Nervous System - s3.amazonaws.com
... • The brain evolved from a set of three hollow bulges at the anterior end of the neural tube called the forebrain, midbrain, and hindbrain. • This evolutionary progression is recapitulated (to repeat the principal stages or phases) during embryonic development, especially in mammals and birds, as th ...
... • The brain evolved from a set of three hollow bulges at the anterior end of the neural tube called the forebrain, midbrain, and hindbrain. • This evolutionary progression is recapitulated (to repeat the principal stages or phases) during embryonic development, especially in mammals and birds, as th ...
The Nervous System
... Write the list of words for each number down. 2. Mark out the one word that does not belong with the group. 3. Write one or two sentences to explain how the other three words are related. ...
... Write the list of words for each number down. 2. Mark out the one word that does not belong with the group. 3. Write one or two sentences to explain how the other three words are related. ...
Introduction To Physiology ~ LECTURE NOTES
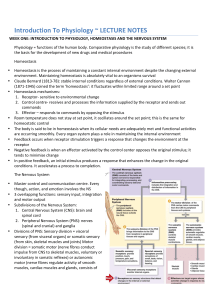
... (1871-‐1945) coined the term ‘homeostasis’: it fluctuates within limited range around a set point Homeostasis mechanisms: 1. Receptor-‐ sensitive to environmental change 2. Control centre-‐ receives and processes ...
... (1871-‐1945) coined the term ‘homeostasis’: it fluctuates within limited range around a set point Homeostasis mechanisms: 1. Receptor-‐ sensitive to environmental change 2. Control centre-‐ receives and processes ...
Chapter 1
... • Distribution of consciousness: Consciousness occurs “throughout” the brain – Means that there is no center of consciousness, – Some researchers believe must be an executive function ...
... • Distribution of consciousness: Consciousness occurs “throughout” the brain – Means that there is no center of consciousness, – Some researchers believe must be an executive function ...
Principles of neural ensemble physiology underlying the operation
... The firing of single cells became so well correlated to the desired motor output that primates could use this single-neuron activity to control the movements of a gauge needle or drive a functional electrical stimulator to produce an isometric contraction. The emergence of multi-electrode recordings ...
... The firing of single cells became so well correlated to the desired motor output that primates could use this single-neuron activity to control the movements of a gauge needle or drive a functional electrical stimulator to produce an isometric contraction. The emergence of multi-electrode recordings ...
Networks of computers analyze how networks of nerves in your
... The machine functions on the precept of parallel computing – the idea that many small machines working together are vastly more efficient than either one small machine or one large machine. Jazz is comprised of 350 smaller computers, or nodes. Each node, if left running continuously for a year, coul ...
... The machine functions on the precept of parallel computing – the idea that many small machines working together are vastly more efficient than either one small machine or one large machine. Jazz is comprised of 350 smaller computers, or nodes. Each node, if left running continuously for a year, coul ...
Lecture 2 - wseh2elt
... And since what comes first constitutes the frame of reference for what comes after, feelings have a say on how the rest of the brain and cognition go about their business. Their influence is immense ...
... And since what comes first constitutes the frame of reference for what comes after, feelings have a say on how the rest of the brain and cognition go about their business. Their influence is immense ...
Chapter 2: Biopsychology Study Guide
... B. biochemical substances that play a large role in behavior, cognition, and emotions C. neurotransmitters are passed through this gap D. between terminal buttons and cell body E. information received here and passed into cell F. bulb-like structures that pass neurons onto other neurons or muscles G ...
... B. biochemical substances that play a large role in behavior, cognition, and emotions C. neurotransmitters are passed through this gap D. between terminal buttons and cell body E. information received here and passed into cell F. bulb-like structures that pass neurons onto other neurons or muscles G ...
Slide 1 - MisterSyracuse.com
... A. Breathing and heart rate B. Movement and digestion C. Leafs falling from trees and growth D. Running and walking 26. The nervous system is a vast system of neurons that controls many processes in the body of an organism. Indeed, even excretion is controlled by the nervous system. In the space bel ...
