Chapter Questions Answer Key - Brain Injury Alliance of Oregon
... B. The Acute Hospital setting is focused on saving the individual’s life and preventing further injury. A person may be in a coma during this phase of support. Surgery may be necessary. ...
... B. The Acute Hospital setting is focused on saving the individual’s life and preventing further injury. A person may be in a coma during this phase of support. Surgery may be necessary. ...
ppt - Brain Dynamics Laboratory
... • Extrinsic or network mechanisms, which require the interaction of excitatory and inhibitory neurons within a population. • Intrinsic and network mechanisms can work alone (e.g., thalamic delta oscillations depend on the intrinsic properties of thalamic relay cells, cortical slow oscillation depend ...
... • Extrinsic or network mechanisms, which require the interaction of excitatory and inhibitory neurons within a population. • Intrinsic and network mechanisms can work alone (e.g., thalamic delta oscillations depend on the intrinsic properties of thalamic relay cells, cortical slow oscillation depend ...
The Cerebellum - Amanda Parsons
... how we move (Hannaford, 2005). At the core of the cerebellum is a structure responsible for functions related to equilibrium and balance, the vermis (Cozolino, 2006). The cerebellum evolved with the brain and body’s increasing need for precise movements, symbolic representations, and expressive comm ...
... how we move (Hannaford, 2005). At the core of the cerebellum is a structure responsible for functions related to equilibrium and balance, the vermis (Cozolino, 2006). The cerebellum evolved with the brain and body’s increasing need for precise movements, symbolic representations, and expressive comm ...
Psychology - Bideford College Sixth Form
... If you find that one link fails, just google the topic you are trying to research. This assignment will be checked on the first day of class for a completion grade. An open note quiz over the material will also be given. All work should be hand written or typed onto the assignment. This can be print ...
... If you find that one link fails, just google the topic you are trying to research. This assignment will be checked on the first day of class for a completion grade. An open note quiz over the material will also be given. All work should be hand written or typed onto the assignment. This can be print ...
MPG-official form - Max Planck Institute for Chemical Ecology
... evaluate the information that is sent via these senses to their brains. They must be able to tell good from bad odors. Good odors are important signals when animals search for food or a mating partner. Female insects also use olfactory signals to select a good oviposition place. Bad smells, on the ...
... evaluate the information that is sent via these senses to their brains. They must be able to tell good from bad odors. Good odors are important signals when animals search for food or a mating partner. Female insects also use olfactory signals to select a good oviposition place. Bad smells, on the ...
IOSR Journal of Computer Engineering (IOSR-JCE)
... Sensory motor actions (james o regan): Sensorimotor approach allow to address the problem of the explanatory gap: that is, the problem of explaining perception, consciousness, and qualia in terms of physical and functional properties of perceptual systems. Vision, we argue, requires knowledgeof sens ...
... Sensory motor actions (james o regan): Sensorimotor approach allow to address the problem of the explanatory gap: that is, the problem of explaining perception, consciousness, and qualia in terms of physical and functional properties of perceptual systems. Vision, we argue, requires knowledgeof sens ...
The Sensorimotor System
... Subject of ongoing research May be involved in programming movements in response to input from dorsolateral prefrontal cortex Many premotor neurons are bimodal – responding to 2 different types of stimuli (most common - somatosensory and visual) ...
... Subject of ongoing research May be involved in programming movements in response to input from dorsolateral prefrontal cortex Many premotor neurons are bimodal – responding to 2 different types of stimuli (most common - somatosensory and visual) ...
PSE4U1 - 10.Unit 4
... – Good insulator covering the axon between nodes, allowing transmission to be fast – Formed by Schwann Cells that wrap around some axons outside the central nervous system – Neurilemma is the outer cell membrane of a Schwann Cell – Nodes of Ranvier are indentations that exist between adjancent Schwa ...
... – Good insulator covering the axon between nodes, allowing transmission to be fast – Formed by Schwann Cells that wrap around some axons outside the central nervous system – Neurilemma is the outer cell membrane of a Schwann Cell – Nodes of Ranvier are indentations that exist between adjancent Schwa ...
Automated image computing reshapes computational neuroscience Open Access
... Studying dynamics and functions of neural circuits Functional connectivity and dynamics of neuronal connections are two other important topics of computational neuroscience. Neuronal dynamics are reflected in structure and activity at a variety of temporal scales, ranging from arbor growth and cell ...
