Understanding Traumatic Brain Injury
... brain that tells where things are found and where they are situated in respect to the body. (greater risk of losing their way). 0 The third part and most important function is its high level of processing all the brain’s input data. ...
... brain that tells where things are found and where they are situated in respect to the body. (greater risk of losing their way). 0 The third part and most important function is its high level of processing all the brain’s input data. ...
Nervous System
... • Frontal - primary motor area (patways are crossed) – Intellectual reasoning – Social acceptability – Complex memories (shared with temporal) – Language comprehension ...
... • Frontal - primary motor area (patways are crossed) – Intellectual reasoning – Social acceptability – Complex memories (shared with temporal) – Language comprehension ...
Major lobes - Ohio University
... Consciousness => states existing for a noticeable period of time, integrating reportable sensory information about different modalities, with an influence on other processes in the brain. Each system, which has internal states and is complex enough to comment on them, will claim that it's consciou ...
... Consciousness => states existing for a noticeable period of time, integrating reportable sensory information about different modalities, with an influence on other processes in the brain. Each system, which has internal states and is complex enough to comment on them, will claim that it's consciou ...
AP Psychology Brain Review- Have A Ball! Learning Target: Identify
... Option 1 “Round Robin Brain”: Each student will be given a different brain part to represent (see cards below). Students will stand in a circle so that all class members can see the brain part each person is representing. A ball will start in the center of the circle, the teacher will read the first ...
... Option 1 “Round Robin Brain”: Each student will be given a different brain part to represent (see cards below). Students will stand in a circle so that all class members can see the brain part each person is representing. A ball will start in the center of the circle, the teacher will read the first ...
Clinical Research Center for Brain Sciences, Herzog Hospital
... Natural age-related decay in prefrontal executive attention functioning: significant inverse association between WM accuracy scores and age throughout the entire adult-life span (r = -.693, p < .001) ...
... Natural age-related decay in prefrontal executive attention functioning: significant inverse association between WM accuracy scores and age throughout the entire adult-life span (r = -.693, p < .001) ...
FIGURE LEGENDS FIGURE 51.1 Normal and pathological brain
... “representational capacity of consciousness” is plotted on the y-axis. Increasing arousal can be measured by the threshold to obtain some specific behavior (for instance, spatial orientation to a sound). Healthy subjects cycle during a 24-hour period from deep sleep with low arousal and very little ...
... “representational capacity of consciousness” is plotted on the y-axis. Increasing arousal can be measured by the threshold to obtain some specific behavior (for instance, spatial orientation to a sound). Healthy subjects cycle during a 24-hour period from deep sleep with low arousal and very little ...
Nervous System: Speech
... Huntington or Wilson disease unwanted movements, such as involuntary jerking movements of an arm or leg or spasmodic movement of facial muscles. • The caudate nucleus, putamen and anterior limb of the internal capsule are collectively known as the corpus striatum (i.e. striated body) based on appear ...
... Huntington or Wilson disease unwanted movements, such as involuntary jerking movements of an arm or leg or spasmodic movement of facial muscles. • The caudate nucleus, putamen and anterior limb of the internal capsule are collectively known as the corpus striatum (i.e. striated body) based on appear ...
Chapter 17 Review Jeopardy
... – A) the inside of the axon is positive compared to the outside because the axon is conducting an impulse – B) the inside of the axon is negative compared to the outside because the axon is conducting an impulse – C) the inside of the axon is positive compared to the outside because the axon is NOT ...
... – A) the inside of the axon is positive compared to the outside because the axon is conducting an impulse – B) the inside of the axon is negative compared to the outside because the axon is conducting an impulse – C) the inside of the axon is positive compared to the outside because the axon is NOT ...
Brain - lms.manhattan.edu
... increase, EEG resembles awake person, dreams and penile erections occur – may help sort & strengthen information from memory ...
... increase, EEG resembles awake person, dreams and penile erections occur – may help sort & strengthen information from memory ...
