Introduction to P880.P20
... a) How are we going to identify the p, kaon and proton? what momentum range do we have to worry about? b) To what precision do we need to measure the momentum of the p and k? will need a magnet will need to measure trajectory in magnetic field c) Do we need to use a calorimeter to measure energy? d) ...
... a) How are we going to identify the p, kaon and proton? what momentum range do we have to worry about? b) To what precision do we need to measure the momentum of the p and k? will need a magnet will need to measure trajectory in magnetic field c) Do we need to use a calorimeter to measure energy? d) ...
Nuclear Physics and Astrophysics
... Coulomb barrier in D-T is same as that of D-D reactions Neglecting initial kinetic energies final neutron emerges with 14.1 MeV Source of fast neutrons This reaction chosen for fusion reactors - large energy release But: difficult to extract energy from neutron Fission: neutrons carry smal ...
... Coulomb barrier in D-T is same as that of D-D reactions Neglecting initial kinetic energies final neutron emerges with 14.1 MeV Source of fast neutrons This reaction chosen for fusion reactors - large energy release But: difficult to extract energy from neutron Fission: neutrons carry smal ...
Calculation of the nucleon axial charge in lattice QCD
... Quantum Chromodynamics is the theory of the Strong Force of nature. The theory dictates how quarks, the fundamental components of ordinary matter, interact by exchanging particles known as gluons. The interactions between quarks and gluons are sufficiently strong to bind them into bound states such ...
... Quantum Chromodynamics is the theory of the Strong Force of nature. The theory dictates how quarks, the fundamental components of ordinary matter, interact by exchanging particles known as gluons. The interactions between quarks and gluons are sufficiently strong to bind them into bound states such ...
Document
... QGP is made which expands into a mixed phase of QGPand hadrons Mystery: The QGP is very strongly interacting: Arnold and Moore suggest heating may be due to instabilities in melting CGC ...
... QGP is made which expands into a mixed phase of QGPand hadrons Mystery: The QGP is very strongly interacting: Arnold and Moore suggest heating may be due to instabilities in melting CGC ...
15.06.18_CAP-Edmonton-CWL
... (iii) fully relativistic – obeying the weak principle of equivalence, no violation of causal structure, well-defined metric. (iv) gravity/spacetime is treated as a quantum field as well as matter ...
... (iii) fully relativistic – obeying the weak principle of equivalence, no violation of causal structure, well-defined metric. (iv) gravity/spacetime is treated as a quantum field as well as matter ...
Glossary: Unit I
... analog: a description of a continuously variable signal or a circuit; an analog signal can be represented as a series of waves. angle of incidence: the angle a ray of light makes with the normal to the surface at the point of incidence. angle of reflection: the angle a reflected ray makes with the n ...
... analog: a description of a continuously variable signal or a circuit; an analog signal can be represented as a series of waves. angle of incidence: the angle a ray of light makes with the normal to the surface at the point of incidence. angle of reflection: the angle a reflected ray makes with the n ...
Atoms and Elements - Oakland Community College
... different numbers of protons, neutrons and electrons The protons and neutrons cluster together in a dense, central core area called the nucleus The protons and neutrons constitute nearly all the atom’s mass The electrons move continuously and rapidly around the nucleus ...
... different numbers of protons, neutrons and electrons The protons and neutrons cluster together in a dense, central core area called the nucleus The protons and neutrons constitute nearly all the atom’s mass The electrons move continuously and rapidly around the nucleus ...
The History of the Atom
... around the nucleus with no loss of energy from their motion. He applied Planck’s idea of small packets or quanta of energy to his electron model. •Electrons in energy levels further from the nucleus have greater energy. •An electron can give off a photon of energy equivalent to the difference in ene ...
... around the nucleus with no loss of energy from their motion. He applied Planck’s idea of small packets or quanta of energy to his electron model. •Electrons in energy levels further from the nucleus have greater energy. •An electron can give off a photon of energy equivalent to the difference in ene ...
