The neuronal structure of the medial geniculate body in the pig
... (15–30 mm) into secondary dendrites. The secondary dendrites branch at a different distance from the cell body. Sporadically, undivided dendrites are also observed. The length of the primary and secondary dendrites is almost equal but the tertiary branches are usually prominently longer. The dendrit ...
... (15–30 mm) into secondary dendrites. The secondary dendrites branch at a different distance from the cell body. Sporadically, undivided dendrites are also observed. The length of the primary and secondary dendrites is almost equal but the tertiary branches are usually prominently longer. The dendrit ...
A103 - Viktor`s Notes for the Neurosurgery Resident
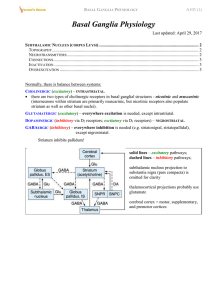
... "direct" pathway (inhibitory) - flows monosynaptically to GPi "indirect" pathway (in sum excitatory) - has intermediate synapses in GPe and subthalamic nucleus. N.B. subthalamic nucleus regulates output of basal ganglia to thalamus! direct and indirect pathways balance one another physiologically. ...
... "direct" pathway (inhibitory) - flows monosynaptically to GPi "indirect" pathway (in sum excitatory) - has intermediate synapses in GPe and subthalamic nucleus. N.B. subthalamic nucleus regulates output of basal ganglia to thalamus! direct and indirect pathways balance one another physiologically. ...
L8 slides
... • DA burst activity drives the direct "Go" pathway neurons in the striatum, which then inhibit the tonic activation in the globus pallidus internal segment (GPi), which releases specific nuclei in the thalamus from inhibition, allowing them to complete a bidirectional excitatory circuit with the fr ...
... • DA burst activity drives the direct "Go" pathway neurons in the striatum, which then inhibit the tonic activation in the globus pallidus internal segment (GPi), which releases specific nuclei in the thalamus from inhibition, allowing them to complete a bidirectional excitatory circuit with the fr ...
Chapter 17
... a. astrocytes are star-shaped cells (with many processes) that perform several functions in support of neurons b. oligodendrocytes have few processes and produce a myelin sheath; each oligodendrocyte can myelinate parts of several axons c. microglia are small, phagocytic neuroglia that protect the n ...
... a. astrocytes are star-shaped cells (with many processes) that perform several functions in support of neurons b. oligodendrocytes have few processes and produce a myelin sheath; each oligodendrocyte can myelinate parts of several axons c. microglia are small, phagocytic neuroglia that protect the n ...
Dopamine control of pyramidal neuron activity in the primary motor
... localized in the layer VI whereas D2 receptors are localized primarily in the layer V (Weiner et al., 1991; Gaspar et al., 1995), which contains the principal output pathway to all other cortical areas and to subcortical targets as the striatum or the pyramidal tract. Taken together, these data sugg ...
... localized in the layer VI whereas D2 receptors are localized primarily in the layer V (Weiner et al., 1991; Gaspar et al., 1995), which contains the principal output pathway to all other cortical areas and to subcortical targets as the striatum or the pyramidal tract. Taken together, these data sugg ...
Uncaging Compunds: - Florida State University
... – Action potentials (Aps) propegate though the axonal arbor and where axons and dendrites overlap in the neuropil a synapse sometimes forms, and synaptic transmission occurs when APs reaches the synapse. – Action potentials invade the presynaptic terminal causing glutamate to be released and then to ...
... – Action potentials (Aps) propegate though the axonal arbor and where axons and dendrites overlap in the neuropil a synapse sometimes forms, and synaptic transmission occurs when APs reaches the synapse. – Action potentials invade the presynaptic terminal causing glutamate to be released and then to ...
doc GIT
... If you stimulate at one point: 1- Activation a particular sensory fiber 2- This sensory fiber activates an effector fiber - Cause activation of a muscle cell. * B/c of the presence of interneurons, there is also activation of an effector neuron that may cause contraction in the longitudinal fibers ( ...
... If you stimulate at one point: 1- Activation a particular sensory fiber 2- This sensory fiber activates an effector fiber - Cause activation of a muscle cell. * B/c of the presence of interneurons, there is also activation of an effector neuron that may cause contraction in the longitudinal fibers ( ...
