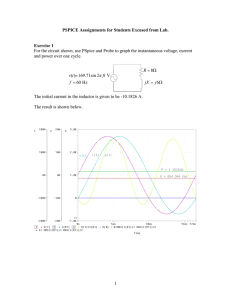
EE2003 Circuit Theory
... 2.2 Nodes, Branches and Loops (1) • A branch represents a single element such as a voltage source or a resistor. • A node is the point of connection between two or more branches. • A loop is any closed path in a circuit. • A network with b branches, n nodes, and l independent loops will satisfy the ...
... 2.2 Nodes, Branches and Loops (1) • A branch represents a single element such as a voltage source or a resistor. • A node is the point of connection between two or more branches. • A loop is any closed path in a circuit. • A network with b branches, n nodes, and l independent loops will satisfy the ...
Lecture 4: Methods of Analysis
... mesh currents. • Again, you may need extra equations if there are other current/voltage sources. • Solve for the unknown currents. ...
... mesh currents. • Again, you may need extra equations if there are other current/voltage sources. • Solve for the unknown currents. ...
5. Magnets and Electromagnetism
... What could be done with object B to make the detected voltage bigger? ...
... What could be done with object B to make the detected voltage bigger? ...
2. What are the two major types of control system?
... (or time derivatives of position velocity and acceleration) 23. Why is negative feedback invariably preferred in closed loop system? The negative feedback results in better stability in steady state and rejects any disturbance ...
... (or time derivatives of position velocity and acceleration) 23. Why is negative feedback invariably preferred in closed loop system? The negative feedback results in better stability in steady state and rejects any disturbance ...
HW02
... of the graph. Vs is input and Vo is output. 1) How many energy storing elements are there? 2) Find the dependent relationships among the inductor currents and capacitor voltage. 3) Determine the minimum number of independent state variables needed. 4) Use these state variables to derive a state apac ...
... of the graph. Vs is input and Vo is output. 1) How many energy storing elements are there? 2) Find the dependent relationships among the inductor currents and capacitor voltage. 3) Determine the minimum number of independent state variables needed. 4) Use these state variables to derive a state apac ...
Slide 1
... concern was providing low cost. A huge communications network was developed in order to allow total control of the system from the supervision central. Using this central it is possible to individually control every street lighting network unit, determinate the timetable of its activations, deactiva ...
... concern was providing low cost. A huge communications network was developed in order to allow total control of the system from the supervision central. Using this central it is possible to individually control every street lighting network unit, determinate the timetable of its activations, deactiva ...
AP_Physics_B_-_Planck_s_Constant_lab
... Purpose: To use an LED to measure the threshold voltage in efforts to graphically determine the value for Planck’s Constant. Materials: Pasco Circuit board, voltmeter, ammeter, various LEDS In this lab we will be introduced to TWO new schematic symbols, This is called a variable resistance, also kno ...
... Purpose: To use an LED to measure the threshold voltage in efforts to graphically determine the value for Planck’s Constant. Materials: Pasco Circuit board, voltmeter, ammeter, various LEDS In this lab we will be introduced to TWO new schematic symbols, This is called a variable resistance, also kno ...
Topology (electrical circuits)
The topology of an electronic circuit is the form taken by the network of interconnections of the circuit components. Different specific values or ratings of the components are regarded as being the same topology. Topology is not concerned with the physical layout of components in a circuit, nor with their positions on a circuit diagram. It is only concerned with what connections exist between the components. There may be numerous physical layouts and circuit diagrams that all amount to the same topology.Strictly speaking, replacing a component with one of an entirely different type is still the same topology. In some contexts, however, these can loosely be described as different topologies. For instance, interchanging inductors and capacitors in a low-pass filter results in a high-pass filter. These might be described as high-pass and low-pass topologies even though the network topology is identical. A more correct term for these classes of object (that is, a network where the type of component is specified but not the absolute value) is prototype network.Electronic network topology is related to mathematical topology, in particular, for networks which contain only two-terminal devices, circuit topology can be viewed as an application of graph theory. In a network analysis of such a circuit from a topological point of view, the network nodes are the vertices of graph theory and the network branches are the edges of graph theory.Standard graph theory can be extended to deal with active components and multi-terminal devices such as integrated circuits. Graphs can also be used in the analysis of infinite networks.