Introduction to Landscape ecology and matrix
... However, if you open up a large forested area by creating small openings, the patches may not be dense enough to sustain certain kinds of animals ...
... However, if you open up a large forested area by creating small openings, the patches may not be dense enough to sustain certain kinds of animals ...
Romanian and Bulgarian timber trade opportunity for the
... Significant large landscape level forests where viable populations of most if not all naturally occurring species exist in natural patterns of distribution and abundance. Forest areas that are in or contain rare, threatened or endangered ecosystems ...
... Significant large landscape level forests where viable populations of most if not all naturally occurring species exist in natural patterns of distribution and abundance. Forest areas that are in or contain rare, threatened or endangered ecosystems ...
Ecological succession Primary succession Secondary succession
... ! Disturbances prevent communities from reaching a state of equilibrium in species diversity or composition ...
... ! Disturbances prevent communities from reaching a state of equilibrium in species diversity or composition ...
Chapter 3.1: Changes occur Naturally In Ecosystems Natural Selection
... Climax Community: Both primary and secondary succession lead to a mature community such as (boreal forest, tropical rainforest, temperate deciduous forest, grassland). These communities can remain stable over long periods of time. They do however continue to change as climate changes. (Abiotic and b ...
... Climax Community: Both primary and secondary succession lead to a mature community such as (boreal forest, tropical rainforest, temperate deciduous forest, grassland). These communities can remain stable over long periods of time. They do however continue to change as climate changes. (Abiotic and b ...
Biomes - Effingham County Schools
... Terrestrial Biomes 1) Tropical Rain Forest 2) Tropical Dry Forest 3) Tropical Savanna 4) Desert 5) Temperate Grasslands 6) Temperate Woodland/Shrubland 7) Temperate Forest 8) Northwestern Coniferous 9) Boreal Forest 10) Tundra ...
... Terrestrial Biomes 1) Tropical Rain Forest 2) Tropical Dry Forest 3) Tropical Savanna 4) Desert 5) Temperate Grasslands 6) Temperate Woodland/Shrubland 7) Temperate Forest 8) Northwestern Coniferous 9) Boreal Forest 10) Tundra ...
BDC321_L05 - Fragmentation & connectivity
... of those of larger plots • Species assemblages in smaller woodlots tend to be lower than in large ones • Fragmentation method, habitat type and surrounding matrix effect all play a role in the effect of fragmentation on species – Temperate forest birds show high resilience to fragmentation into wood ...
... of those of larger plots • Species assemblages in smaller woodlots tend to be lower than in large ones • Fragmentation method, habitat type and surrounding matrix effect all play a role in the effect of fragmentation on species – Temperate forest birds show high resilience to fragmentation into wood ...
Vocabulary Review
... niche: the habitat and lifestyles of a population (habitat, climate, and types of food) community: made up of the populations that live in the same area habitat: the place where an organism lives temperature: the amount of heat in the air and the major factor in determining the biome biome: biome: g ...
... niche: the habitat and lifestyles of a population (habitat, climate, and types of food) community: made up of the populations that live in the same area habitat: the place where an organism lives temperature: the amount of heat in the air and the major factor in determining the biome biome: biome: g ...
Unit 2 Community Ecology Ecosystems and the Biosphere
... • Fires, Floods, Landslides, Hurricanes, and Volcanic eruptions can cause ecological succession • Over time the life changes in stages. • Primary succession= area that has NOT supported life(bare rock or sand dune). • Secondary succession= replacement of species over time following a disruption. • P ...
... • Fires, Floods, Landslides, Hurricanes, and Volcanic eruptions can cause ecological succession • Over time the life changes in stages. • Primary succession= area that has NOT supported life(bare rock or sand dune). • Secondary succession= replacement of species over time following a disruption. • P ...
C22L3 Quiz
... succession in new areas of land with little or no soil, such as a lava flow or sand dune, is primary succession. The first species that colonize new or undisturbed land are pioneer species. ...
... succession in new areas of land with little or no soil, such as a lava flow or sand dune, is primary succession. The first species that colonize new or undisturbed land are pioneer species. ...
Understanding Our Environment
... Coral reefs among most threatened marine ecosystems. - 90% face threats from sea temperature change, destructive fishing methods, coral mining, sediment runoff and other human disturbance. ...
... Coral reefs among most threatened marine ecosystems. - 90% face threats from sea temperature change, destructive fishing methods, coral mining, sediment runoff and other human disturbance. ...
Demographic dynamics of isolated populations of brown collared
... also affect quality and quantity of food resource, plant density, size and distribution in the fragmented forest. Lemurs in the littoral forest of South-Eastern Madagascar are under pressure from human disturbances, such as habitat loss and hunting. The distribution and population density of the bro ...
... also affect quality and quantity of food resource, plant density, size and distribution in the fragmented forest. Lemurs in the littoral forest of South-Eastern Madagascar are under pressure from human disturbances, such as habitat loss and hunting. The distribution and population density of the bro ...
Study Guide Lesson 2
... Species: a group of organisms that can interbreed and produce fertile offspring. Habitat: the environment in which a species normally lives or the location of a living organism. Population: a group of organisms of the same species who live in the same area at the same time. Community: a group of pop ...
... Species: a group of organisms that can interbreed and produce fertile offspring. Habitat: the environment in which a species normally lives or the location of a living organism. Population: a group of organisms of the same species who live in the same area at the same time. Community: a group of pop ...
SWES 474 - Research Paper #1
... “have been influenced by an ecological chain reaction that encompasses numerous species and large scales of space and time” ...
