Algebra A
... 2.3 Solving Multi-Step Equations Multi-Step Equations – Multi-step equations are equations that need more than one operation to solve them. Consecutive Integers – Consecutive integers are integers in counting order. Number Theory – The study of numbers and the relationships between them. ...
... 2.3 Solving Multi-Step Equations Multi-Step Equations – Multi-step equations are equations that need more than one operation to solve them. Consecutive Integers – Consecutive integers are integers in counting order. Number Theory – The study of numbers and the relationships between them. ...
Grade/ Descriptor Formula Standard
... flooring and the length, by viewing the area formula as a multiplication equation with an unknown factor. 5.MD.A.1 Convert among different-sized standard measurement units within a given measurement system (e.g., convert 5 cm to 0.05 m), and use these conversions in solving multi-step, real world pr ...
... flooring and the length, by viewing the area formula as a multiplication equation with an unknown factor. 5.MD.A.1 Convert among different-sized standard measurement units within a given measurement system (e.g., convert 5 cm to 0.05 m), and use these conversions in solving multi-step, real world pr ...
Chapter 7 Notes
... I. Definitions A) Algebraic Expression – A group of number or variables connected by +, -, *, / (Except by Zero), Raising to power or roots. B) Equation – A statement where two Algebraic Expressions are Equal. C) Theorem – Linear Equations in one variable: An equation is Linear if and only if it can ...
... I. Definitions A) Algebraic Expression – A group of number or variables connected by +, -, *, / (Except by Zero), Raising to power or roots. B) Equation – A statement where two Algebraic Expressions are Equal. C) Theorem – Linear Equations in one variable: An equation is Linear if and only if it can ...
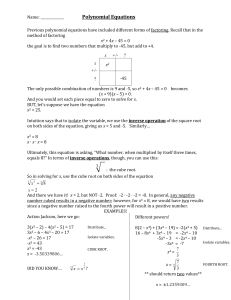
Previous polynomial equations have included
... And you would set each piece equal to zero to solve for x. BUT, let’s suppose we have the equation x2 = 25. Intuition says that to isolate the variable, we use the inverse operation of the square root on both sides of the equation, giving us x = 5 and -5. Similarly… x3 = 8 x∙x∙x=8 Ultimately, this e ...
... And you would set each piece equal to zero to solve for x. BUT, let’s suppose we have the equation x2 = 25. Intuition says that to isolate the variable, we use the inverse operation of the square root on both sides of the equation, giving us x = 5 and -5. Similarly… x3 = 8 x∙x∙x=8 Ultimately, this e ...