Chapter 4 Atoms and Elements
... neutrons, which compose most of the atom’s mass and are grouped together in a dense nucleus. • Electrons comprise most of the atom’s volume. • Protons and neutrons have similar masses (1 amu), while electrons have a much smaller mass. © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... neutrons, which compose most of the atom’s mass and are grouped together in a dense nucleus. • Electrons comprise most of the atom’s volume. • Protons and neutrons have similar masses (1 amu), while electrons have a much smaller mass. © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
04_Lecture Atoms and Elements
... 4.6 Looking for Patterns: Nonmetals • Nonmetals occupy the upper right side of the periodic table. • The dividing line between metals and nonmetals is the zigzag diagonal line running from boron to astatine. • Nonmetals have more varied properties; some are solids at room temperature, while others ...
... 4.6 Looking for Patterns: Nonmetals • Nonmetals occupy the upper right side of the periodic table. • The dividing line between metals and nonmetals is the zigzag diagonal line running from boron to astatine. • Nonmetals have more varied properties; some are solids at room temperature, while others ...
04_Lecture Atoms and Elements
... • Each naturally occurring sample of most elements has the same percent natural abundance of each isotope. • The atomic mass of an element is a weighted average of the masses of the individual isotopes. © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... • Each naturally occurring sample of most elements has the same percent natural abundance of each isotope. • The atomic mass of an element is a weighted average of the masses of the individual isotopes. © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
Ch 4 Powerpoint
... arrangement of elements in which the elements are separated into groups based on a set of repeating properties The periodic table allows you to easily compare the properties of one element to another ...
... arrangement of elements in which the elements are separated into groups based on a set of repeating properties The periodic table allows you to easily compare the properties of one element to another ...
Chapter 2 Chemical Basis of Life
... One exception is hydrogen, which fills its outer shell with 2 electrons ...
... One exception is hydrogen, which fills its outer shell with 2 electrons ...
The Indivisible - Hicksville Public Schools
... • John Dalton revived the idea of the atom in the early 1800s based on numerous chemical reactions. • Dalton’s atomic theory easily explained conservation of mass in a reaction as the result of the combination, separation, or rearrangement of atoms. ...
... • John Dalton revived the idea of the atom in the early 1800s based on numerous chemical reactions. • Dalton’s atomic theory easily explained conservation of mass in a reaction as the result of the combination, separation, or rearrangement of atoms. ...
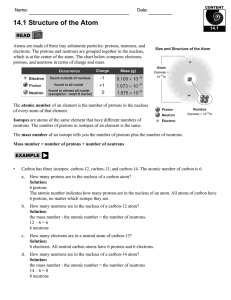
14.1 Structure of the Atom
... Using dot diagrams to represent chemical reactivity Once you have a dot diagram for an element, you can predict how an atom will achieve a full valence shell. For instance, it is easy to see that chlorine has one empty space in its valence shell. It is likely that chlorine will try to gain one elect ...
... Using dot diagrams to represent chemical reactivity Once you have a dot diagram for an element, you can predict how an atom will achieve a full valence shell. For instance, it is easy to see that chlorine has one empty space in its valence shell. It is likely that chlorine will try to gain one elect ...
Chapter 4 Atomic Structure
... • Atoms are EXTREMELY SMALL! – A COPPER PENNY contains approximately 2.4 x 1022 atoms of copper. – The population of the Earth is approximately ...
... • Atoms are EXTREMELY SMALL! – A COPPER PENNY contains approximately 2.4 x 1022 atoms of copper. – The population of the Earth is approximately ...
PP atoms - Lake County Schools
... 2. Atoms of the same element are identical whereas atoms of different elements differ 3. Atoms cannot be subdivided, created, or destroyed 4. Atoms of different elements combine in simple whole-number ratios to form chemical compounds 5. In chemical reactions, atoms are combined, separated, or rearr ...
