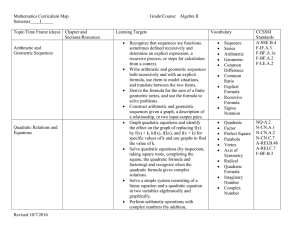
PDF
... the roots of which are the numbers (1) and only these. The coefficients gi of the polynomial g(x) are symmetric polynomials in the numbers ϑ1 , ϑ2 , . . . , ϑn and also symmetric polynomials in the numbers α(i) . The fundamental theorem of symmetric polynomials implies now that the symmetric polynom ...
... the roots of which are the numbers (1) and only these. The coefficients gi of the polynomial g(x) are symmetric polynomials in the numbers ϑ1 , ϑ2 , . . . , ϑn and also symmetric polynomials in the numbers α(i) . The fundamental theorem of symmetric polynomials implies now that the symmetric polynom ...
PED-HSM11A2TR-08-1103-001
... Solve each compound inequality. Graph the solutions. 16. 3x – 1 5 or 2x – 4 x ...
... Solve each compound inequality. Graph the solutions. 16. 3x – 1 5 or 2x – 4 x ...
Clipboard Math 23
... Clipboard Math #23 DO NOT WRITE ON THIS PAPER. Put all answers on answer sheet! 1.) GEOMETRY GEMS: Jane's yard is shaped like a pentagon that is 20.5 feet on each side. What is the perimeter of her yard? 2.) COORDINATE POINTS: Plot the following points: X(0,4) ; Y(-2, 3) ; Z(-5, -1) 3.) FLUTTERING F ...
... Clipboard Math #23 DO NOT WRITE ON THIS PAPER. Put all answers on answer sheet! 1.) GEOMETRY GEMS: Jane's yard is shaped like a pentagon that is 20.5 feet on each side. What is the perimeter of her yard? 2.) COORDINATE POINTS: Plot the following points: X(0,4) ; Y(-2, 3) ; Z(-5, -1) 3.) FLUTTERING F ...
Beginning & Intermediate Algebra, 4ed
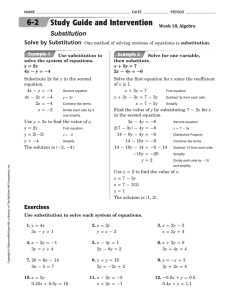
... Example: Solve the following system of equations using the addition method. 6x – 3y = –3 and 4x + 5y = –9 Multiply both sides of the first equation by 5 and the second equation by 3. First equation, 5(6x – 3y) = 5(–3) 30x – 15y = –15 Use the distributive property. Second equation, 3(4x + 5y) = 3(–9) ...
... Example: Solve the following system of equations using the addition method. 6x – 3y = –3 and 4x + 5y = –9 Multiply both sides of the first equation by 5 and the second equation by 3. First equation, 5(6x – 3y) = 5(–3) 30x – 15y = –15 Use the distributive property. Second equation, 3(4x + 5y) = 3(–9) ...
1.1 Algebraic Expression and Real Numbers
... The set of whole numbers includes the natural numbers and 0. Zero is a whole number, but is not a natural number. The set of integers includes all the whole numbers and their negatives. Every whole number is an integer, and every natural number is an integer. These sets are just getting bigger and b ...
... The set of whole numbers includes the natural numbers and 0. Zero is a whole number, but is not a natural number. The set of integers includes all the whole numbers and their negatives. Every whole number is an integer, and every natural number is an integer. These sets are just getting bigger and b ...