This is Your Brain. This Is How It Works.
... Broca’s area is behind the frontal lobes. This area is the center of our speech. It also relates to other language areas such as writing and reading. ...
... Broca’s area is behind the frontal lobes. This area is the center of our speech. It also relates to other language areas such as writing and reading. ...
glossary of terms
... Kinesphere (reach space): “the sphere around the body whose periphery can be reached by easily extended limbs without stepping away from that place which is the point of support when standing on on ...
... Kinesphere (reach space): “the sphere around the body whose periphery can be reached by easily extended limbs without stepping away from that place which is the point of support when standing on on ...
Session 2. Synaptic Plasticity (Chair, H. Kamiguchi)
... The formation of long-term memory requires both new RNA and protein synthesis, whereas short-term memory requires only covalent modifications of constitutively expressed preexisting proteins. The core molecular features of the transcriptional regulation involved in long-term memory is to be evolutio ...
... The formation of long-term memory requires both new RNA and protein synthesis, whereas short-term memory requires only covalent modifications of constitutively expressed preexisting proteins. The core molecular features of the transcriptional regulation involved in long-term memory is to be evolutio ...
Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System
... Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)All of the ___________________ outside of the central nervous system. ...
... Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)All of the ___________________ outside of the central nervous system. ...
Slide ()
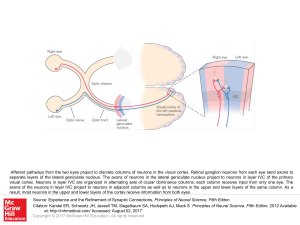
... separate layers of the lateral geniculate nucleus. The axons of neurons in the lateral geniculate nucleus project to neurons in layer IVC of the primary visual cortex. Neurons in layer IVC are organized in alternating sets of ocular dominance columns; each column receives input from only one eye. Th ...
... separate layers of the lateral geniculate nucleus. The axons of neurons in the lateral geniculate nucleus project to neurons in layer IVC of the primary visual cortex. Neurons in layer IVC are organized in alternating sets of ocular dominance columns; each column receives input from only one eye. Th ...
Abstract Browser - The Journal of Neuroscience
... therefore important to individuals’ normal social functioning. Previous neuroimaging studies have highlighted the involvement of the insular and ventromedial prefrontal (vmPFC) cortices in representing norms. However, the necessity and dissociability of their involvement remain unclear. Using model- ...
... therefore important to individuals’ normal social functioning. Previous neuroimaging studies have highlighted the involvement of the insular and ventromedial prefrontal (vmPFC) cortices in representing norms. However, the necessity and dissociability of their involvement remain unclear. Using model- ...
Slide 1
... DA directly depresses sympathetic output and DA synthesis has a diurnal rhythm DA usually hyperpolarizes and depresses sympathetic activity ...
... DA directly depresses sympathetic output and DA synthesis has a diurnal rhythm DA usually hyperpolarizes and depresses sympathetic activity ...
Chapter 12 – The Nervous System ()
... Multiple sclerosis, also called MS, affects the nerve cells in the brain and spinal cord. This disorder causes the myelin sheath which surrounds the nerve cells to become inflamed or damaged, disrupting nerve impulses. Disruption of the nerve impulses can cause a variety of symptoms including; 1. Bl ...
... Multiple sclerosis, also called MS, affects the nerve cells in the brain and spinal cord. This disorder causes the myelin sheath which surrounds the nerve cells to become inflamed or damaged, disrupting nerve impulses. Disruption of the nerve impulses can cause a variety of symptoms including; 1. Bl ...
w - Fizyka UMK
... • CAM Brain (ATR Kyoto) – failed attempt to evolve the largescale cellular neural network; based on a bad idea that one can evolve functions without knowing them. It is impossible to repeat evolutionary process (lack of data about initial organisms and environment, almost infinite number of evolutio ...
... • CAM Brain (ATR Kyoto) – failed attempt to evolve the largescale cellular neural network; based on a bad idea that one can evolve functions without knowing them. It is impossible to repeat evolutionary process (lack of data about initial organisms and environment, almost infinite number of evolutio ...
Neuroanatomical Background to Understanding the Brain of the
... simply that these areas are grossly damaged, but that the circuitry connecting these areas with each other and with several key regions, are either interrupted by mechanical or toxic damage, or dysregulated by several endogenous factors. These factors may include abnormal neurotransmitter systems, s ...