... 2. Atoms of the same element are identical whereas atoms of different elements differ 3. Atoms cannot be subdivided, created, or destroyed 4. Atoms of different elements combine in simple whole-number ratios to form chemical compounds 5. In chemical reactions, atoms are combined, separated, or rearr ...
Slide 1 - Herricks
... Rules 1. Determine the correct formula for all the reactants and products 2. Write the skeletal equation by placing the formulas for the reactants on the left and the formulas for the products on the right with a yields sign () in between. If two or more reactants or products are involved, separate ...
... Rules 1. Determine the correct formula for all the reactants and products 2. Write the skeletal equation by placing the formulas for the reactants on the left and the formulas for the products on the right with a yields sign () in between. If two or more reactants or products are involved, separate ...
Atomic Model Stations - Moore Public Schools
... 6. Look over your data tables for protons, neutrons and electrons. Two things you notice are A. _ _____________________________________________ B. _ ____________________________________________________ 7. Put 3 protons into the nucleus of the atom. Then ...
... 6. Look over your data tables for protons, neutrons and electrons. Two things you notice are A. _ _____________________________________________ B. _ ____________________________________________________ 7. Put 3 protons into the nucleus of the atom. Then ...
Gizmo Lab Bohr Models 2014
... because it is composed of only one kind of atom. Water is also a pure substance, but it contains two different kinds of atoms: oxygen and hydrogen, so it is not an element. Pizza is a mixture made of up many different types of substances, so it would not be classified as a pure substance. Gizmo Warm ...
... because it is composed of only one kind of atom. Water is also a pure substance, but it contains two different kinds of atoms: oxygen and hydrogen, so it is not an element. Pizza is a mixture made of up many different types of substances, so it would not be classified as a pure substance. Gizmo Warm ...
1 Dalton`s Atomic Theory THE NATURE OF ATOMS (p.44)
... Groups (vertical columns) and periods (horizontal rows) of periodic table are named after orbitals that are partially filled: e.g. S is in group VI (six valence electrons) [Ne] 3s2 3p4 and period 3 (valence electrons are in n = 3 shell) e.g. Ca is in group II (two valence electrons) [Ar] 4s2 and per ...
... Groups (vertical columns) and periods (horizontal rows) of periodic table are named after orbitals that are partially filled: e.g. S is in group VI (six valence electrons) [Ne] 3s2 3p4 and period 3 (valence electrons are in n = 3 shell) e.g. Ca is in group II (two valence electrons) [Ar] 4s2 and per ...
ATOMS - Mr. Deets
... Law of Multiple Proportions – if two or more different compounds are composed of the same two elements, then the ratio of the masses of the second element combined with a certain mass of the first element is always a ratio of small whole numbers Example CO2 and CO : ratio of oxygen is always 2:1 ...
... Law of Multiple Proportions – if two or more different compounds are composed of the same two elements, then the ratio of the masses of the second element combined with a certain mass of the first element is always a ratio of small whole numbers Example CO2 and CO : ratio of oxygen is always 2:1 ...
Directed Reading B
... 9. What were the surprising results of Rutherford’s gold-foil experiment? Some of the particles bounced straight back, and some were deflected (bounced to the side). This led to his theory that atoms are mostly empty space with a small nucleus in the middle with positive charges that can repel the p ...
... 9. What were the surprising results of Rutherford’s gold-foil experiment? Some of the particles bounced straight back, and some were deflected (bounced to the side). This led to his theory that atoms are mostly empty space with a small nucleus in the middle with positive charges that can repel the p ...
The number of neutrons in the nucleus of a specific atom is equal to its
... Electrons have most of the mass but occupy very little of the volume of the atom. Protons and neutrons have most of the mass but occupy very little of the volume of the atom. ...
... Electrons have most of the mass but occupy very little of the volume of the atom. Protons and neutrons have most of the mass but occupy very little of the volume of the atom. ...
Chemical Change
... contact, heat moves from the object at the higher temperature to the object at the lower temperature. Scientist use two equivalent units of temperature, the ...