THE NERVOUS SYSTEM CONCEPT 2: THE VERTEBRATE BRAIN
... serotonin and melatonin, thus aiding sleep. Although we know very little about the function of sleep, it is clear that sleep is essential for survival. Sleep is an active state, at least for the brain. By placing electrodes at multiple sites on the scalp, we can record patterns of electrical activit ...
... serotonin and melatonin, thus aiding sleep. Although we know very little about the function of sleep, it is clear that sleep is essential for survival. Sleep is an active state, at least for the brain. By placing electrodes at multiple sites on the scalp, we can record patterns of electrical activit ...
Central Nervous ppt
... occipital, and parietal lobes - Receives input from all sensory association areas and stores complex memory patterns associated with sensation - Sends assessment of sensations to prefrontal cortex which adds emotional overtones - Injury to gnostic area causes one to become an imbecile - interpretati ...
... occipital, and parietal lobes - Receives input from all sensory association areas and stores complex memory patterns associated with sensation - Sends assessment of sensations to prefrontal cortex which adds emotional overtones - Injury to gnostic area causes one to become an imbecile - interpretati ...
Biology 30 NERVOUS SYSTEM - Salisbury Composite High School
... -blocks the re-uptake of dopamine, causing an adrenaline like effect from the dopamine -as dopamine levels increase in the synapse, the body produces less, thus making cocaine very physically addicting Close to Home Animation: Cocaine ...
... -blocks the re-uptake of dopamine, causing an adrenaline like effect from the dopamine -as dopamine levels increase in the synapse, the body produces less, thus making cocaine very physically addicting Close to Home Animation: Cocaine ...
THE BRAIN & FIVE SENSES
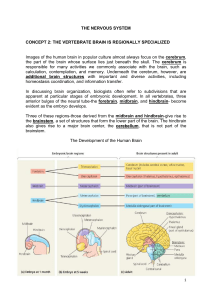
... Just above the Medulla, the brainstem enlarges to form the PONS. PONS mean BRIDGE, and this area of the brain stem contains mostly white matter that provides a link between the cerebral cortex and the cerebellum. Above the PONS and continuous with it is the MIDBRAIN, the smallest division of the lo ...
... Just above the Medulla, the brainstem enlarges to form the PONS. PONS mean BRIDGE, and this area of the brain stem contains mostly white matter that provides a link between the cerebral cortex and the cerebellum. Above the PONS and continuous with it is the MIDBRAIN, the smallest division of the lo ...
There are about 3 million miles of axons in the human brain. The
... important for the rapid-eye movements of REM sleep (one of the 5 stages of sleep and usually makes up 90-120 minutes of an adult’s sleep) and may be important for turning REM sleep on and off. • Functions of the MIDBRAIN include controlling responses to sight, eye Movement, pupil dilation, hearing a ...
... important for the rapid-eye movements of REM sleep (one of the 5 stages of sleep and usually makes up 90-120 minutes of an adult’s sleep) and may be important for turning REM sleep on and off. • Functions of the MIDBRAIN include controlling responses to sight, eye Movement, pupil dilation, hearing a ...
European Commission
... Another IMI project, EUROPAIN, is paving the way for new treatments for chronic pain, a condition affecting one in five Europeans. The team has identified the molecule behind the pain of sunburn, a discovery which could also shed light on the pain caused by other inflammatory conditions like arthri ...
... Another IMI project, EUROPAIN, is paving the way for new treatments for chronic pain, a condition affecting one in five Europeans. The team has identified the molecule behind the pain of sunburn, a discovery which could also shed light on the pain caused by other inflammatory conditions like arthri ...
neurons
... neuroscience—the scientific study of the nervous system. As neuroscientists, biopsychologists bring their expertise in behavior and behavioral research to ...
... neuroscience—the scientific study of the nervous system. As neuroscientists, biopsychologists bring their expertise in behavior and behavioral research to ...
September 21, 2011
... Hyperarousal – “fight or flight” response “Plan B”: Dissociation – withdrawal of attention from external events and focus on internal experience (fantasy; see movie Precious) in which child assumes special powers Different neurobiological pathways are involved in these two responses For most ...
... Hyperarousal – “fight or flight” response “Plan B”: Dissociation – withdrawal of attention from external events and focus on internal experience (fantasy; see movie Precious) in which child assumes special powers Different neurobiological pathways are involved in these two responses For most ...