... Studying dynamics and functions of neural circuits Functional connectivity and dynamics of neuronal connections are two other important topics of computational neuroscience. Neuronal dynamics are reflected in structure and activity at a variety of temporal scales, ranging from arbor growth and cell ...
Slide () - Anesthesiology - American Society of Anesthesiologists
... Myelinating oligodendrocytes at a midrostrocaudal level: All panels are stained immunochemically with antibodies to myelin basic protein (MBP). A presents an overview showing different stages of myelination at a midrostrocaudal level of a control brain. In the cerebrocortical mantel, and in the tran ...
... Myelinating oligodendrocytes at a midrostrocaudal level: All panels are stained immunochemically with antibodies to myelin basic protein (MBP). A presents an overview showing different stages of myelination at a midrostrocaudal level of a control brain. In the cerebrocortical mantel, and in the tran ...
CNS_Part2
... behavior. The third group, the mesocortical, projects only to the prefrontal cortex. This area of cortex is involved with various cognitive functions, memory, behavioral planning and abstract thinking, as well as in emotional aspects, especially in relation to stress. The earlier mentioned reward sy ...
... behavior. The third group, the mesocortical, projects only to the prefrontal cortex. This area of cortex is involved with various cognitive functions, memory, behavioral planning and abstract thinking, as well as in emotional aspects, especially in relation to stress. The earlier mentioned reward sy ...
11.4: The Peripheral Nervous System
... the binding of the neurotransmitters that transmit the signal interpreted as pain. When the neurotransmitters do not bind to the receptor sites, we do not feel pain. The neurotranmitters act as natural drugs. 4. Answers may vary. Sample answer: Strenuous exercise is known to result in the production ...
... the binding of the neurotransmitters that transmit the signal interpreted as pain. When the neurotransmitters do not bind to the receptor sites, we do not feel pain. The neurotranmitters act as natural drugs. 4. Answers may vary. Sample answer: Strenuous exercise is known to result in the production ...
The Human Nervous System
... The Neuron ~functional unit of the nervous system! All neurons have 3 main parts: 1. Dendrites receive information from another cell and transmit the message to the cell body. 2. The cell body contains the nucleus, mitochondria and other organelles typical of eukaryotic cells 3. The axon conducts m ...
... The Neuron ~functional unit of the nervous system! All neurons have 3 main parts: 1. Dendrites receive information from another cell and transmit the message to the cell body. 2. The cell body contains the nucleus, mitochondria and other organelles typical of eukaryotic cells 3. The axon conducts m ...
nitz - UCSD Cognitive Science
... medial entorhinal cortex contains grid cells, grid X head-direction cells, and head-direction cells – each cell type is also velocity sensitive, thus allowing for determination of position according to path integration (i.e., tracking of direction and speed over time) all within one structure ...
... medial entorhinal cortex contains grid cells, grid X head-direction cells, and head-direction cells – each cell type is also velocity sensitive, thus allowing for determination of position according to path integration (i.e., tracking of direction and speed over time) all within one structure ...
The Dark Side of Product Attachment: An fMRI Study of Reactivity of
... other studies have found that addictive product users, when exposed to these cues, may have an ability to inhibit the craving response and its effects (Artiges et al. 2009; Goldstein et al. 2007a; Stippekohl et al. 2010; Volkow and Fowler 2000; Volkow et al. 2010). On the other hand, non-users have ...
... other studies have found that addictive product users, when exposed to these cues, may have an ability to inhibit the craving response and its effects (Artiges et al. 2009; Goldstein et al. 2007a; Stippekohl et al. 2010; Volkow and Fowler 2000; Volkow et al. 2010). On the other hand, non-users have ...
Autism And Mirror Neurons
... Autistic children had: • MORE activity in the right visual and left anterior parietal areas (visual and motor attention) • LESS activity in the insula and amygdala (emotion) • NO activity in the mirror neuron system of the inferior frontal gyrus ...
... Autistic children had: • MORE activity in the right visual and left anterior parietal areas (visual and motor attention) • LESS activity in the insula and amygdala (emotion) • NO activity in the mirror neuron system of the inferior frontal gyrus ...