... contact, heat moves from the object at the higher temperature to the object at the lower temperature. Scientist use two equivalent units of temperature, the ...
Biologically Important Inorganic Elements Occurrence and Availability
... • Why has iron been used so widely in biology although Fe3+, its most stable oxidation state, is highly insoluble at pH 7 Complex biological mechanisms have been developed to accommodate the low solubility of Fe(OH)3 (Ksp = 1 x 1038) ~ pH 7, and take advantage of its high "availability". • Co2+ an ...
... • Why has iron been used so widely in biology although Fe3+, its most stable oxidation state, is highly insoluble at pH 7 Complex biological mechanisms have been developed to accommodate the low solubility of Fe(OH)3 (Ksp = 1 x 1038) ~ pH 7, and take advantage of its high "availability". • Co2+ an ...
Chapter 23 (Section 3) Pregnancy, Birth, and Childhood (Pages 735
... *e. There are currently 118 known ELEMENTS and 92 are found in nature, while the others are SYNTHETICALLY (man-made), but we only use between 30-40 elements daily *1. The discovery of all the ELEMENTS to date has taken THOUSANDS of years *2. In ancient times, it was believed there were “4” ELEMENTS: ...
... *e. There are currently 118 known ELEMENTS and 92 are found in nature, while the others are SYNTHETICALLY (man-made), but we only use between 30-40 elements daily *1. The discovery of all the ELEMENTS to date has taken THOUSANDS of years *2. In ancient times, it was believed there were “4” ELEMENTS: ...
Protons + Neutrons
... Hydrogen – 1 (has one particle in the nucleus *the one particle in the nucleus is a proton Hydrogen – 2 (has 2 particles in the nucleus) *Subtract the atomic number from the new atomic mass to get the new number of neutrons) Hydrogen – 3 (has three particles in the nucleus) *Only one particle ...
... Hydrogen – 1 (has one particle in the nucleus *the one particle in the nucleus is a proton Hydrogen – 2 (has 2 particles in the nucleus) *Subtract the atomic number from the new atomic mass to get the new number of neutrons) Hydrogen – 3 (has three particles in the nucleus) *Only one particle ...
Periodic table
The periodic table is a tabular arrangement of the chemical elements, ordered by their atomic number (number of protons in the nucleus), electron configurations, and recurring chemical properties. The table also shows four rectangular blocks: s-, p- d- and f-block. In general, within one row (period) the elements are metals on the lefthand side, and non-metals on the righthand side.The rows of the table are called periods; the columns are called groups. Six groups (columns) have names as well as numbers: for example, group 17 elements are the halogens; and group 18, the noble gases. The periodic table can be used to derive relationships between the properties of the elements, and predict the properties of new elements yet to be discovered or synthesized. The periodic table provides a useful framework for analyzing chemical behavior, and is widely used in chemistry and other sciences.Although precursors exist, Dmitri Mendeleev is generally credited with the publication, in 1869, of the first widely recognized periodic table. He developed his table to illustrate periodic trends in the properties of the then-known elements. Mendeleev also predicted some properties of then-unknown elements that would be expected to fill gaps in this table. Most of his predictions were proved correct when the elements in question were subsequently discovered. Mendeleev's periodic table has since been expanded and refined with the discovery or synthesis of further new elements and the development of new theoretical models to explain chemical behavior.All elements from atomic numbers 1 (hydrogen) to 118 (ununoctium) have been discovered or reportedly synthesized, with elements 113, 115, 117, and 118 having yet to be confirmed. The first 94 elements exist naturally, although some are found only in trace amounts and were synthesized in laboratories before being found in nature. Elements with atomic numbers from 95 to 118 have only been synthesized in laboratories. It has been shown that einsteinium and fermium once occurred in nature but currently do not. Synthesis of elements having higher atomic numbers is being pursued. Numerous synthetic radionuclides of naturally occurring elements have also been produced in laboratories.