– Thyroxine T4 (90%) – Triiodothyronine T3
... T4 and T3 must dissociate from thyroxine binding globulin (TBG) in plasma before entering into the cells. In the cells, T4 is deiodinated to T3 that enters nucleus and attaches to specific receptors which promotes mRNA and protein synthesis. PHARMACOKINETICS ...
... T4 and T3 must dissociate from thyroxine binding globulin (TBG) in plasma before entering into the cells. In the cells, T4 is deiodinated to T3 that enters nucleus and attaches to specific receptors which promotes mRNA and protein synthesis. PHARMACOKINETICS ...
Chapter 15-B Endocrine Glands
... contraction • Regulated by a positive feedback mechanism to oxytocin in the blood • This leads to increased intensity of uterine ...
... contraction • Regulated by a positive feedback mechanism to oxytocin in the blood • This leads to increased intensity of uterine ...
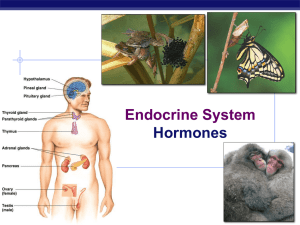
Endocrine System
... molecules that influence specific target cells in the pituitary gland. 8 . The embryonic germ layers ______________________, ______________________, and ______________________ all contribute to the development of the endocrine system. 9 . The mesodermal ridge that joins the adrenal cortex is in the ...
... molecules that influence specific target cells in the pituitary gland. 8 . The embryonic germ layers ______________________, ______________________, and ______________________ all contribute to the development of the endocrine system. 9 . The mesodermal ridge that joins the adrenal cortex is in the ...
the muscular system
... The amount of hormone released by the endocrine gland or tissue is determined by the body’s need for the hormone at any given time. This is the basis to which the endocrine system operates. Hormone producing cells have available to them information from sensing and signaling systems that permit them ...
... The amount of hormone released by the endocrine gland or tissue is determined by the body’s need for the hormone at any given time. This is the basis to which the endocrine system operates. Hormone producing cells have available to them information from sensing and signaling systems that permit them ...
Transcript I
... Typically, these are small molecules, but there are some exceptions. These are polypeptide hormones that really are proteins such as growth hormone. Example: oxytocin—a cyclic peptide because it is made cyclic by disulfide bond formation. You can see that it has 8 amino acids to make the pepti ...
... Typically, these are small molecules, but there are some exceptions. These are polypeptide hormones that really are proteins such as growth hormone. Example: oxytocin—a cyclic peptide because it is made cyclic by disulfide bond formation. You can see that it has 8 amino acids to make the pepti ...
CRYDERS-Endocrine System
... rate and force of contraction; cause blood vessels to constrict in skin, kidneys, gastrointestinal tract, and other viscera ...
... rate and force of contraction; cause blood vessels to constrict in skin, kidneys, gastrointestinal tract, and other viscera ...
Chapter 14
... 1. Glands can be classified structurally and functionally as endocrine or exocrine. 2. Both the nervous and endocrine systems work together through different modes of action to regulate body activities and maintain homeostasis. 3. Hormones are transported by the blood to target cells where they are ...
... 1. Glands can be classified structurally and functionally as endocrine or exocrine. 2. Both the nervous and endocrine systems work together through different modes of action to regulate body activities and maintain homeostasis. 3. Hormones are transported by the blood to target cells where they are ...
EndocrineDiseases pt1 2016
... Thyroid supplement – L-thyroxine Oral, synthetic levothyroxine Daily administration ...
... Thyroid supplement – L-thyroxine Oral, synthetic levothyroxine Daily administration ...
lecture #10
... easily travels through the blood - hydrophilic but cannot diffuse through plasma membrane! therefore absolutely requires the expression of receptors on the cell surface – integral membrane proteins that act ...
... easily travels through the blood - hydrophilic but cannot diffuse through plasma membrane! therefore absolutely requires the expression of receptors on the cell surface – integral membrane proteins that act ...
... underlying the song system, and androgens activate it. Bird testes produce circulating androgens which enter neurons containing aromatse, an enzyme which converts androgens to estrogen. These neurons are generally found in the hypothalamus, as well as in the structures constituting the neural circui ...
The Endocrine Physiology 2 Inputs that Control
... of Ca2+ become very high. It acts by inhibiting degradation of bone by osteoclasts. On day to day basis calcitonin is not secreted and mostly homeostasis is maintained by partathormone and 1, 25 dihydroxy ...
... of Ca2+ become very high. It acts by inhibiting degradation of bone by osteoclasts. On day to day basis calcitonin is not secreted and mostly homeostasis is maintained by partathormone and 1, 25 dihydroxy ...
