The Endangered Species Act of 1973
... merely to consider the protection of endangered species, rather than a formal and fundamental requirement of preservation. See 5 ENVIR. L. REP. 50189 (1975). For further discussion of ...
... merely to consider the protection of endangered species, rather than a formal and fundamental requirement of preservation. See 5 ENVIR. L. REP. 50189 (1975). For further discussion of ...
Species Diversity of Aquatic Invertebrates in St. Olaf
... 2001). Thus we predicted that the larger St. Olaf ponds (Baseball Pond and Big Pond) would have higher species diversity than Regents pond, which is very small. Shoreline development has been shown to have a negative impact on many aquatic communities. In comparisons between forested and agricultura ...
... 2001). Thus we predicted that the larger St. Olaf ponds (Baseball Pond and Big Pond) would have higher species diversity than Regents pond, which is very small. Shoreline development has been shown to have a negative impact on many aquatic communities. In comparisons between forested and agricultura ...
Non-Indigenous Species
... commersonii, Siganus luridus, and Stephanolepis diaspros. The surveys will be carried out twice – one was held in January 2013 and another will be held in May 2013 – the aim is that they are carried out before and after noticeable temperature changes have occurred at specif ...
... commersonii, Siganus luridus, and Stephanolepis diaspros. The surveys will be carried out twice – one was held in January 2013 and another will be held in May 2013 – the aim is that they are carried out before and after noticeable temperature changes have occurred at specif ...
Declaration of critical habitat for the endangered population of little
... ‘ridgetop’ in residential areas (ie the rocky foreshore upslope to the boundary of the backyard is included as critical habitat, but the backyard and residential area is not included, Figure 1). The critical habitat includes aquatic areas (extending 50m out from the mean high water (MHW) mark) to fa ...
... ‘ridgetop’ in residential areas (ie the rocky foreshore upslope to the boundary of the backyard is included as critical habitat, but the backyard and residential area is not included, Figure 1). The critical habitat includes aquatic areas (extending 50m out from the mean high water (MHW) mark) to fa ...
ASET postprint
... on close inspection, to show subtle differences in the way they forage in the canopy of trees. Evidently, if ecologists proceed strictly in the way suggested by Slobodkin, the competitive exclusion principle will never be refuted, and therefore has no empirical content, at least not in the Popperian ...
... on close inspection, to show subtle differences in the way they forage in the canopy of trees. Evidently, if ecologists proceed strictly in the way suggested by Slobodkin, the competitive exclusion principle will never be refuted, and therefore has no empirical content, at least not in the Popperian ...
Quantifying the effects of urban stormwater management – towards
... below) and improve local climate through evaporation (see category “urban climate” below). Rainwater can also be used directly (in toilets, gardens, etc.) or indirectly to cool and heat buildings in the process of evaporation and condensation-absorption as demonstrated in the WaterGy prototype in Be ...
... below) and improve local climate through evaporation (see category “urban climate” below). Rainwater can also be used directly (in toilets, gardens, etc.) or indirectly to cool and heat buildings in the process of evaporation and condensation-absorption as demonstrated in the WaterGy prototype in Be ...
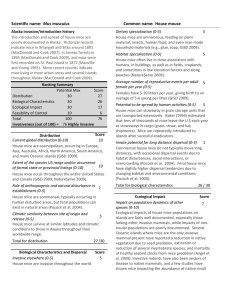
House mouse Scientific name: Mus musculus
... species threatened (0‐3) House mice usually inhabit disturbed areas and have not been reported to threaten any valuable native species. Insular populations of mice are more likely to impact natural areas and native species (Angel et al. 2009). No impacts to that degree have been reported in A ...
... species threatened (0‐3) House mice usually inhabit disturbed areas and have not been reported to threaten any valuable native species. Insular populations of mice are more likely to impact natural areas and native species (Angel et al. 2009). No impacts to that degree have been reported in A ...
The Roots of Diversity: Below Ground Species Richness and
... species diversity where morphological identification of fine roots is difficult. We combine DNA-based root identification with a DNA barcode database and above ground stem locations in a floristically diverse lowland tropical wet forest on Barro Colorado Island, Panama, where all trees and lianas .1 ...