... simply that these areas are grossly damaged, but that the circuitry connecting these areas with each other and with several key regions, are either interrupted by mechanical or toxic damage, or dysregulated by several endogenous factors. These factors may include abnormal neurotransmitter systems, s ...
Document
... Electrical stimulation (ESB) Transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) Brain imaging – – computerized tomography – positron emission tomography – magnetic resonance imaging ...
... Electrical stimulation (ESB) Transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) Brain imaging – – computerized tomography – positron emission tomography – magnetic resonance imaging ...
Document
... • CAM Brain (ATR Kyoto) – failed attempt to evolve the largescale cellular neural network; based on a bad idea that one can evolve functions without knowing them. It is impossible to repeat evolutionary process (lack of data about initial organisms and environment, almost infinite number of evolutio ...
... • CAM Brain (ATR Kyoto) – failed attempt to evolve the largescale cellular neural network; based on a bad idea that one can evolve functions without knowing them. It is impossible to repeat evolutionary process (lack of data about initial organisms and environment, almost infinite number of evolutio ...
Brain Plasticity and Emotional Regulation
... (de-afferented their arms) and forced them to learn to eat. ...
... (de-afferented their arms) and forced them to learn to eat. ...
ASCENDING TRACTS
... Dorsal column pathway: • Carries fine touch, vibration and conscious proprioception signals • 1st neuron enters spinal cord through dorsal root; ascends to medulla (brain stem) • 2nd neuron crosses over in medulla; ascends to thalamus • 3rd neuron projects to somatosensory cortex ...
... Dorsal column pathway: • Carries fine touch, vibration and conscious proprioception signals • 1st neuron enters spinal cord through dorsal root; ascends to medulla (brain stem) • 2nd neuron crosses over in medulla; ascends to thalamus • 3rd neuron projects to somatosensory cortex ...
7-4_DescendingPathways_HubaT
... In this picture you can see the 31 pairs of spinal nerves. Spinal nerves are grouped according to the place where they emerge from the spinal cord. Spinal nerves are responsible for carrying information between the central nervous system and other parts of the body. The spinal cord is the center of ...
... In this picture you can see the 31 pairs of spinal nerves. Spinal nerves are grouped according to the place where they emerge from the spinal cord. Spinal nerves are responsible for carrying information between the central nervous system and other parts of the body. The spinal cord is the center of ...
NervousSystem3
... basis ponti. Axons of the cells of the pontine nuclei as pontocerebellar fibers collectively form the middle cerebellar peduncles and end in the cerebellar cortex. Descending motor fibers of the red nucleus of the midbrain give off collaterals to the inferior olivary nucleus of the medulla, which pr ...
... basis ponti. Axons of the cells of the pontine nuclei as pontocerebellar fibers collectively form the middle cerebellar peduncles and end in the cerebellar cortex. Descending motor fibers of the red nucleus of the midbrain give off collaterals to the inferior olivary nucleus of the medulla, which pr ...
Objectives - Nervous System
... Function of the Nervous System The nervous system and the endocrine system cooperate in regulating and controlling the activities of the other body systems The nervous system may be divided into two ...
... Function of the Nervous System The nervous system and the endocrine system cooperate in regulating and controlling the activities of the other body systems The nervous system may be divided into two ...
Fridtjof Nansen Science Symposium 2011
... strains of C. elegans. Neuropeptides like vasopressin and oxytocin and their receptors are also implicated in mammalian social behaviors, suggesting a common genetic vocabulary for sociality. How do genes and the enviroment interact to generate behavior? In C. elegans, a specialized “social brain” i ...
... strains of C. elegans. Neuropeptides like vasopressin and oxytocin and their receptors are also implicated in mammalian social behaviors, suggesting a common genetic vocabulary for sociality. How do genes and the enviroment interact to generate behavior? In C. elegans, a specialized “social brain” i ...
Full Text PDF - Jaypee Journals
... include anencephaly and encephalocele, and caudal NTDs spina bifida, myelomeningocele and meningocele (Figs 3A and B). NTDs are among the most common human malformations encountered in newborns. By around day 20 (even before the closure of the neural tube), the primordia of three brain vesicles (for ...