You Light Up My Life - Teaching Learning Center
... Signaling molecules are hormones and secretions that can bind to target cells and elicit in them a response. Hormones are secreted by endocrine glands, endocrine cells, and some neurons. Local signaling molecules are released by some cells; these work only on nearby tissues. Pheromones are signaling ...
... Signaling molecules are hormones and secretions that can bind to target cells and elicit in them a response. Hormones are secreted by endocrine glands, endocrine cells, and some neurons. Local signaling molecules are released by some cells; these work only on nearby tissues. Pheromones are signaling ...
ENDOCRINE.Hypothalamus.and.Pituitary
... Stimulates GH secretion Inhibits GH (and other hormone) ...
... Stimulates GH secretion Inhibits GH (and other hormone) ...
The Endocrine System
... • It also controls many of your body’s daily activities and influences almost every cell, organ, and function of our bodies. • It regulates mood, growth and development, tissue function, metabolism, and sexual function, and reproductive processes. ...
... • It also controls many of your body’s daily activities and influences almost every cell, organ, and function of our bodies. • It regulates mood, growth and development, tissue function, metabolism, and sexual function, and reproductive processes. ...
The Endocrine System
... • It also controls many of your body’s daily activities and influences almost every cell, organ, and function of our bodies. • It regulates mood, growth and development, tissue function, metabolism, and sexual function, and reproductive processes. ...
... • It also controls many of your body’s daily activities and influences almost every cell, organ, and function of our bodies. • It regulates mood, growth and development, tissue function, metabolism, and sexual function, and reproductive processes. ...
The Endocrine System
... but mainly affects bones and muscles. • The liver must grow as well but not as much as bones and muscles. • Muscle and bone will have high affinity receptors for GH so they can respond often to the presence of GH. Liver will have low affinity receptors so it responds to GH sometimes, but not as much ...
... but mainly affects bones and muscles. • The liver must grow as well but not as much as bones and muscles. • Muscle and bone will have high affinity receptors for GH so they can respond often to the presence of GH. Liver will have low affinity receptors so it responds to GH sometimes, but not as much ...
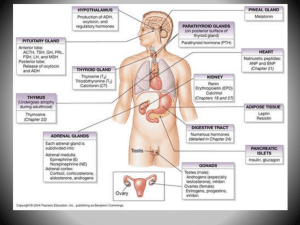
Structure and Functions of Important Endocrine Glands
... salivary glands, stomach, liver, pancreas • The chemical substances released by exocrine glands include sweat, digestive enzymes and tears (through tear ducts) • Endocrine glands on the other hand, release or secrete more than 20 major hormones or chemicals directly into the bloodstream where they c ...
... salivary glands, stomach, liver, pancreas • The chemical substances released by exocrine glands include sweat, digestive enzymes and tears (through tear ducts) • Endocrine glands on the other hand, release or secrete more than 20 major hormones or chemicals directly into the bloodstream where they c ...
Unit 22.2: The Endocrine System
... • The pineal gland is a tiny gland located at the base of the brain. It secretes the hormone melatonin. This hormone controls sleep-wake cycles and several other processes. • The pancreas is located near the stomach. Its hormones include insulin and glucagon. These two hormones work together to cont ...
... • The pineal gland is a tiny gland located at the base of the brain. It secretes the hormone melatonin. This hormone controls sleep-wake cycles and several other processes. • The pancreas is located near the stomach. Its hormones include insulin and glucagon. These two hormones work together to cont ...
Background Information for the Teacher`s Guide
... stable, relatively constant condition of properties. Regulating glucose levels in the blood is one example of how the endocrine system maintains homeostasis. When glucose amounts in the blood rise above the normal glucose level, the pancreas secretes the hormone insulin. This allows the cells in mu ...
... stable, relatively constant condition of properties. Regulating glucose levels in the blood is one example of how the endocrine system maintains homeostasis. When glucose amounts in the blood rise above the normal glucose level, the pancreas secretes the hormone insulin. This allows the cells in mu ...
Chapter 16 * Endocrine System
... acid with 5-carbon ring) that serve important and widespread integrative functions in the body but do not meet the usual definition of a hormone (Figure 16-13; Table 16-4) Called tissue hormones because the secretion is produced in a tissue and diffuses only a short distance to other cells within ...
... acid with 5-carbon ring) that serve important and widespread integrative functions in the body but do not meet the usual definition of a hormone (Figure 16-13; Table 16-4) Called tissue hormones because the secretion is produced in a tissue and diffuses only a short distance to other cells within ...