... species diversity where morphological identification of fine roots is difficult. We combine DNA-based root identification with a DNA barcode database and above ground stem locations in a floristically diverse lowland tropical wet forest on Barro Colorado Island, Panama, where all trees and lianas .1 ...
Abiotic vs. Biotic Influences on Habitat Selection of Coexisting
... influences on bird distributions and habitat choice. However, nest-site shifts and microhabitat use also appear to be influenced by interactions among coexisting species. Moreover, shifts in habitat use by all species caused nest predation (i.e., biotic) costs that increased with increasing distance ...
... influences on bird distributions and habitat choice. However, nest-site shifts and microhabitat use also appear to be influenced by interactions among coexisting species. Moreover, shifts in habitat use by all species caused nest predation (i.e., biotic) costs that increased with increasing distance ...
Differences in diet between two rodent species, Mastomys
... Mastomys natalensis and G. vicinus also overlapped considerably in their food niche. In part, the differences may be due to the differences in the proportion of plant materials they consumed. For G. vicinus, plant materials were the most frequently consumed items, while for M. natalensis seeds/grain ...
... Mastomys natalensis and G. vicinus also overlapped considerably in their food niche. In part, the differences may be due to the differences in the proportion of plant materials they consumed. For G. vicinus, plant materials were the most frequently consumed items, while for M. natalensis seeds/grain ...
Theme 1. Protection of Natural Resources
... increasing resource consumption rates. The global decline of biodiversity is now recognized as one of the most serious environmental issues facing humanity. Recognition of the worldwide impact of the decline of biodiversity inspired the global community to negotiate the United Nations Convention on ...
... increasing resource consumption rates. The global decline of biodiversity is now recognized as one of the most serious environmental issues facing humanity. Recognition of the worldwide impact of the decline of biodiversity inspired the global community to negotiate the United Nations Convention on ...
Plant diversity consequences of a herbivore-driven biome
... those of the independent Indicator Species Analysis of Dufrêne & Legendre (1997) according to McCune & Grace (2002). The Shannon-Wiener index of diversity was calculated as in Krebs (1989), but using ln base e. The values of this index were also converted to their number equivalents which expresses ...
... those of the independent Indicator Species Analysis of Dufrêne & Legendre (1997) according to McCune & Grace (2002). The Shannon-Wiener index of diversity was calculated as in Krebs (1989), but using ln base e. The values of this index were also converted to their number equivalents which expresses ...
Middle Rio Grande Basin
... methods, and collected data on the current conditions and resident species. At each site, they developed ...
... methods, and collected data on the current conditions and resident species. At each site, they developed ...
1 BUSHMEAT AND EUROPEAN MIGRATORY BIRDS
... many societies that a bird-catcher found his place in one of music’s most successful masterpieces, as sang in this renowned cavatina. Catching birds is a relatively simple and rewarding use of wildlife; it does not require the means and effort needed to hunt large game. It can pass rather unnoticed, ...
... many societies that a bird-catcher found his place in one of music’s most successful masterpieces, as sang in this renowned cavatina. Catching birds is a relatively simple and rewarding use of wildlife; it does not require the means and effort needed to hunt large game. It can pass rather unnoticed, ...
Plasticity and trait-mediated indirect interactions among plants
... (Callaway 2007). But it is important to note that facilitation by one species on another may correspond with reciprocal negative, positive or neutral responses. Direct positive interactions may incorporate a wider range of mechanisms than direct negative interactions (Callaway 2007). Like competitio ...
... (Callaway 2007). But it is important to note that facilitation by one species on another may correspond with reciprocal negative, positive or neutral responses. Direct positive interactions may incorporate a wider range of mechanisms than direct negative interactions (Callaway 2007). Like competitio ...
Wellborn et al. (1996)
... Mechanistic approaches in ecology seek to functionally link traits of individuals to higher level processes such as the dynamics of populations and multispecies interactions, determinants of species distributions, and development and maintenance of community structure (175, 191). Studies conducted a ...
