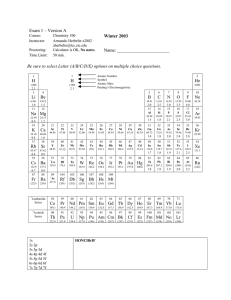
Preview Sample 2
... 31. Sulfur 35 (35S) is an isotope of 32S. These elements differ in their number of neutrons. TRUE ...
... 31. Sulfur 35 (35S) is an isotope of 32S. These elements differ in their number of neutrons. TRUE ...
- TestbankU
... B) the number of protons in the element C) the number of protons plus neutrons in the element D) the number of protons plus electrons in the element Answer: C Bloom's Taxonomy: Application/Analysis Section: 2.2 6) In what way are elements in the same column of the periodic table the same? They have ...
... B) the number of protons in the element C) the number of protons plus neutrons in the element D) the number of protons plus electrons in the element Answer: C Bloom's Taxonomy: Application/Analysis Section: 2.2 6) In what way are elements in the same column of the periodic table the same? They have ...
Question 2
... This is done by gaining, losing, or sharing its electrons. The number of electrons gained, lost, or shared by an atom to complete its octet is called the combining capacity or valency of that atom. Both hydrogen and sodium contain one electron each in their outermost shells. Thus, both can lose one ...
... This is done by gaining, losing, or sharing its electrons. The number of electrons gained, lost, or shared by an atom to complete its octet is called the combining capacity or valency of that atom. Both hydrogen and sodium contain one electron each in their outermost shells. Thus, both can lose one ...
FREE Sample Here
... B) the number of protons in the element C) the number of protons plus neutrons in the element D) the number of protons plus electrons in the element Answer: C Bloom's Taxonomy: Application/Analysis Section: 2.2 6) In what way are elements in the same column of the periodic table the same? They have ...
... B) the number of protons in the element C) the number of protons plus neutrons in the element D) the number of protons plus electrons in the element Answer: C Bloom's Taxonomy: Application/Analysis Section: 2.2 6) In what way are elements in the same column of the periodic table the same? They have ...
The Alkaline Earth Metals (Group 2) - Chemwiki
... 1. To describe how to isolate the alkaline earth metals. 2. To be familiar with the reactions, compounds, and complexes of the alkaline earth metals. Like the alkali metals, the alkaline earth metals are so reactive that they are never found in elemental form in nature. Because they form +2 ions tha ...
... 1. To describe how to isolate the alkaline earth metals. 2. To be familiar with the reactions, compounds, and complexes of the alkaline earth metals. Like the alkali metals, the alkaline earth metals are so reactive that they are never found in elemental form in nature. Because they form +2 ions tha ...
Chapter 2 - Woodhaven High School
... If two elements, A and B, form more than one compound, the masses of B that combine with a given mass of A are in the ratio of small whole numbers. Dalton predicted this law and observed it while developing his atomic theory. When two or more compounds exist from the same elements, they can not h ...
... If two elements, A and B, form more than one compound, the masses of B that combine with a given mass of A are in the ratio of small whole numbers. Dalton predicted this law and observed it while developing his atomic theory. When two or more compounds exist from the same elements, they can not h ...
Atoms
... energy is needed to hold the parts of an atom together • Some mass converted to this binding energy in a nuclear reaction so the calculation gives a value that is a little larger than reality • (E = mc2) ...
... energy is needed to hold the parts of an atom together • Some mass converted to this binding energy in a nuclear reaction so the calculation gives a value that is a little larger than reality • (E = mc2) ...
The Greek Concept of Atomos: The Indivisible Atom - Mr
... were considered to be infallible.) At age 21, he presented a thesis based on this idea: "all that Aristotle has said is false." His opponents could not just appeal to the authority of Aristotle to refute him, since that would be begging the question. After attacking his ideas for a whole day and be ...
... were considered to be infallible.) At age 21, he presented a thesis based on this idea: "all that Aristotle has said is false." His opponents could not just appeal to the authority of Aristotle to refute him, since that would be begging the question. After attacking his ideas for a whole day and be ...
FREE Sample Here
... B) the number of protons in the element C) the number of protons plus neutrons in the element D) the number of protons plus electrons in the element Answer: C Bloom's Taxonomy: Application/Analysis Section: 2.2 6) In what way are elements in the same column of the periodic table the same? They have ...
... B) the number of protons in the element C) the number of protons plus neutrons in the element D) the number of protons plus electrons in the element Answer: C Bloom's Taxonomy: Application/Analysis Section: 2.2 6) In what way are elements in the same column of the periodic table the same? They have ...
atom - Physicsland
... – lightest and most abundant is hydrogen • to date, 115 are known – 90 occur in nature – others produced in laboratory are unstable Words atom and element can be used interchangeably Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Addison-Wesley ...
