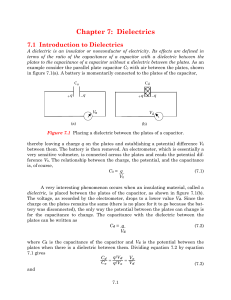
Electromechanical Dynamics, Part 2 - Solution Manual, Woodson Melcher
... Since the points outside the block have J=O, and uniform static fields (for ...
... Since the points outside the block have J=O, and uniform static fields (for ...
Answer Key_Midterm Review
... STA: (2)(A)| (6)(C) TOP: 2-4 Problem 5 Identifying Transformations KEY: transformation | translation | compression ANS: C PTS: 1 DIF: L3 REF: 2-4 Transformations of Absolute Value Functions OBJ: 2-4.1 To graph absolute value functions STA: (2)(A)| (6)(C) TOP: 2-4 Problem 6 Writing an Absolute Value ...
... STA: (2)(A)| (6)(C) TOP: 2-4 Problem 5 Identifying Transformations KEY: transformation | translation | compression ANS: C PTS: 1 DIF: L3 REF: 2-4 Transformations of Absolute Value Functions OBJ: 2-4.1 To graph absolute value functions STA: (2)(A)| (6)(C) TOP: 2-4 Problem 6 Writing an Absolute Value ...
Math Review
... On the previous pages you saw a list of the topics covered in each class. In this part, you are given the opportunity to take short quizzes that allow you to see if you are ready for a particular class. ...
... On the previous pages you saw a list of the topics covered in each class. In this part, you are given the opportunity to take short quizzes that allow you to see if you are ready for a particular class. ...
Power Losses in Steel Pipe Delivering Very Large Currents
... and the magnetic field strength H. In this paper the Finite Difference Time Domain (FDTD) numerical method is used to solve the applicable Maxwell’s equations. This method is able to deal with the transitory response of the magnetization process and account for the fact that the steady state magneti ...
... and the magnetic field strength H. In this paper the Finite Difference Time Domain (FDTD) numerical method is used to solve the applicable Maxwell’s equations. This method is able to deal with the transitory response of the magnetization process and account for the fact that the steady state magneti ...
Partial differential equation

In mathematics, a partial differential equation (PDE) is a differential equation that contains unknown multivariable functions and their partial derivatives. (A special case are ordinary differential equations (ODEs), which deal with functions of a single variable and their derivatives.) PDEs are used to formulate problems involving functions of several variables, and are either solved by hand, or used to create a relevant computer model.PDEs can be used to describe a wide variety of phenomena such as sound, heat, electrostatics, electrodynamics, fluid flow, elasticity, or quantum mechanics. These seemingly distinct physical phenomena can be formalised similarly in terms of PDEs. Just as ordinary differential equations often model one-dimensional dynamical systems, partial differential equations often model multidimensional systems. PDEs find their generalisation in stochastic partial differential equations.