Chapter 2 Powerpoint - Destiny High School
... • GOAL-DIRECTED BEHAVIOR, CONCENTRATION, EMOTIONAL CONTROL AND TEMPERAMENT, MOTOR PROJECTION AND ASSOCIATION AREAS, COORDINATES MESSAGES FROM OTHER LOBES, ...
... • GOAL-DIRECTED BEHAVIOR, CONCENTRATION, EMOTIONAL CONTROL AND TEMPERAMENT, MOTOR PROJECTION AND ASSOCIATION AREAS, COORDINATES MESSAGES FROM OTHER LOBES, ...
The brain - Epilepsy Society
... functions it is responsible for. More recent scanning techniques have shown how similar functions such as language and memory may also be located in various areas of the brain. This is particularly significant if injury or surgery affects a specific part of the brain – other areas may begin to com ...
... functions it is responsible for. More recent scanning techniques have shown how similar functions such as language and memory may also be located in various areas of the brain. This is particularly significant if injury or surgery affects a specific part of the brain – other areas may begin to com ...
The Neural Mechanisms of Learning
... Canadian psychologist Donald Hebb had an idea that learning involves the establishment and strengthening of neural connections at the synapse. E.g. Learning the piano establishes new neural connections and practising strengthens the connections. ...
... Canadian psychologist Donald Hebb had an idea that learning involves the establishment and strengthening of neural connections at the synapse. E.g. Learning the piano establishes new neural connections and practising strengthens the connections. ...
Malleable vs. Fixed Intelligence
... Neurons have three main parts: 1. The soma (a.k.a cell body) 2. The axon 3. The dendrites ...
... Neurons have three main parts: 1. The soma (a.k.a cell body) 2. The axon 3. The dendrites ...
Unit II Practice Exam – Answer Key
... Which of the following was a major problem with phrenology? a. It was “ahead of its time” and no one believed it could be true b. The brain is not neatly organized into structures that correspond to our categories of behavior c. The brains of humans and animals are much less similar than they theory ...
... Which of the following was a major problem with phrenology? a. It was “ahead of its time” and no one believed it could be true b. The brain is not neatly organized into structures that correspond to our categories of behavior c. The brains of humans and animals are much less similar than they theory ...
Neuroplasticity

Neuroplasticity, also known as brain plasticity, is an umbrella term that encompasses both synaptic plasticity and non-synaptic plasticity—it refers to changes in neural pathways and synapses due to changes in behavior, environment, neural processes, thinking, and emotions – as well as to changes resulting from bodily injury. The concept of neuroplasticity has replaced the formerly-held position that the brain is a physiologically static organ, and explores how – and in which ways – the brain changes in the course of a lifetime.Neuroplasticity occurs on a variety of levels, ranging from cellular changes (due to learning) to large-scale changes involved in cortical remapping in response to injury. The role of neuroplasticity is widely recognized in healthy development, learning, memory, and recovery from brain damage. During most of the 20th century, neuroscientists maintained a scientific consensus that brain structure was relatively immutable after a critical period during early childhood. This belief has been challenged by findings revealing that many aspects of the brain remain plastic even into adulthood.Hubel and Wiesel had demonstrated that ocular dominance columns in the lowest neocortical visual area, V1, remained largely immutable after the critical period in development. Researchers also studied critical periods with respect to language; the resulting data suggested that sensory pathways were fixed after the critical period. However, studies determined that environmental changes could alter behavior and cognition by modifying connections between existing neurons and via neurogenesis in the hippocampus and in other parts of the brain, including in the cerebellum.Decades of research have shown that substantial changes occur in the lowest neocortical processing areas, and that these changes can profoundly alter the pattern of neuronal activation in response to experience. Neuroscientific research indicates that experience can actually change both the brain's physical structure (anatomy) and functional organization (physiology). As of 2014 neuroscientists are engaged in a reconciliation of critical-period studies (demonstrating the immutability of the brain after development) with the more recent research showing how the brain can, and does, change in response to hitherto unsuspected stimuli.