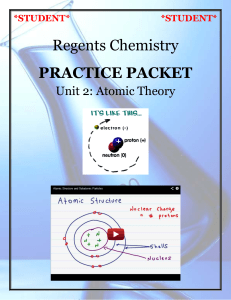
Atomic Structure
... Discontinuous (Particle) Theory of Matter = (~400 B.C., Democritus, Leucippus ) matter is made up of particles so small and indestructible that they cannot be divided into anything smaller. “Atom” comes from the Greek word atomos, meaning ________________. law of conservation of mass (1770’s, Antoin ...
... Discontinuous (Particle) Theory of Matter = (~400 B.C., Democritus, Leucippus ) matter is made up of particles so small and indestructible that they cannot be divided into anything smaller. “Atom” comes from the Greek word atomos, meaning ________________. law of conservation of mass (1770’s, Antoin ...
atoms - schultz915
... identical. Atoms of any one element are different from those of any other element. ...
... identical. Atoms of any one element are different from those of any other element. ...
elements in a family have the same number of
... valence electrons. Most elements in this family share electrons when forming compounds. Oxygen is the most abundant element in the earth’s crust. It is extremely active and combines with almost all elements. ...
... valence electrons. Most elements in this family share electrons when forming compounds. Oxygen is the most abundant element in the earth’s crust. It is extremely active and combines with almost all elements. ...
File
... electrons. Valence electrons are always in the highest energy level. These are the electrons that participate in forming _________ bonds. I Do: Draw the Bohr diagram for Hydrogen: How many electrons are in the highest energy level? ___ How many valence electrons does Hydrogen have? ____ Draw the Lew ...
... electrons. Valence electrons are always in the highest energy level. These are the electrons that participate in forming _________ bonds. I Do: Draw the Bohr diagram for Hydrogen: How many electrons are in the highest energy level? ___ How many valence electrons does Hydrogen have? ____ Draw the Lew ...
rutherford gold foil experiment for the structure of atom
... proton and neutron are heavy particles of atom which are present inside the nucleus. This was the reason that alpha particles bounced back when collided with nucleus because mass of an atom is present in its nucleus. vi. Physical properties of the isotopes are different but their chemical properties ...
... proton and neutron are heavy particles of atom which are present inside the nucleus. This was the reason that alpha particles bounced back when collided with nucleus because mass of an atom is present in its nucleus. vi. Physical properties of the isotopes are different but their chemical properties ...
Homework Packet - Chemistry from AZ
... horizontal rows called periods are numbered 1 to 7; elements in the same period have the same number of principle energy levels (PEL’s) or shells vertical columns called groups or families, are numbered 1 to 18; elements in the same group have the same number of valence electrons and therefore have ...
... horizontal rows called periods are numbered 1 to 7; elements in the same period have the same number of principle energy levels (PEL’s) or shells vertical columns called groups or families, are numbered 1 to 18; elements in the same group have the same number of valence electrons and therefore have ...
Composition and Structure of the Atom Atom: basic unit of an
... Atomic mass unit (amu): Unit used to express mass of an atom relative to the mass of a hydrogen atom; one amu = the mass of 1 H atom Atomic weight: Mass of an average atom of an element, expressed in atomic mass units Example: Hydrogen atomic weight = 1.01 amu Carbon atomic weight = 12.01 amu ...
... Atomic mass unit (amu): Unit used to express mass of an atom relative to the mass of a hydrogen atom; one amu = the mass of 1 H atom Atomic weight: Mass of an average atom of an element, expressed in atomic mass units Example: Hydrogen atomic weight = 1.01 amu Carbon atomic weight = 12.01 amu ...
key concepts of matter
... levels in the electron cloud. There are a certain number of electrons that each energy level can hold. Key Concept 3: Electrons located in the outermost shell of the electron cloud are called “valence electrons” and have the highest energy. Key Concept 4: Valence electrons determine the chemical pro ...
... levels in the electron cloud. There are a certain number of electrons that each energy level can hold. Key Concept 3: Electrons located in the outermost shell of the electron cloud are called “valence electrons” and have the highest energy. Key Concept 4: Valence electrons determine the chemical pro ...
Atomic - My CCSD
... determined the ray WAS made (-) particles by allowing the ray to pass through a hole in the anode and then through a magnetic field. He determined that the negative particles emanate from the cathode, they had structure and he ...
... determined the ray WAS made (-) particles by allowing the ray to pass through a hole in the anode and then through a magnetic field. He determined that the negative particles emanate from the cathode, they had structure and he ...
Key Concept 1: An atom is the smallest unit of an element that
... cloud. There are a certain number of electrons that each energy level can hold. ...
... cloud. There are a certain number of electrons that each energy level can hold. ...
atomic number on the periodic table
... • Dmitri Mendeleev, a Russian scientist born in Siberia in 1834, is known as the father of the periodic table of the elements • The periodic table is designed to help you predict chemical and physical properties of elements ...