Subthalamic High-frequency Deep Brain Stimulation Evaluated in a
... activated with continuously unipolar stimulation (electrode negative, case positive, amplitude 3V, frequency 160 Hz, pulse-width 60 µs). Additional PET-scans with 15O-water and 15Ooxygen were then acquired 5 min, 30 min, 60 min, 120 min and 240 min after stimulation onset ("poststimulation"). The P ...
... activated with continuously unipolar stimulation (electrode negative, case positive, amplitude 3V, frequency 160 Hz, pulse-width 60 µs). Additional PET-scans with 15O-water and 15Ooxygen were then acquired 5 min, 30 min, 60 min, 120 min and 240 min after stimulation onset ("poststimulation"). The P ...
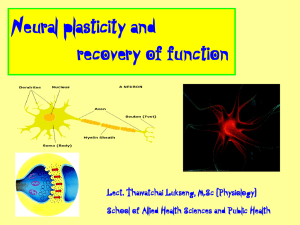
Neural plasticity and recovery of function
... – Recovery of arm movement is usually less complete than leg movement – Full arm recovery, if it occurs, is usually complete by 8 weeks – At 3 months, 5% of all stroke have significant shoulder pain and 8% have decreased ROM ...
... – Recovery of arm movement is usually less complete than leg movement – Full arm recovery, if it occurs, is usually complete by 8 weeks – At 3 months, 5% of all stroke have significant shoulder pain and 8% have decreased ROM ...
Motor Systems II Loops and Tracts
... A collection of inter-connected, midline, nuclei located lateral to the thalamus Includes the striatum (caudate and putamen), globus pallidus (external and internal), subthalamic nucleus and substantia nigra ...
... A collection of inter-connected, midline, nuclei located lateral to the thalamus Includes the striatum (caudate and putamen), globus pallidus (external and internal), subthalamic nucleus and substantia nigra ...
The Nervous System
... brain; controls processes vital to physical functioning of the body • Reptilian complex: layer of brain over the brain stem. The seat of status and territory; enables more complicated behaviors in life. ...
... brain; controls processes vital to physical functioning of the body • Reptilian complex: layer of brain over the brain stem. The seat of status and territory; enables more complicated behaviors in life. ...
Unit III: Biological Basis of Behavior
... New technologies are enabling neuroscientists to access the brain in new ways providing remarkable insight • lesioning: destruction of brain tissue – helps to provide insight into brain function • stimulation: using electrical, chemical, magnetic activity to facilitate brain function • Electroenceph ...
... New technologies are enabling neuroscientists to access the brain in new ways providing remarkable insight • lesioning: destruction of brain tissue – helps to provide insight into brain function • stimulation: using electrical, chemical, magnetic activity to facilitate brain function • Electroenceph ...
Neuroplasticity

Neuroplasticity, also known as brain plasticity, is an umbrella term that encompasses both synaptic plasticity and non-synaptic plasticity—it refers to changes in neural pathways and synapses due to changes in behavior, environment, neural processes, thinking, and emotions – as well as to changes resulting from bodily injury. The concept of neuroplasticity has replaced the formerly-held position that the brain is a physiologically static organ, and explores how – and in which ways – the brain changes in the course of a lifetime.Neuroplasticity occurs on a variety of levels, ranging from cellular changes (due to learning) to large-scale changes involved in cortical remapping in response to injury. The role of neuroplasticity is widely recognized in healthy development, learning, memory, and recovery from brain damage. During most of the 20th century, neuroscientists maintained a scientific consensus that brain structure was relatively immutable after a critical period during early childhood. This belief has been challenged by findings revealing that many aspects of the brain remain plastic even into adulthood.Hubel and Wiesel had demonstrated that ocular dominance columns in the lowest neocortical visual area, V1, remained largely immutable after the critical period in development. Researchers also studied critical periods with respect to language; the resulting data suggested that sensory pathways were fixed after the critical period. However, studies determined that environmental changes could alter behavior and cognition by modifying connections between existing neurons and via neurogenesis in the hippocampus and in other parts of the brain, including in the cerebellum.Decades of research have shown that substantial changes occur in the lowest neocortical processing areas, and that these changes can profoundly alter the pattern of neuronal activation in response to experience. Neuroscientific research indicates that experience can actually change both the brain's physical structure (anatomy) and functional organization (physiology). As of 2014 neuroscientists are engaged in a reconciliation of critical-period studies (demonstrating the immutability of the brain after development) with the more recent research showing how the brain can, and does, change in response to hitherto unsuspected stimuli.