... A. Breathing and heart rate B. Movement and digestion C. Leafs falling from trees and growth D. Running and walking 26. The nervous system is a vast system of neurons that controls many processes in the body of an organism. Indeed, even excretion is controlled by the nervous system. In the space bel ...
different types of dementia
... Pick’s Disease, Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease, Huntington’s Disease, Parkinson’s Disease, and Lewy Body Disease. Pick’s Disease is more common in women, usually occurring at an early age. Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease is caused by an infectious organism and is progressive. Huntington’s Disease is an inherit ...
... Pick’s Disease, Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease, Huntington’s Disease, Parkinson’s Disease, and Lewy Body Disease. Pick’s Disease is more common in women, usually occurring at an early age. Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease is caused by an infectious organism and is progressive. Huntington’s Disease is an inherit ...
The Nervous System PowerPoint
... Helps control the functioning of most internal organs Acts as the major center for controlling the ANS Controls hormone secretion by anterior and posterior pituitary glands indirectly helps control hormone secretion by most other endocrine glands Contains centers for controlling body temperature ...
... Helps control the functioning of most internal organs Acts as the major center for controlling the ANS Controls hormone secretion by anterior and posterior pituitary glands indirectly helps control hormone secretion by most other endocrine glands Contains centers for controlling body temperature ...
NERVOUS SYSTEM CNS-Central Nervous System PNS
... 2. While he could be confused with having prion-related disorders or Alzheimer’s disease because of his symptoms, he is actually suffering from something else. What neurovascular condition is he suffering from? Explain what this condition is. ...
... 2. While he could be confused with having prion-related disorders or Alzheimer’s disease because of his symptoms, he is actually suffering from something else. What neurovascular condition is he suffering from? Explain what this condition is. ...
3NervCase
... damage to what area of the patient's cortex? a. auditory cortex b. somatosensory association area c. motor association area d. primary motor cortex e. primary somatosensory cortex 8. The difficulties that the patient has with language indicate which area of the cerebrum was damaged by the stroke? A. ...
... damage to what area of the patient's cortex? a. auditory cortex b. somatosensory association area c. motor association area d. primary motor cortex e. primary somatosensory cortex 8. The difficulties that the patient has with language indicate which area of the cerebrum was damaged by the stroke? A. ...
Unit Three Nervous System
... • Regulation is the life process by which cells and organisms respond to changes in and around them. • The actions of the nervous and endocrine systems control and regulate the body. • These two systems allow us to adjust to internal as well as external environmental changes. ...
... • Regulation is the life process by which cells and organisms respond to changes in and around them. • The actions of the nervous and endocrine systems control and regulate the body. • These two systems allow us to adjust to internal as well as external environmental changes. ...
Jeopardy Bio Basis of Human Behavior
... Division of the NS that transmits commands for voluntary movement from the CNS to the muscles ...
... Division of the NS that transmits commands for voluntary movement from the CNS to the muscles ...
Build Your Own Brain! - Virtual Labs
... controls our body by sending electrical signals through our nerves. Our nerves act like wires because they can carry messages to and from different parts of our body. All the senses we have like, hearing, vision, and taste are controlled by different parts of our brain. There are different compartme ...
... controls our body by sending electrical signals through our nerves. Our nerves act like wires because they can carry messages to and from different parts of our body. All the senses we have like, hearing, vision, and taste are controlled by different parts of our brain. There are different compartme ...
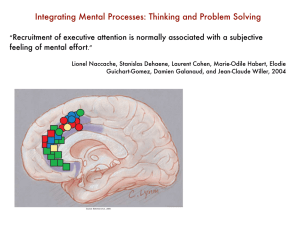
Integrating Mental Processes: Thinking and Problem Solving
... Overlapping semantic networks for concepts ‘tigerd and ‘elephantd. ...
... Overlapping semantic networks for concepts ‘tigerd and ‘elephantd. ...
A neuron receives input from other neurons
... it can learn (reorganize itself) from experience. this means that partial recovery from damage is possible if healthy units can learn to take over the functions previously carried out by the damaged areas. ...
... it can learn (reorganize itself) from experience. this means that partial recovery from damage is possible if healthy units can learn to take over the functions previously carried out by the damaged areas. ...