Zeitschrift für Naturforschung / C / 31 (1976) - Max-Planck
... and the reverse direction ( — * \ ) . The broken line indicates the level of the resting potential ( —55 mV). The lower trace (ac-coupled; calibration: 10m V /50m sec) shows parts of the upper trace in higher time resolution illustrating the charac teristic stimulation-dependent patterns of synapti ...
... and the reverse direction ( — * \ ) . The broken line indicates the level of the resting potential ( —55 mV). The lower trace (ac-coupled; calibration: 10m V /50m sec) shows parts of the upper trace in higher time resolution illustrating the charac teristic stimulation-dependent patterns of synapti ...
Physiology Ch 45 p543-557 [4-25
... may be blocked in its transmission from one neuron to the next, it may be changed from single impulse into repetitive imule, and it may be integrated with other impulses Types of Synapses: Chemical and Electrical – all synapses used for signal transmission in the CNS are CHEMICAL SYNAPSES, where fir ...
... may be blocked in its transmission from one neuron to the next, it may be changed from single impulse into repetitive imule, and it may be integrated with other impulses Types of Synapses: Chemical and Electrical – all synapses used for signal transmission in the CNS are CHEMICAL SYNAPSES, where fir ...
Introduction to Psychology
... 13. The ________________________ is located in the hindbrain and is involved in vital functions such as heart rate, blood pressure, and breathing. 14. The ___________________________, located below the thalamus, plays a role in the regulation of body temperature, storage of nutrients, motivation and ...
... 13. The ________________________ is located in the hindbrain and is involved in vital functions such as heart rate, blood pressure, and breathing. 14. The ___________________________, located below the thalamus, plays a role in the regulation of body temperature, storage of nutrients, motivation and ...
bulbar pseudobulbar
... If a lesion occurs in the brain stem and damages both the nucleus of a cranial nerve and one side of the upper motor neurons of the pyramidal tract, a condition known as alternating hemiplegia may result. This involves paralysis of different structures on each side of the body. The lesion on the nu ...
... If a lesion occurs in the brain stem and damages both the nucleus of a cranial nerve and one side of the upper motor neurons of the pyramidal tract, a condition known as alternating hemiplegia may result. This involves paralysis of different structures on each side of the body. The lesion on the nu ...
Stat 6601 Project: Neural Networks (V&R 6.3)
... • Dendrites – Receive information • Cell Body – Process information • Axon – Carries processed information to other neurons • Synapse – Junction between Axon end and Dendrites of other Neurons ...
... • Dendrites – Receive information • Cell Body – Process information • Axon – Carries processed information to other neurons • Synapse – Junction between Axon end and Dendrites of other Neurons ...
Synaptic and cellular organization of layer 1 of the
... the exception of two studies that document the synaptic connections between L1 cells. Cruikshank et al. have observed IPSPs between L1 cells to have slow kinetics and strong short term depression (Cruikshank et al., 2012). Chu et al. have described inhibitory synaptic connections between Late and No ...
... the exception of two studies that document the synaptic connections between L1 cells. Cruikshank et al. have observed IPSPs between L1 cells to have slow kinetics and strong short term depression (Cruikshank et al., 2012). Chu et al. have described inhibitory synaptic connections between Late and No ...
Morphology of HRP-Injected Spinocervical Tract Neurons: Effect of
... several tissue sections, it was necessary to trace some dendrites in several pieces, a piece from each section. After all of the dendritic tree pieces in each of the tissue sections had been digitized and stored, the computer merged the cut ends of the dendrite in one section to their attachments in ...
... several tissue sections, it was necessary to trace some dendrites in several pieces, a piece from each section. After all of the dendritic tree pieces in each of the tissue sections had been digitized and stored, the computer merged the cut ends of the dendrite in one section to their attachments in ...
Molecules and mechanisms of dendrite development in Drosophila
... Dendrites – processes of neurons that are primarily specialized for information input – are one of nature’s remarkable architectural feats, and the diverse growth patterns shown by dendritic arbors raise important developmental questions. The particular shapes of dendrites are important in neuronal ...
... Dendrites – processes of neurons that are primarily specialized for information input – are one of nature’s remarkable architectural feats, and the diverse growth patterns shown by dendritic arbors raise important developmental questions. The particular shapes of dendrites are important in neuronal ...
Dorsal Horn Structure/Function
... activation of a G protein coupled, inward-rectifying potassium channel. The observed presynaptic effect is a decrease in spontaneous excitatory postsynaptic potentials (EPSPs), presumably mediated by a decrease in free intracellular calcium in presynaptic terminals. In addition, there are some cells ...