... Mechanistic approaches in ecology seek to functionally link traits of individuals to higher level processes such as the dynamics of populations and multispecies interactions, determinants of species distributions, and development and maintenance of community structure (175, 191). Studies conducted a ...
Desirable mathematical properties of indicators for biodiversity change
... Species richness is certainly sensitive to appearing and disappearing species (T5), but not oversensitive: if one out of 3 species appears in the system in year 2, indices are not extremely different (compare species richness in Tables 2 and 4). But changes in species richness are intrinsically scal ...
... Species richness is certainly sensitive to appearing and disappearing species (T5), but not oversensitive: if one out of 3 species appears in the system in year 2, indices are not extremely different (compare species richness in Tables 2 and 4). But changes in species richness are intrinsically scal ...
Patch Size and Population Density: The Effect of Immigration
... the theory of island biogeography is often the starting point for studies of habitat fragmentation, MacArthur and Wilson (1967) did not explicitly address how densities of individual species should vary on islands of different sizes. In fact, the theory assumes that abundances of individual species ...
... the theory of island biogeography is often the starting point for studies of habitat fragmentation, MacArthur and Wilson (1967) did not explicitly address how densities of individual species should vary on islands of different sizes. In fact, the theory assumes that abundances of individual species ...
Habitat selection as a major resource partitioning mechanism
... olocation studies may well provide insights into the structure of bat communities "e[g[ Fenton 0871\ 0874^ Neuweiler 0873^ Aldridge + Rautenbach 0876^ Fin! dley 0882^ Kalko 0884^ Arita 0886#\ but they both represent indirect approaches since they consider the attributes through which organisms acqui ...
... olocation studies may well provide insights into the structure of bat communities "e[g[ Fenton 0871\ 0874^ Neuweiler 0873^ Aldridge + Rautenbach 0876^ Fin! dley 0882^ Kalko 0884^ Arita 0886#\ but they both represent indirect approaches since they consider the attributes through which organisms acqui ...
Determinants of Distribution
... • populations can be either source (birth rate exceeds death rate; b > d) or sink (death rate exceed birth rate; d > b) populations • sink populations depend on immigration (i) from source populations • peripheral populations of a species range are often sink populations b) Species may be absent in ...
... • populations can be either source (birth rate exceeds death rate; b > d) or sink (death rate exceed birth rate; d > b) populations • sink populations depend on immigration (i) from source populations • peripheral populations of a species range are often sink populations b) Species may be absent in ...
Hierarchical Bayesian models in ecology: Reconstructing
... to specific relationship types, allowing competition and other relationships to be revealed alongside trophic interactions. The objective of the present paper is to adapt a method recently proposed in computational systems biology (Lèbre et al., 2010) for inferring gene interactions from time series ...
... to specific relationship types, allowing competition and other relationships to be revealed alongside trophic interactions. The objective of the present paper is to adapt a method recently proposed in computational systems biology (Lèbre et al., 2010) for inferring gene interactions from time series ...
CBD Strategy and Action Plan
... established national clearing-house mechanisms for biodiversity and biosafety. The coordinating mechanisms for biodiversity conservation and implementation of the CBD and related agreements have been basically established at national level. Related departments have set up their own management bodies ...
... established national clearing-house mechanisms for biodiversity and biosafety. The coordinating mechanisms for biodiversity conservation and implementation of the CBD and related agreements have been basically established at national level. Related departments have set up their own management bodies ...
Reconciliation ecology

Reconciliation ecology is the branch of ecology which studies ways to encourage biodiversity in human-dominated ecosystems. Michael Rosenzweig first articulated the concept in his book Win-Win Ecology, based on the theory that there is not enough area for all of earth’s biodiversity to be saved within designated nature preserves. Therefore, humans should increase biodiversity in human-dominated landscapes. By managing for biodiversity in ways that do not decrease human utility of the system, it is a ""win-win"" situation for both human use and native biodiversity. The science is based in the ecological foundation of human land-use trends and species-area relationships. It has many benefits beyond protection of biodiversity, and there are numerous examples of it around the globe. Aspects of reconciliation ecology can already be found in management legislation, but there are challenges in both public acceptance and ecological success of reconciliation attempts.