Neuron PowerPoint
... branch of psychology that studies how the body influences behavior and mental processes some biological psychologists call themselves behavioral neuroscientists, neuropsychologists, behavior geneticists, physiological psychologists, or biopsychologists ...
... branch of psychology that studies how the body influences behavior and mental processes some biological psychologists call themselves behavioral neuroscientists, neuropsychologists, behavior geneticists, physiological psychologists, or biopsychologists ...
3-1-neuron _1
... branch of psychology that studies how the body influences behavior and mental processes some biological psychologists call themselves behavioral neuroscientists, neuropsychologists, behavior geneticists, physiological psychologists, or biopsychologists ...
... branch of psychology that studies how the body influences behavior and mental processes some biological psychologists call themselves behavioral neuroscientists, neuropsychologists, behavior geneticists, physiological psychologists, or biopsychologists ...
Chapter 2: Neuroscience and Biological Foundations
... Neuroscience: field studying how biological processes relate to behavioral and mental processes Neurons: cells that communicate information by sending and receiving signals to other neurons – There are as many as 1 TRILLION neurons within the nervous system ...
... Neuroscience: field studying how biological processes relate to behavioral and mental processes Neurons: cells that communicate information by sending and receiving signals to other neurons – There are as many as 1 TRILLION neurons within the nervous system ...
Neuron PowerPoint
... branch of psychology that studies how the body influences behavior and mental processes some biological psychologists call themselves behavioral neuroscientists, neuropsychologists, behavior geneticists, physiological psychologists, or biopsychologists ...
... branch of psychology that studies how the body influences behavior and mental processes some biological psychologists call themselves behavioral neuroscientists, neuropsychologists, behavior geneticists, physiological psychologists, or biopsychologists ...
(1 Mark).
... Contributions of studies to the investigation of cognitive processes of the brain and implications for the understanding of consciousness including: Spatial neglect caused by stroke or brain injury 0 Spatial Neglect is a common syndrome following a stroke, most commonly in the right hemisphere. 0 P ...
... Contributions of studies to the investigation of cognitive processes of the brain and implications for the understanding of consciousness including: Spatial neglect caused by stroke or brain injury 0 Spatial Neglect is a common syndrome following a stroke, most commonly in the right hemisphere. 0 P ...
Neuroplasticity

Neuroplasticity, also known as brain plasticity, is an umbrella term that encompasses both synaptic plasticity and non-synaptic plasticity—it refers to changes in neural pathways and synapses due to changes in behavior, environment, neural processes, thinking, and emotions – as well as to changes resulting from bodily injury. The concept of neuroplasticity has replaced the formerly-held position that the brain is a physiologically static organ, and explores how – and in which ways – the brain changes in the course of a lifetime.Neuroplasticity occurs on a variety of levels, ranging from cellular changes (due to learning) to large-scale changes involved in cortical remapping in response to injury. The role of neuroplasticity is widely recognized in healthy development, learning, memory, and recovery from brain damage. During most of the 20th century, neuroscientists maintained a scientific consensus that brain structure was relatively immutable after a critical period during early childhood. This belief has been challenged by findings revealing that many aspects of the brain remain plastic even into adulthood.Hubel and Wiesel had demonstrated that ocular dominance columns in the lowest neocortical visual area, V1, remained largely immutable after the critical period in development. Researchers also studied critical periods with respect to language; the resulting data suggested that sensory pathways were fixed after the critical period. However, studies determined that environmental changes could alter behavior and cognition by modifying connections between existing neurons and via neurogenesis in the hippocampus and in other parts of the brain, including in the cerebellum.Decades of research have shown that substantial changes occur in the lowest neocortical processing areas, and that these changes can profoundly alter the pattern of neuronal activation in response to experience. Neuroscientific research indicates that experience can actually change both the brain's physical structure (anatomy) and functional organization (physiology). As of 2014 neuroscientists are engaged in a reconciliation of critical-period studies (demonstrating the immutability of the brain after development) with the more recent research showing how the brain can, and does, change in response to hitherto unsuspected stimuli.