... activation of a G protein coupled, inward-rectifying potassium channel. The observed presynaptic effect is a decrease in spontaneous excitatory postsynaptic potentials (EPSPs), presumably mediated by a decrease in free intracellular calcium in presynaptic terminals. In addition, there are some cells ...
sample - McLoon Lab
... A. membrane dopamine transporter proteins / inhibitory GABAergic neurons B. postsynaptic dopamine receptors / inhibitory GABAergic neurons C. membrane dopamine transporter proteins / dopamine neuron cell bodies D. dopamine neuron cell bodies / inhibitory GABAergic neurons Lecture 37 learning & memor ...
... A. membrane dopamine transporter proteins / inhibitory GABAergic neurons B. postsynaptic dopamine receptors / inhibitory GABAergic neurons C. membrane dopamine transporter proteins / dopamine neuron cell bodies D. dopamine neuron cell bodies / inhibitory GABAergic neurons Lecture 37 learning & memor ...
6-Cerebellum 2009
... (4) Stellate cells ( inhibitory to Purkinje ): Similar to Basket cells they are excited by Parallel fibers of Granule cells , & their output inhibits Purkinje cell discharge by a process of Feed-Forward Inhibition . They differ from Basket cells only in being more superficially located in the cort ...
... (4) Stellate cells ( inhibitory to Purkinje ): Similar to Basket cells they are excited by Parallel fibers of Granule cells , & their output inhibits Purkinje cell discharge by a process of Feed-Forward Inhibition . They differ from Basket cells only in being more superficially located in the cort ...
PDF
... both Vldlr and Apoer2, exhibit identical behavior and neuroanatomy and provide strong evidence for the involvement of these proteins in the same signaling pathway (22). The Reln-positive CR neuron is one of the first neurons to mature during early cortical development. It was initially described in ...
... both Vldlr and Apoer2, exhibit identical behavior and neuroanatomy and provide strong evidence for the involvement of these proteins in the same signaling pathway (22). The Reln-positive CR neuron is one of the first neurons to mature during early cortical development. It was initially described in ...
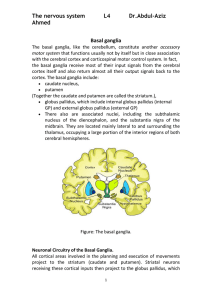
1.In the direct pathway
... 1.the substantia nigra, send Dopamine secreting neuron into the striatum. Dopamine has an excitatory effect upon cells in the striatum that are part of the Direct Pathway. This is via D1 receptors. Dopamine ...
... 1.the substantia nigra, send Dopamine secreting neuron into the striatum. Dopamine has an excitatory effect upon cells in the striatum that are part of the Direct Pathway. This is via D1 receptors. Dopamine ...
Preferential Termination of Corticorubral Axons on Spine
... Shatz, 1993; Goodman, 1996), but relatively little is known about what interactions occur within the final target. It is presumed that a cascade of complex events must take place at the target, because not only the presynaptic axons but also the postsynaptic cells must be continuously growing and re ...
... Shatz, 1993; Goodman, 1996), but relatively little is known about what interactions occur within the final target. It is presumed that a cascade of complex events must take place at the target, because not only the presynaptic axons but also the postsynaptic cells must be continuously growing and re ...
Chapter 12: Neural Tissue
... 4 Steps in the Generation of Action Potentials 1. Depolarization to threshold 2. Activation of Na+ channels: ...
... 4 Steps in the Generation of Action Potentials 1. Depolarization to threshold 2. Activation of Na+ channels: ...
ch12Boundarygabor
... Striate cortex (primary visual centre) • Neurons are edge detectors fires when an edge of a particular (LGN) orientation is present infrequent output ...
... Striate cortex (primary visual centre) • Neurons are edge detectors fires when an edge of a particular (LGN) orientation is present infrequent output ...
NERVOUS SYSTEM GENERALITY – INTRODUCTION
... - the 2 major efferent systems are: 1. the somatic nervous system (SNS), including all the somatic motor neurons that innervate skeletal muscles. 2. the autonomic nervous system (ANS), including the visceral motor neurons that innervate all other peripheral effectors (smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, ...
... - the 2 major efferent systems are: 1. the somatic nervous system (SNS), including all the somatic motor neurons that innervate skeletal muscles. 2. the autonomic nervous system (ANS), including the visceral motor neurons that innervate all other peripheral effectors (smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, ...