... “have been influenced by an ecological chain reaction that encompasses numerous species and large scales of space and time” ...
Variety in ecosystems - Grange Academy
... Large chunky beaks are used for crushing seeds while small fine beaks show an insect based diet. Desert plants are adapted to survive in very dry conditions. They have specially adapted roots, reduced leaf surface area (spines) and thick waxy cuticles on the leaves. ...
... Large chunky beaks are used for crushing seeds while small fine beaks show an insect based diet. Desert plants are adapted to survive in very dry conditions. They have specially adapted roots, reduced leaf surface area (spines) and thick waxy cuticles on the leaves. ...
Effects of Climate C..
... Impact on Biodiversity in Small Island States Increases in the frequency of hurricanes or wind speed could negatively affect habitats. Mangroves, seagrass beds, other coastal ecosystems and associated biodiversity will be affected. Saltwater intrusion into freshwater habitats Potential loss of cora ...
... Impact on Biodiversity in Small Island States Increases in the frequency of hurricanes or wind speed could negatively affect habitats. Mangroves, seagrass beds, other coastal ecosystems and associated biodiversity will be affected. Saltwater intrusion into freshwater habitats Potential loss of cora ...
Community and ecosystem diversity
... 2. Impact of habitat fragmentation and hunting on key animal species (hornbills, gorillas,…) for plant species regeneration. Many African plants depend on medium-‐sized to large animals for their dispersal and ...
... 2. Impact of habitat fragmentation and hunting on key animal species (hornbills, gorillas,…) for plant species regeneration. Many African plants depend on medium-‐sized to large animals for their dispersal and ...
Masafuera island (also called Alejandro Selkirk island) is impressive
... Masafuera is also unique because of its flora and fauna. Endemic ferns, trees and birds are the reason why Masafuera Island is part of the Archipelago from Juan Fernandez National Park (about 800km away from the continental Chilean shoreline) and an important Biosphere Reserve by UNESCO. One of thes ...
... Masafuera is also unique because of its flora and fauna. Endemic ferns, trees and birds are the reason why Masafuera Island is part of the Archipelago from Juan Fernandez National Park (about 800km away from the continental Chilean shoreline) and an important Biosphere Reserve by UNESCO. One of thes ...
Biodiversity- Ash and Leah
... Dodo nests destroyed by sailor’s animals, including: rats, cats, and pigs ...
... Dodo nests destroyed by sailor’s animals, including: rats, cats, and pigs ...
Fact Sheet Contact: Daniel Boone Phone: 928-523
... Muir stated, “When we try to pick out anything by itself we find that it is bound fast by a thousand invisible cords that cannot be broken, to everything in the universe.” This film takes these connections to a whole new scientific level by exploring the frontiers of ecology with one of the smallest ...
... Muir stated, “When we try to pick out anything by itself we find that it is bound fast by a thousand invisible cords that cannot be broken, to everything in the universe.” This film takes these connections to a whole new scientific level by exploring the frontiers of ecology with one of the smallest ...
Name___________________ Class_______ Date
... physical factors of the environment. The concept of an ecosystem can apply to units of different sizes. For example, a large body of fresh water could be considered an ecosystem, and so could a small piece of dead wood. Both contain a community of species that interact with one another and with the ...
... physical factors of the environment. The concept of an ecosystem can apply to units of different sizes. For example, a large body of fresh water could be considered an ecosystem, and so could a small piece of dead wood. Both contain a community of species that interact with one another and with the ...
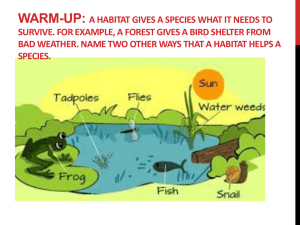
Warm-UP: A habitat gives a species what it needs to survive. For
... The biosphere is the portion of the Earth that supports life. This includes the top of Earths’s crust (lithosphere), the water on Earth’s surface (hydrosphere), and the atmosphere. ...
... The biosphere is the portion of the Earth that supports life. This includes the top of Earths’s crust (lithosphere), the water on Earth’s surface (hydrosphere), and the atmosphere. ...
Title: Fine-scale and Microhabitat Factors Influencing Terrestrial
... them in the world. However, a lack of data exists documenting species-specific responses to finescale natural environmental variables, especially in sparsely distributed mature forest of central Appalachian. Furthermore, because terrestrial salamander communities are known to have differential respo ...
... them in the world. However, a lack of data exists documenting species-specific responses to finescale natural environmental variables, especially in sparsely distributed mature forest of central Appalachian. Furthermore, because terrestrial salamander communities are known to have differential respo ...
Biological Dynamics of Forest Fragments Project

The Biological Dynamics of Forest Fragments Project, originally called the Minimum Critical Size of Ecosystems Project is a large-scale ecological experiment looking at the effects of habitat fragmentation on tropical rainforest; it is one of the most expensive biology experiments ever run. The experiment, which was established in 1979 is located near Manaus, in the Brazilian Amazon. The project is jointly managed by the Smithsonian Institution and INPA, the Brazilian Institute for Research in the Amazon.The project was initiated in 1979 by Thomas Lovejoy to investigate the SLOSS debate. Initially named the Minimum Critical Size of Ecosystems Project, the project created forest fragments of sizes 1 hectare (2 acres), 10 hectares (25 acres), and 100 hectares (247 acres). Data were collected prior to the creation of the fragments and studies of the effects of fragmentation now exceed 25 years.As of October 2010 562 publications and 143 graduate dissertations and theses had emerged from the project.