Lab #3 Report: KVL and KCL Adam Stokes Partner: Davis Roberts 9
... The voltage and current in a circuit can be calculated by writing out a system of KVL and KCL equations and then solving for the missing variables. The values can also be found by using an ammeter and voltmeter and measuring in parallel (for voltage) and series (for current). For circuit 3, multisim ...
... The voltage and current in a circuit can be calculated by writing out a system of KVL and KCL equations and then solving for the missing variables. The values can also be found by using an ammeter and voltmeter and measuring in parallel (for voltage) and series (for current). For circuit 3, multisim ...
basic circuit analysis
... define the mesh currents flowing around each of the open areas defined by the network. For consistency, we usually select a clockwise direction for each of the mesh currents, but this is not a requirement. 2. Write network equations, stopping after the number of equations is equal to the number of m ...
... define the mesh currents flowing around each of the open areas defined by the network. For consistency, we usually select a clockwise direction for each of the mesh currents, but this is not a requirement. 2. Write network equations, stopping after the number of equations is equal to the number of m ...
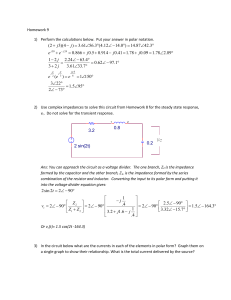
2 sin 2 2 90 1 2.5 90 .4 2 90 2 90 2 90 1.5 164.3 1 3.32 15.7 3.2 1.6
... Ans: You can approach the circuit as a voltage divider. The one branch, Z2 is the impedance formed by the capacitor and the other branch, Z1, is the impedance formed by the series combination of the resistor and inductor. Converting the input to its polar form and putting it into the voltage divider ...
... Ans: You can approach the circuit as a voltage divider. The one branch, Z2 is the impedance formed by the capacitor and the other branch, Z1, is the impedance formed by the series combination of the resistor and inductor. Converting the input to its polar form and putting it into the voltage divider ...
BSNL_TTA_Networktransmission
... 1. Pick up wrong statement (a) A group of interconnected individual components known as circuit elements is called a network. (b) A humped network is an arrangement of physically separate resistors, inductors and capacitors. (c) Distributed network is one, which the resistive, inductive and capaciti ...
... 1. Pick up wrong statement (a) A group of interconnected individual components known as circuit elements is called a network. (b) A humped network is an arrangement of physically separate resistors, inductors and capacitors. (c) Distributed network is one, which the resistive, inductive and capaciti ...
Network Analysis Superposition
... Superposition tells us that branch currents and voltages are always proportional to the ‘driving’ currents or voltages. This means that resistor networks are LINEAR CIRCUITS Network analysis We know that we can replace complex networks of sources and resistors by single sources (Thévenin, Norton), s ...
... Superposition tells us that branch currents and voltages are always proportional to the ‘driving’ currents or voltages. This means that resistor networks are LINEAR CIRCUITS Network analysis We know that we can replace complex networks of sources and resistors by single sources (Thévenin, Norton), s ...
Creating a Simple Scatter Plot and Calculating Slope in Google
... Next step: calculating slope. To calculate slope, I will click in the cell labeled “C2” (Column C, Row 2). In this cell, I will instruct the Spreadsheet program to evaluate the Slope function, by ...
... Next step: calculating slope. To calculate slope, I will click in the cell labeled “C2” (Column C, Row 2). In this cell, I will instruct the Spreadsheet program to evaluate the Slope function, by ...
We analyze circuits for several reasons • Understand how they work
... Let N be the set of all networks Define subset P of N as Set of all networks that can be drawn in two dimensions without lines crossing Such a network is called planar Most circuits we will deal with care planar For a planar network We can define a special type of loop We call it a mesh A mesh is a ...
... Let N be the set of all networks Define subset P of N as Set of all networks that can be drawn in two dimensions without lines crossing Such a network is called planar Most circuits we will deal with care planar For a planar network We can define a special type of loop We call it a mesh A mesh is a ...
MAT110 Graph Theory Vocabulary
... PATH: a series of consecutive edges in which no edge is repeated. LENGTH: the number of edges in a path EULER PATH: a path containing all of the edges EULER CIRCUIT: an Euler path that begins and ends at the same vertex EULERIAN GRAPH: a graph with all even vertices which contains an Euler circuit A ...
... PATH: a series of consecutive edges in which no edge is repeated. LENGTH: the number of edges in a path EULER PATH: a path containing all of the edges EULER CIRCUIT: an Euler path that begins and ends at the same vertex EULERIAN GRAPH: a graph with all even vertices which contains an Euler circuit A ...
Syllabus
... Teaching Assistant: Balkır Kayaaltı, [email protected] Gurkan Sonmez, [email protected] Grading: Quiz 20%, two midterms with 25% each, final exam 30%. ...
... Teaching Assistant: Balkır Kayaaltı, [email protected] Gurkan Sonmez, [email protected] Grading: Quiz 20%, two midterms with 25% each, final exam 30%. ...
unit 2 network theorems
... 1. Norton’s equivalent circuit with In, Zn, Zl can be constructed 2. To find Norton’s current, short circuit load 3. To find Norton’s equivalent impedance 4. Who am I ...
... 1. Norton’s equivalent circuit with In, Zn, Zl can be constructed 2. To find Norton’s current, short circuit load 3. To find Norton’s equivalent impedance 4. Who am I ...
Chap 4 Methods of Analysis
... resistance, Rs, maximum power is delivered to a load resistance, RL, when Rs = RL. Alternatively, the theorem says that for an independent current source in parallel with an internal resistance, Rs, maximum power is delivered to a load resistance, RL, when Rs = RL. topology A branch of geometry co ...
... resistance, Rs, maximum power is delivered to a load resistance, RL, when Rs = RL. Alternatively, the theorem says that for an independent current source in parallel with an internal resistance, Rs, maximum power is delivered to a load resistance, RL, when Rs = RL. topology A branch of geometry co ...
Lab: " Ohm`s Law "
... The next instruction includes how to set up the meters. Be sure that you have wired the circuit as described then have your teacher check your work before turning on the power supply. B. Choose three resistors. R1 = _________ Ω R2 = __________ Ω R3 = __________ Ω. Connect one of the resistors to the ...
... The next instruction includes how to set up the meters. Be sure that you have wired the circuit as described then have your teacher check your work before turning on the power supply. B. Choose three resistors. R1 = _________ Ω R2 = __________ Ω R3 = __________ Ω. Connect one of the resistors to the ...
Topology (electrical circuits)
The topology of an electronic circuit is the form taken by the network of interconnections of the circuit components. Different specific values or ratings of the components are regarded as being the same topology. Topology is not concerned with the physical layout of components in a circuit, nor with their positions on a circuit diagram. It is only concerned with what connections exist between the components. There may be numerous physical layouts and circuit diagrams that all amount to the same topology.Strictly speaking, replacing a component with one of an entirely different type is still the same topology. In some contexts, however, these can loosely be described as different topologies. For instance, interchanging inductors and capacitors in a low-pass filter results in a high-pass filter. These might be described as high-pass and low-pass topologies even though the network topology is identical. A more correct term for these classes of object (that is, a network where the type of component is specified but not the absolute value) is prototype network.Electronic network topology is related to mathematical topology, in particular, for networks which contain only two-terminal devices, circuit topology can be viewed as an application of graph theory. In a network analysis of such a circuit from a topological point of view, the network nodes are the vertices of graph theory and the network branches are the edges of graph theory.Standard graph theory can be extended to deal with active components and multi-terminal devices such as integrated circuits. Graphs can also be used in the analysis of infinite networks.