... include anencephaly and encephalocele, and caudal NTDs spina bifida, myelomeningocele and meningocele (Figs 3A and B). NTDs are among the most common human malformations encountered in newborns. By around day 20 (even before the closure of the neural tube), the primordia of three brain vesicles (for ...
Motor Pathways
... – Vestibulospinal tract: balance (axial muscles); automatic postural adjustments ...
... – Vestibulospinal tract: balance (axial muscles); automatic postural adjustments ...
ANPS 019 Black 11-09
... THE CEREBRUM Is the largest part of the brain Controls all conscious thoughts and intellectual functions Processes somatic and visceral sensory and motor functions FUNCTIONAL PRINCIPLES OF THE CEREBRUM Each cerebral hemisphere receives sensory information from and sends motor commands to, the opposi ...
... THE CEREBRUM Is the largest part of the brain Controls all conscious thoughts and intellectual functions Processes somatic and visceral sensory and motor functions FUNCTIONAL PRINCIPLES OF THE CEREBRUM Each cerebral hemisphere receives sensory information from and sends motor commands to, the opposi ...
BRAINS OF NORWAY
... rhetoric as he mentally walked around, allowing each landmark to activate the individual sections from memory. The fascination with memory and location continued into the twentieth century, when behavioural scientists first hypothesized that animals carry an abstract map of space inside their heads. ...
... rhetoric as he mentally walked around, allowing each landmark to activate the individual sections from memory. The fascination with memory and location continued into the twentieth century, when behavioural scientists first hypothesized that animals carry an abstract map of space inside their heads. ...
Midterm 1 - studyfruit
... ○ Phrenology - science of correlating structure of the head with personality traits ■ developed in 1809 by Joseph Gall who believed bumps on the surface of the skull reflected bumps on the surface of the brain ● Gall and followers mapped 100s of people’s skulls, relating the differing shapes to pers ...
... ○ Phrenology - science of correlating structure of the head with personality traits ■ developed in 1809 by Joseph Gall who believed bumps on the surface of the skull reflected bumps on the surface of the brain ● Gall and followers mapped 100s of people’s skulls, relating the differing shapes to pers ...
3FA3M8-C-B4-Handout
... Found - different patterns of neuronal plasticity in both subjects Schizophrenics rely more on adaptive properties of the visual field cortex, and healthy volunteers rely more on the properties of motor cortex ...
... Found - different patterns of neuronal plasticity in both subjects Schizophrenics rely more on adaptive properties of the visual field cortex, and healthy volunteers rely more on the properties of motor cortex ...
Neuroplasticity

Neuroplasticity, also known as brain plasticity, is an umbrella term that encompasses both synaptic plasticity and non-synaptic plasticity—it refers to changes in neural pathways and synapses due to changes in behavior, environment, neural processes, thinking, and emotions – as well as to changes resulting from bodily injury. The concept of neuroplasticity has replaced the formerly-held position that the brain is a physiologically static organ, and explores how – and in which ways – the brain changes in the course of a lifetime.Neuroplasticity occurs on a variety of levels, ranging from cellular changes (due to learning) to large-scale changes involved in cortical remapping in response to injury. The role of neuroplasticity is widely recognized in healthy development, learning, memory, and recovery from brain damage. During most of the 20th century, neuroscientists maintained a scientific consensus that brain structure was relatively immutable after a critical period during early childhood. This belief has been challenged by findings revealing that many aspects of the brain remain plastic even into adulthood.Hubel and Wiesel had demonstrated that ocular dominance columns in the lowest neocortical visual area, V1, remained largely immutable after the critical period in development. Researchers also studied critical periods with respect to language; the resulting data suggested that sensory pathways were fixed after the critical period. However, studies determined that environmental changes could alter behavior and cognition by modifying connections between existing neurons and via neurogenesis in the hippocampus and in other parts of the brain, including in the cerebellum.Decades of research have shown that substantial changes occur in the lowest neocortical processing areas, and that these changes can profoundly alter the pattern of neuronal activation in response to experience. Neuroscientific research indicates that experience can actually change both the brain's physical structure (anatomy) and functional organization (physiology). As of 2014 neuroscientists are engaged in a reconciliation of critical-period studies (demonstrating the immutability of the brain after development) with the more recent research showing how the brain can, and does, change in response to hitherto unsuspected stimuli.