
Teaching with the Brain-Based Natural Human Learning FACES
... stupid. With appropriate help she became an excellent reader. Only 5% of students have ADD, but more than 25% are given ritalin, which stifles normal brain growth. These students say they are so bored they can't sit still, be quiet, listen and obey; they want to think, figure things out themselves, ...
... stupid. With appropriate help she became an excellent reader. Only 5% of students have ADD, but more than 25% are given ritalin, which stifles normal brain growth. These students say they are so bored they can't sit still, be quiet, listen and obey; they want to think, figure things out themselves, ...
Dissection of the Sheep Brain
... Twelve pairs of cranial nerves arise from the underside of the brain: 2 pairs arise from the cerebrum and 10 pairs of cranial nerves arise from the brainstem. These cranial nerves are designated by numbers and names. The number indicates the order in which the nerve arises from the brain, form anter ...
... Twelve pairs of cranial nerves arise from the underside of the brain: 2 pairs arise from the cerebrum and 10 pairs of cranial nerves arise from the brainstem. These cranial nerves are designated by numbers and names. The number indicates the order in which the nerve arises from the brain, form anter ...
Retina Rods retina receptors that detect black, white, and gray
... Visual-cliff =a laboratory device for testing depth perception in infants and young animals Believed to be initiated in infants with crawling; believed to be innate Binocular cues depth cues, such as retinal disparity, that depend on the use of two eyes Retinal disparity=a binocular cue for perceivi ...
... Visual-cliff =a laboratory device for testing depth perception in infants and young animals Believed to be initiated in infants with crawling; believed to be innate Binocular cues depth cues, such as retinal disparity, that depend on the use of two eyes Retinal disparity=a binocular cue for perceivi ...
The Language of the Brain
... responses contrast with the sluggish stream of hormones coursing through the bloodstream. The signals most important for this discussion, though, are the spikes, which are sharp rises in voltage that course through and between neurons. For cell-to-cell communication, spikes lasting a few millisecond ...
... responses contrast with the sluggish stream of hormones coursing through the bloodstream. The signals most important for this discussion, though, are the spikes, which are sharp rises in voltage that course through and between neurons. For cell-to-cell communication, spikes lasting a few millisecond ...
Bolt IRM Mod 03
... been able to diagnose the illness by taking advantage of the fact that the myelin sheath speeds axonal conduction velocity. In one simple test, the neurologist stimulates the eye with a checkerboard pattern and then assesses the time it takes the impulse to cross the optic nerve (the electrical resp ...
... been able to diagnose the illness by taking advantage of the fact that the myelin sheath speeds axonal conduction velocity. In one simple test, the neurologist stimulates the eye with a checkerboard pattern and then assesses the time it takes the impulse to cross the optic nerve (the electrical resp ...
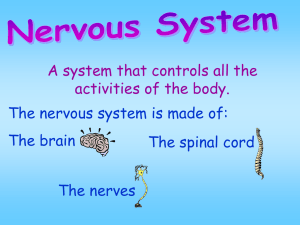
The Nervous System
... • The major communication link between the brain and the rest of the body • A reflex is a quick automatic response to a stimulus ...
... • The major communication link between the brain and the rest of the body • A reflex is a quick automatic response to a stimulus ...
Neural Basis of Motor Control
... becomes more positive and becomes depolarized. It takes longer for potassium channels to open. When they do open, potassium rushes out of the cell, reversing the depolarization. Also at about this time, sodium channels start to close. This causes the action potential to go back toward -70 mV (a repo ...
... becomes more positive and becomes depolarized. It takes longer for potassium channels to open. When they do open, potassium rushes out of the cell, reversing the depolarization. Also at about this time, sodium channels start to close. This causes the action potential to go back toward -70 mV (a repo ...
TeachingwiththeBrain-BasedNaturalHumanFACES_forprint
... stupid. With appropriate help she became an excellent reader. Only 5% of students have ADD, but more than 25% are given ritalin, which stifles normal brain growth. These students say they are so bored they can't sit still, be quiet, listen and obey; they want to think, figure things out themselves, ...
... stupid. With appropriate help she became an excellent reader. Only 5% of students have ADD, but more than 25% are given ritalin, which stifles normal brain growth. These students say they are so bored they can't sit still, be quiet, listen and obey; they want to think, figure things out themselves, ...
