* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lecture 4: Methods of Analysis
Nanofluidic circuitry wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Operational amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Mathematics of radio engineering wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Wilson current mirror wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Topology (electrical circuits) wikipedia , lookup
Current mirror wikipedia , lookup
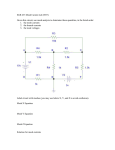
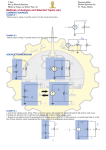
Methods of Analysis Circuits 1 Fall 2005 Harding University Jonathan White Outline Nodal Analysis • Define a symbol for all unknown node voltages. • Write KCL at each node where variables occur • Using Ohm’s Law, solve resulting equations. Mesh Currents • Set up the currents • Use KVL Methods to solve linear equations • • • • Substitution Determinants Calculator Method from Numerical Methods Nodal Analysis Steps: • Define a voltage at every node in the circuit Note: Some may be known, such as the source and ground • Write KCL at the nodes where the unknown voltages exist • Now, plug into these KCL equations with the unknown voltages, remembering how Ohm’s Law works. In this case, I = (VH – VL)/R, because we are writing voltages for nodes, not just resistors. Since current flows from a higher potential to a lower potential, the voltage over a resistor that is connected to 2 nodes is just VH – VL • Other current and voltage sources must be factored in to either the KCL equations or the unknown voltages. They sometimes actually make the equations easier. • Solve for the unknown voltages. Nodal Analysis Example 1 Find all voltages and currents. Nodal Analysis Example 2 Find Vo + Vo - Mesh Currents Steps: • Label each unknown current in each mesh, going clockwise. A mesh is a loop which does not contain any other loops within it. Also, write down the polarities of the currents as they go through each resistor. • Write KVL equations for each mesh. In this case, use V=I*R. When resistors are in both meshes, I=(I1-I2). • Use Ohm’s Law to express the voltages in terms of the mesh currents. • Again, you may need extra equations if there are other current/voltage sources. • Solve for the unknown currents. Mesh Current Example - 1 Calculate the mesh currents. Mesh Current Example - 2 Find the current through the 1 ohm R Methods of Solving Sets of Equations Calculator • rref function • solve function Linear Algebra Substitution Graphing Euclid’s Method