A Primer on Complex Numbers
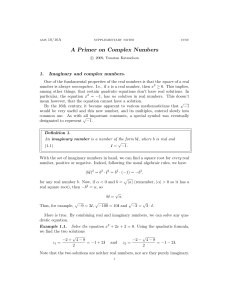
... The two solutions of the quadratic equation in Example 1.1 have the same real part and their imaginary parts are opposite. I.e., using the notation above, we have Re(z1 ) = Re(z2 ) and Im(z1 ) = −Im(z2 ). This is not a coincidence, and there is also a name for this. Definition 3. The complex conjuga ...
... The two solutions of the quadratic equation in Example 1.1 have the same real part and their imaginary parts are opposite. I.e., using the notation above, we have Re(z1 ) = Re(z2 ) and Im(z1 ) = −Im(z2 ). This is not a coincidence, and there is also a name for this. Definition 3. The complex conjuga ...
A Primer on Complex Numbers
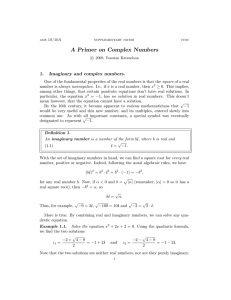
... The two solutions of the quadratic equation in Example 1.1 have the same real part and their imaginary parts are opposite. I.e., using the notation above, we have Re(z1 ) = Re(z2 ) and Im(z1 ) = −Im(z2 ). This is not a coincidence, and there is also a name for this. Definition 3. The complex conjuga ...
... The two solutions of the quadratic equation in Example 1.1 have the same real part and their imaginary parts are opposite. I.e., using the notation above, we have Re(z1 ) = Re(z2 ) and Im(z1 ) = −Im(z2 ). This is not a coincidence, and there is also a name for this. Definition 3. The complex conjuga ...
Page 1 of 11 Secondary 1 Mathematics Topic 1 – Prime Numbers
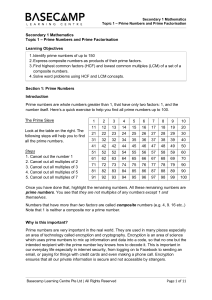
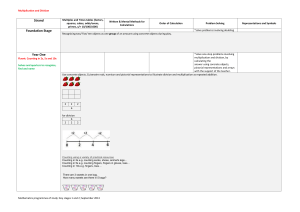
... Once you have done that, highlight the remaining numbers. All these remaining numbers are prime numbers. You see that they are not multiples of any numbers except 1 and themselves. Numbers that have more than two factors are called composite numbers (e.g. 4, 9. 16 etc..) Note that 1 is neither a com ...
... Once you have done that, highlight the remaining numbers. All these remaining numbers are prime numbers. You see that they are not multiples of any numbers except 1 and themselves. Numbers that have more than two factors are called composite numbers (e.g. 4, 9. 16 etc..) Note that 1 is neither a com ...
Sets Math 130 Linear Algebra
... with several subsets of a set, and there are oper- sets that create bigger sets, the most important beations of intersection, union, and difference that ing creating products of sets. These depend on the describe new subsets in terms of previously known concept of ordered pairs of elements. The nota ...
... with several subsets of a set, and there are oper- sets that create bigger sets, the most important beations of intersection, union, and difference that ing creating products of sets. These depend on the describe new subsets in terms of previously known concept of ordered pairs of elements. The nota ...
RNS3 REAL NUMBER SYSTEM
... around the outer portion of their circular temples was about three times the number of paces through the center. In mathematics, the Greek letter π (pronounced “pi”) is used to represent this ratio. ...
... around the outer portion of their circular temples was about three times the number of paces through the center. In mathematics, the Greek letter π (pronounced “pi”) is used to represent this ratio. ...
Algebra with Career Applicaons Prime Factorizaon Greatest
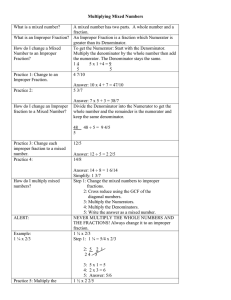
... wrien as a rao of two integers, provided that the denominator is not zero. In other words, fracons are raonal numbers. Raonal numbers can be fracons, improper fracons, mixed numbers, or decimals that either end or repeat. ...
... wrien as a rao of two integers, provided that the denominator is not zero. In other words, fracons are raonal numbers. Raonal numbers can be fracons, improper fracons, mixed numbers, or decimals that either end or repeat. ...
class-4-math-international-sa-1-practice
... 75. (32-5) is not equal to (5-32). Is it true? Justify your answer. 76. Sam likes to collect stamps. He collected 5328 stamps of different countries. Out of which 371 stamps was gifted to him by their parents. How many stamps does he have in total? 77. Johan published story books and released 2583 c ...
... 75. (32-5) is not equal to (5-32). Is it true? Justify your answer. 76. Sam likes to collect stamps. He collected 5328 stamps of different countries. Out of which 371 stamps was gifted to him by their parents. How many stamps does he have in total? 77. Johan published story books and released 2583 c ...
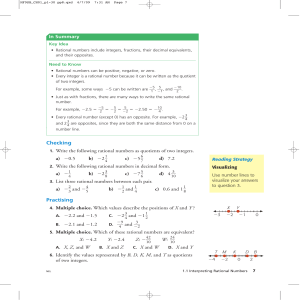
Rational and Irrational Numbers
... expressed as the ratio of two integers. The history of irrational numbers begins with a discovery by the Pythagorean School in ancient Greece. A member of the school discovered that the diagonal of a unit square could not be expressed as the ratio of any two whole numbers. The motto of the school wa ...
... expressed as the ratio of two integers. The history of irrational numbers begins with a discovery by the Pythagorean School in ancient Greece. A member of the school discovered that the diagonal of a unit square could not be expressed as the ratio of any two whole numbers. The motto of the school wa ...