Limbic System
... Absent in some areas (vomiting center and the hypothalamus), allowing these areas to monitor the chemical composition of the blood Stress increases the ability of chemicals to pass through the blood-brain barrier ...
... Absent in some areas (vomiting center and the hypothalamus), allowing these areas to monitor the chemical composition of the blood Stress increases the ability of chemicals to pass through the blood-brain barrier ...
Notes on Learning to Compute and Computing to Learn
... a statistically significant difference between the neuron’s response to a stimulus combination compared to its response to the individual component stimulus [21]. There is some evidence, based on experiments on cats, that certain areas of the cats’ nervous system comprise unimodal neurons, at least ...
... a statistically significant difference between the neuron’s response to a stimulus combination compared to its response to the individual component stimulus [21]. There is some evidence, based on experiments on cats, that certain areas of the cats’ nervous system comprise unimodal neurons, at least ...
How messages travel through the body?
... brain of a newborn baby during birth. Lack of oxygen or injury usually causes the brain damage. The victims may have trouble walking, speaking and using his/her hands. ...
... brain of a newborn baby during birth. Lack of oxygen or injury usually causes the brain damage. The victims may have trouble walking, speaking and using his/her hands. ...
Autistic brains `organized differently`
... to take part in normal society. The researchers believe their findings may lead towards new ways of helping people to live with the condition. "For example, this may show a means to help people to literacy in a much more natural way than the usual methods of helping autistic people," said Dr Laurent ...
... to take part in normal society. The researchers believe their findings may lead towards new ways of helping people to live with the condition. "For example, this may show a means to help people to literacy in a much more natural way than the usual methods of helping autistic people," said Dr Laurent ...
Somatic Sensory System
... • Somotopic map called homunculus that shows that the largest number of neurons in S1 receive sensory information from hand and mouth ...
... • Somotopic map called homunculus that shows that the largest number of neurons in S1 receive sensory information from hand and mouth ...
Can Digital Games Be a Way of Improving the Neuroplasticity in
... this study, researchers identified new neurons and observed neurogenesis occurring in the hippocampal region, a brain region that controls certain types of memory [16]. Studies have shown through the used PET, and MRI brain scanning technology, those new neural cells are generated through life as we ...
... this study, researchers identified new neurons and observed neurogenesis occurring in the hippocampal region, a brain region that controls certain types of memory [16]. Studies have shown through the used PET, and MRI brain scanning technology, those new neural cells are generated through life as we ...
Control Coordination
... your sympathetic nervous system prepares your body for emergencies. It shunts your blood to your muscles and increases your blood pressure, heart rate and breathing rate, enabling you to cope with stressful situations. Rest and digest ...
... your sympathetic nervous system prepares your body for emergencies. It shunts your blood to your muscles and increases your blood pressure, heart rate and breathing rate, enabling you to cope with stressful situations. Rest and digest ...
The Cerebral Cortex and Its Functions
... The human brain hemispheres are covered in its greater part by an external layer of gray color called cerebral cortex. A deep cut into the brain would show that this gray surface has a thickness varying from 1 to 4 mm. Its largest part is composed by nerve cells (neurons) which receive impulses from ...
... The human brain hemispheres are covered in its greater part by an external layer of gray color called cerebral cortex. A deep cut into the brain would show that this gray surface has a thickness varying from 1 to 4 mm. Its largest part is composed by nerve cells (neurons) which receive impulses from ...
What is EEG? Elana Zion
... would not probe inside to explore, of course). In addition, EEG equipment is relatively inexpensive compared with other devices and simple to operate. The main disadvantage of EEG recording is poor spatial resolution. Since measurements are taken at the scalp, the received signal is, essentially, th ...
... would not probe inside to explore, of course). In addition, EEG equipment is relatively inexpensive compared with other devices and simple to operate. The main disadvantage of EEG recording is poor spatial resolution. Since measurements are taken at the scalp, the received signal is, essentially, th ...
cerebral cortex
... • It is about the areas of cerebral cortex, whose neurons emit impulses for muscle activity • their axons therefore continue into lower levels of CNS as descending (motor) pathways • Within the cerebral cortex, there are especially located specific control areas for functions controlling striated mu ...
... • It is about the areas of cerebral cortex, whose neurons emit impulses for muscle activity • their axons therefore continue into lower levels of CNS as descending (motor) pathways • Within the cerebral cortex, there are especially located specific control areas for functions controlling striated mu ...