... • Dmitri Mendeleev, a Russian scientist born in Siberia in 1834, is known as the father of the periodic table of the elements • The periodic table is designed to help you predict chemical and physical properties of elements ...
Note Packet for Students
... To the casual observer, all pennies that you use seem to be identical in size, thickness, and composition. But just as elements have one or more isotopes with different masses, the pennies in circulation have different masses. In this investigation, you are going to use pennies with different masses ...
... To the casual observer, all pennies that you use seem to be identical in size, thickness, and composition. But just as elements have one or more isotopes with different masses, the pennies in circulation have different masses. In this investigation, you are going to use pennies with different masses ...
Chem 115 POGIL Worksheet
... The extra mass of 0.0989436 u represents the mass converted into energy when the fundamental particles combine in forming the atom. This energy, called the binding energy, can be calculated with Einstein’s equation, E = mc2, where m is the mass converted into energy, and c is the speed of light in a ...
... The extra mass of 0.0989436 u represents the mass converted into energy when the fundamental particles combine in forming the atom. This energy, called the binding energy, can be calculated with Einstein’s equation, E = mc2, where m is the mass converted into energy, and c is the speed of light in a ...
Periodic Properties of the Elements
... Melting points are generally lower than metals Have seven diatomic molecules (Br2,I2,N2,Cl2,H2,O2,F2) React with metals to form salts ...
... Melting points are generally lower than metals Have seven diatomic molecules (Br2,I2,N2,Cl2,H2,O2,F2) React with metals to form salts ...
Atomic Structure Notes file
... The atoms of an element can differ in mass from each other because they have differing numbers of neutrons. Those with more neutrons will weigh more and be more massive. The atomic mass (often referred to as atomic weight) of an element is calculated by adding together the number of protons and the ...
... The atoms of an element can differ in mass from each other because they have differing numbers of neutrons. Those with more neutrons will weigh more and be more massive. The atomic mass (often referred to as atomic weight) of an element is calculated by adding together the number of protons and the ...
Practice Packet
... amounts of energy and move in areas called orbitals Developed after the famous discovery that energy can behave as both waves & particles ...
... amounts of energy and move in areas called orbitals Developed after the famous discovery that energy can behave as both waves & particles ...
Unit 3 PowerPoint
... Periodic Table with periods based on atomic mass and families (groups) based on similar chemical and physical properties • Mosley – English physicist that used X-ray spectroscopy to find the Atomic Number of elements and place elements into a Periodic Table with periods based on atomic number and fa ...
... Periodic Table with periods based on atomic mass and families (groups) based on similar chemical and physical properties • Mosley – English physicist that used X-ray spectroscopy to find the Atomic Number of elements and place elements into a Periodic Table with periods based on atomic number and fa ...
Atoms, Molecules and Ions
... same size, mass and chemical properties. The atoms of one element are different from the atoms of all other elements. 3. Compounds are composed of atoms of more than one element. In any compound, the ratio of the numbers of atoms of any two of the elements present is either an integer or a simple fr ...
... same size, mass and chemical properties. The atoms of one element are different from the atoms of all other elements. 3. Compounds are composed of atoms of more than one element. In any compound, the ratio of the numbers of atoms of any two of the elements present is either an integer or a simple fr ...
The Atom - South Dade Senior High
... separate samples of neon gas, the same element, but they had different masses, how could this be? • The answer again is isotopes, if the number of neutrons is different the mass will be as well. ...
... separate samples of neon gas, the same element, but they had different masses, how could this be? • The answer again is isotopes, if the number of neutrons is different the mass will be as well. ...
atom - BSCSChemistryA
... • Dalton’s Atomic Theory (1808) – All matter consists of atoms which cannot be created, destroyed or split ...
... • Dalton’s Atomic Theory (1808) – All matter consists of atoms which cannot be created, destroyed or split ...
Chapter 4 PPT
... Law of Multiple Proportions If two elements form more than one compound between them, then the ratios of the masses of the second element which combine with a fixed mass of the first element will be ratios of small whole numbers. (not decimals) For example, H2O and H2O2. Law of Constant Proportions ...
... Law of Multiple Proportions If two elements form more than one compound between them, then the ratios of the masses of the second element which combine with a fixed mass of the first element will be ratios of small whole numbers. (not decimals) For example, H2O and H2O2. Law of Constant Proportions ...
IT IS ELEMENTARY - the OLLI at UCI Blog
... and animal origin • These elements or their very simple compounds can kill—most commonly by interfering with cellular access to oxygen • Nitrogen N2 • Carbon dioxide CO2 • Carbon monoxide CO • Hydrogen cyanide HCN ...
... and animal origin • These elements or their very simple compounds can kill—most commonly by interfering with cellular access to oxygen • Nitrogen N2 • Carbon dioxide CO2 • Carbon monoxide CO • Hydrogen cyanide HCN ...