i. increases metabolic rate • b. Calcitonin – regulation of electrolytes – i. stimulates storage of Ca+2 and PO4-2 in bones and teeth – 2. Parathyroid • a. Parathryroid Hormone ( ...
... Endocrine Anatomy (cont.) • B. Thyroid and Parathyroid Glands – 1. Thyroid - controlled by TSH • a. Thyroxine (T3/T4) – i. increases metabolic rate • b. Calcitonin – regulation of electrolytes – i. stimulates storage of Ca+2 and PO4-2 in bones and teeth – 2. Parathyroid • a. Parathryroid Hormone ( ...
Human Physiology Unit 3A: Endocrine System
... Ex: Insulin binds TK to allow glucose to be taken into the cell, which lowers blood sugar levels ...
... Ex: Insulin binds TK to allow glucose to be taken into the cell, which lowers blood sugar levels ...
The Endocrine System
... system of glands that secrete hormones to regulate bodily functions hormones regulate many functions of an organism including mood, growth, development, & metabolism. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=S_vQZDH9hY (awesome!) ...
... system of glands that secrete hormones to regulate bodily functions hormones regulate many functions of an organism including mood, growth, development, & metabolism. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=S_vQZDH9hY (awesome!) ...
Natural Hormone Replacement Therapy
... So why are most doctors saying that hormone replacement for menopause is dangerous? ...
... So why are most doctors saying that hormone replacement for menopause is dangerous? ...
Natural Hormone Replacement Therapy
... So why are most doctors saying that hormone replacement for menopause is dangerous? ...
... So why are most doctors saying that hormone replacement for menopause is dangerous? ...
The Endocrine System
... secrete hormones directly into the bloodstream. The endocrine system helps control the following processes and systems: Growth and development Homeostasis (the internal salt water balance of body systems) Metabolism (body energy levels) Reproduction Response to stimuli (stress and/or injury) The End ...
... secrete hormones directly into the bloodstream. The endocrine system helps control the following processes and systems: Growth and development Homeostasis (the internal salt water balance of body systems) Metabolism (body energy levels) Reproduction Response to stimuli (stress and/or injury) The End ...