Red Brain, Blue Brain: Evaluative Processes Differ
... available party registration records with the names of participants (35 males, 47 females) who had previously taken part in an experiment designed to examine risk-taking behavior during functional brain imaging. Ideally, we would have also directly inquired about the individuals’ ideological self-id ...
... available party registration records with the names of participants (35 males, 47 females) who had previously taken part in an experiment designed to examine risk-taking behavior during functional brain imaging. Ideally, we would have also directly inquired about the individuals’ ideological self-id ...
[j26]Chapter 8#
... ___ 27. The fingers and face have a higher density of sensory receptors and more muscles for innervation, and so, have a correspondingly larger representation on the sensory and motor regions of the cerebral cortex, respectively. ___ 28. The parietal lobe is the primary area for vision and for the c ...
... ___ 27. The fingers and face have a higher density of sensory receptors and more muscles for innervation, and so, have a correspondingly larger representation on the sensory and motor regions of the cerebral cortex, respectively. ___ 28. The parietal lobe is the primary area for vision and for the c ...
Neural Oscillators on the Edge: Harnessing Noise to Promote Stability
... Abnormal neural oscillations are implicated in certain disease states, for example repetitive firing of injured axons evoking painful paresthesia, and rhythmic discharges of cortical neurons in patients with epilepsy. In other clinical conditions, the pathological state manifests as a vulnerability ...
... Abnormal neural oscillations are implicated in certain disease states, for example repetitive firing of injured axons evoking painful paresthesia, and rhythmic discharges of cortical neurons in patients with epilepsy. In other clinical conditions, the pathological state manifests as a vulnerability ...
How Does Caffeine Affect the Central Nervous System? (CNS)
... Nehlig, A., J. L. Daval, and G. Debry. "Caffeine ...
... Nehlig, A., J. L. Daval, and G. Debry. "Caffeine ...
BIOS 1300 SI EXAM 4 REVIEW –WORKSHEET 2 SI Leader: Merrin
... 1. The seahorse-like structure in the limbic system responsible for storage and retrieval of new long-term memories is the: a. corpus callosum b. amygdaloid body c. hippocampus d. cingulated gyrus Fill-In 1. Parkinson’s disease is associated with inadequate production of the neurotransmitter ______ ...
... 1. The seahorse-like structure in the limbic system responsible for storage and retrieval of new long-term memories is the: a. corpus callosum b. amygdaloid body c. hippocampus d. cingulated gyrus Fill-In 1. Parkinson’s disease is associated with inadequate production of the neurotransmitter ______ ...
Neuroplasticity

Neuroplasticity, also known as brain plasticity, is an umbrella term that encompasses both synaptic plasticity and non-synaptic plasticity—it refers to changes in neural pathways and synapses due to changes in behavior, environment, neural processes, thinking, and emotions – as well as to changes resulting from bodily injury. The concept of neuroplasticity has replaced the formerly-held position that the brain is a physiologically static organ, and explores how – and in which ways – the brain changes in the course of a lifetime.Neuroplasticity occurs on a variety of levels, ranging from cellular changes (due to learning) to large-scale changes involved in cortical remapping in response to injury. The role of neuroplasticity is widely recognized in healthy development, learning, memory, and recovery from brain damage. During most of the 20th century, neuroscientists maintained a scientific consensus that brain structure was relatively immutable after a critical period during early childhood. This belief has been challenged by findings revealing that many aspects of the brain remain plastic even into adulthood.Hubel and Wiesel had demonstrated that ocular dominance columns in the lowest neocortical visual area, V1, remained largely immutable after the critical period in development. Researchers also studied critical periods with respect to language; the resulting data suggested that sensory pathways were fixed after the critical period. However, studies determined that environmental changes could alter behavior and cognition by modifying connections between existing neurons and via neurogenesis in the hippocampus and in other parts of the brain, including in the cerebellum.Decades of research have shown that substantial changes occur in the lowest neocortical processing areas, and that these changes can profoundly alter the pattern of neuronal activation in response to experience. Neuroscientific research indicates that experience can actually change both the brain's physical structure (anatomy) and functional organization (physiology). As of 2014 neuroscientists are engaged in a reconciliation of critical-period studies (demonstrating the immutability of the brain after development) with the more recent research showing how the brain can, and does, change in response to hitherto unsuspected stimuli.


















![[j26]Chapter 8#](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/009531099_1-530d7c194a24d89985e18840d7e0199e-300x300.png)