... – lightest and most abundant is hydrogen • to date, 115 are known – 90 occur in nature – others produced in laboratory are unstable Words atom and element can be used interchangeably Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Addison-Wesley ...
the scale of the electron
... 1. Explaining the Atomic Dynamics The purpose of science is to provide explanations. Scientific progress results in an increase of explanatory strength, explanatory simplicity or both at the same time. Nearly all academic theories, however, offer us mere descriptions instead of genuine explanations ...
... 1. Explaining the Atomic Dynamics The purpose of science is to provide explanations. Scientific progress results in an increase of explanatory strength, explanatory simplicity or both at the same time. Nearly all academic theories, however, offer us mere descriptions instead of genuine explanations ...
Campbell Biology, 10e (Reece) Chapter 2 The Chemical Context of
... B) the number of protons in the element C) the number of protons plus neutrons in the element D) the number of protons plus electrons in the element Answer: C Bloom's Taxonomy: Application/Analysis Section: 2.2 6) In what way are elements in the same column of the periodic table the same? They have ...
... B) the number of protons in the element C) the number of protons plus neutrons in the element D) the number of protons plus electrons in the element Answer: C Bloom's Taxonomy: Application/Analysis Section: 2.2 6) In what way are elements in the same column of the periodic table the same? They have ...
Chemistry M.4 Lesson 1 Atom and Periodic Table
... The Periodic Table was then arranged according to increasing atomic number. Henry mosely The table was as it is now and cleared up the Tellurium and Iodine problem. Periodic Law : the physical and chemical properties of elements are periodic functions of their atomic number and electrons arrange ...
... The Periodic Table was then arranged according to increasing atomic number. Henry mosely The table was as it is now and cleared up the Tellurium and Iodine problem. Periodic Law : the physical and chemical properties of elements are periodic functions of their atomic number and electrons arrange ...
Atoms, Molecules and Moles
... Note that atoms of hydrogen and carbon each have three possibilities for the numbers of neutrons, and that it is even possible for a hydrogen atom to exist without a neutron. Clearly the number of neutrons is not crucial to determining if an atom is carbon, hydrogen, or helium. Although hydrogen, he ...
... Note that atoms of hydrogen and carbon each have three possibilities for the numbers of neutrons, and that it is even possible for a hydrogen atom to exist without a neutron. Clearly the number of neutrons is not crucial to determining if an atom is carbon, hydrogen, or helium. Although hydrogen, he ...
1-4 What Are The Parts Of An Atom and How Are They Arranged
... however, do interact. Using what you know about protons and electrons, what do you think will happen when an electron approaches a proton? Will the two subatomic particles be attracted to each other or repelled from each other? As we have seen before “opposites attract, likes repel.” Since electrons ...
... however, do interact. Using what you know about protons and electrons, what do you think will happen when an electron approaches a proton? Will the two subatomic particles be attracted to each other or repelled from each other? As we have seen before “opposites attract, likes repel.” Since electrons ...
Chapter02_LEC - Mr. Fischer.com
... in its nucleus • the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom is called the atomic number the elements are arranged on the Periodic Table in order of their atomic numbers ...
... in its nucleus • the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom is called the atomic number the elements are arranged on the Periodic Table in order of their atomic numbers ...
Chemistry: A Molecular Approach
... in its nucleus • the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom is called the atomic number the elements are arranged on the Periodic Table in order of their atomic numbers ...
... in its nucleus • the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom is called the atomic number the elements are arranged on the Periodic Table in order of their atomic numbers ...
Periodic table
The periodic table is a tabular arrangement of the chemical elements, ordered by their atomic number (number of protons in the nucleus), electron configurations, and recurring chemical properties. The table also shows four rectangular blocks: s-, p- d- and f-block. In general, within one row (period) the elements are metals on the lefthand side, and non-metals on the righthand side.The rows of the table are called periods; the columns are called groups. Six groups (columns) have names as well as numbers: for example, group 17 elements are the halogens; and group 18, the noble gases. The periodic table can be used to derive relationships between the properties of the elements, and predict the properties of new elements yet to be discovered or synthesized. The periodic table provides a useful framework for analyzing chemical behavior, and is widely used in chemistry and other sciences.Although precursors exist, Dmitri Mendeleev is generally credited with the publication, in 1869, of the first widely recognized periodic table. He developed his table to illustrate periodic trends in the properties of the then-known elements. Mendeleev also predicted some properties of then-unknown elements that would be expected to fill gaps in this table. Most of his predictions were proved correct when the elements in question were subsequently discovered. Mendeleev's periodic table has since been expanded and refined with the discovery or synthesis of further new elements and the development of new theoretical models to explain chemical behavior.All elements from atomic numbers 1 (hydrogen) to 118 (ununoctium) have been discovered or reportedly synthesized, with elements 113, 115, 117, and 118 having yet to be confirmed. The first 94 elements exist naturally, although some are found only in trace amounts and were synthesized in laboratories before being found in nature. Elements with atomic numbers from 95 to 118 have only been synthesized in laboratories. It has been shown that einsteinium and fermium once occurred in nature but currently do not. Synthesis of elements having higher atomic numbers is being pursued. Numerous synthetic radionuclides of naturally occurring elements have also been produced in laboratories.