Higgs-part
... W and Z bosons (V) pick up mass from interaction with new scalar field Modifies V propagator from massless to effectively massive ...
... W and Z bosons (V) pick up mass from interaction with new scalar field Modifies V propagator from massless to effectively massive ...
Solutions
... 16. To probe the unknown charge of a nucleus, an alpha-particle of charge q = +2e, where e is the fundamental charge, and mass, m,, is launched directly toward it from far away with speed, v . The alpha-particle reaches a point of closest approach before turning around. Assume the unknown nucleus r ...
... 16. To probe the unknown charge of a nucleus, an alpha-particle of charge q = +2e, where e is the fundamental charge, and mass, m,, is launched directly toward it from far away with speed, v . The alpha-particle reaches a point of closest approach before turning around. Assume the unknown nucleus r ...
Electron Degeneracy Pressure
... What does it mean? The smaller mass particle will have the highest uncertainty in the speed, and therefore the higher uncertainty in kinetic energy. The smallest mass particles in the core will be electrons, and as they are confined to a smaller and smaller core, they will move faster and faster, th ...
... What does it mean? The smaller mass particle will have the highest uncertainty in the speed, and therefore the higher uncertainty in kinetic energy. The smallest mass particles in the core will be electrons, and as they are confined to a smaller and smaller core, they will move faster and faster, th ...
Fall.2008.Week5.Lesson.1 - reich
... • If two atoms of the same element have different numbers of neutrons they are called Isotopes. ...
... • If two atoms of the same element have different numbers of neutrons they are called Isotopes. ...
Institute of Physics and Nuclear Engineering "Horia Hulubei"
... The mechanism for energy transport in proteins has been an active area of research for over 30 years, but still is not yet elucidated. Many years ago, an attractive model was proposed by Davydov. In this model the amide I oscillations act as baskets for the storage of biological energy released in t ...
... The mechanism for energy transport in proteins has been an active area of research for over 30 years, but still is not yet elucidated. Many years ago, an attractive model was proposed by Davydov. In this model the amide I oscillations act as baskets for the storage of biological energy released in t ...
Document
... Quark model & flux tube model are incomplete and should be revisited. Also we have to think what questions we have to ask lattice QCD. Does Q start a new Regge trajectory? -> implications for high energy scattering of hadrons ! What about duality? Can Q become stable in nuclear matter? -> phys ...
... Quark model & flux tube model are incomplete and should be revisited. Also we have to think what questions we have to ask lattice QCD. Does Q start a new Regge trajectory? -> implications for high energy scattering of hadrons ! What about duality? Can Q become stable in nuclear matter? -> phys ...
... side, be it vapor, a second solid crystal, or some other foreign substrate. As the solid-substrate separation decreases, long-ranged intermolecular forces come into play and contribute towards the total free energy of the system. At bulk coexistence, if the free energy is minimized by the insertion ...
Student Seminar Subatomic Physics, blok 1+2 2002/03
... Chapter 2: Approaches to nuclear structure The atomic nucleus is a system of a large number of strongly interacting particles. Three is in this case already a large number. Due to the strong interaction, which makes perturbative approaches less suitable and due to the number of particles it is stil ...
... Chapter 2: Approaches to nuclear structure The atomic nucleus is a system of a large number of strongly interacting particles. Three is in this case already a large number. Due to the strong interaction, which makes perturbative approaches less suitable and due to the number of particles it is stil ...
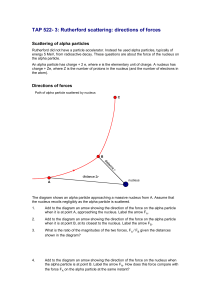
TAP 522- 3: Rutherford scattering: directions of forces
... hill. Imagine that you are riding on the alpha particle as it goes by the nucleus. Are you riding uphill, downhill or momentarily along a contour of the hill: ...
... hill. Imagine that you are riding on the alpha particle as it goes by the nucleus. Are you riding uphill, downhill or momentarily along a contour of the hill: ...