I can
... The products of a chemical reaction must have somehow existed from the start in another location. All acids are harmful; all bases are safe. Solutions are always liquid. Solids and gases cannot be solutions. FCAT Clarification SC.8.P.8.5-9: Students will explain that atoms are the smallest ...
... The products of a chemical reaction must have somehow existed from the start in another location. All acids are harmful; all bases are safe. Solutions are always liquid. Solids and gases cannot be solutions. FCAT Clarification SC.8.P.8.5-9: Students will explain that atoms are the smallest ...
PHY202 - National Open University of Nigeria
... the phenomenon of radioactivity. We would discuss radioactive decay series and the various processes by which nuclei decay. The understanding of the Bohr’s model of the hydrogen atom in modern physics, particularly in quantum mechanics is the simplest atomic system and is important for several reaso ...
... the phenomenon of radioactivity. We would discuss radioactive decay series and the various processes by which nuclei decay. The understanding of the Bohr’s model of the hydrogen atom in modern physics, particularly in quantum mechanics is the simplest atomic system and is important for several reaso ...
Observation of the Higgs Boson - Purdue Physics
... • Add another set of fields that they interact with which gives the same effect as mass: – A massless particle travels at the speed of light – Massless particles that “stick” to the Higgs field are slowed down – Photons and gluons don’t couple to the Higgs field so they remain massless. ...
... • Add another set of fields that they interact with which gives the same effect as mass: – A massless particle travels at the speed of light – Massless particles that “stick” to the Higgs field are slowed down – Photons and gluons don’t couple to the Higgs field so they remain massless. ...
Document
... How to express the magnitude and vector properties of the field strength? The field strength at any point could be represented by an arrow drawn to scale. However, when several charges are present, the use of arrows of varying length and orientations becomes confusing. Instead we represent the elect ...
... How to express the magnitude and vector properties of the field strength? The field strength at any point could be represented by an arrow drawn to scale. However, when several charges are present, the use of arrows of varying length and orientations becomes confusing. Instead we represent the elect ...
Chapter 5
... The choice is arbitrary since the change in the potential energy is the important quantity Choose a convenient location for the zero reference height ...
... The choice is arbitrary since the change in the potential energy is the important quantity Choose a convenient location for the zero reference height ...
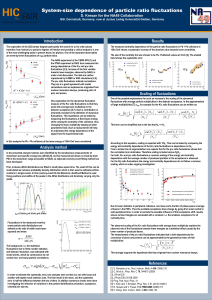
91.5x122 cm Poster Template
... The exploration of the QCD phase diagram particularly the search for a (1st order) phase transition from hadronic to partonic degrees of freedom and possibly a critical endpoint, is one of the most challenging tasks in present heavy ion physics. One of the important observables are event-by-event fl ...
... The exploration of the QCD phase diagram particularly the search for a (1st order) phase transition from hadronic to partonic degrees of freedom and possibly a critical endpoint, is one of the most challenging tasks in present heavy ion physics. One of the important observables are event-by-event fl ...
Quantum Field Theory
... In the case of the hydrogen atom the effect of taking into account the lowest order quantum field theory correction is a splitting in the degenerate doublets of the solution to the Dirac equation: states with different orbital angular momentum coupling to the same value of j. At the second level the ...
... In the case of the hydrogen atom the effect of taking into account the lowest order quantum field theory correction is a splitting in the degenerate doublets of the solution to the Dirac equation: states with different orbital angular momentum coupling to the same value of j. At the second level the ...
Electrostatic potential
... while the electric potential is derived using the electrical energy between the charges, however I do not understand what you mean when you say that electric field is the ?gradient? of the electric potential. Since V is the change in potential energy, would another way to calculate it be V = delta P ...
... while the electric potential is derived using the electrical energy between the charges, however I do not understand what you mean when you say that electric field is the ?gradient? of the electric potential. Since V is the change in potential energy, would another way to calculate it be V = delta P ...
Matter and Atoms
... Two kinds of particles make up the nucleus— protons and neutrons. A proton is a positively charged particle in the nucleus of an atom. A neutron is an uncharged particle in the nucleus of an atom. An electron is a negatively charged particle that occupies the space in an atom outside the nucleus. ...
... Two kinds of particles make up the nucleus— protons and neutrons. A proton is a positively charged particle in the nucleus of an atom. A neutron is an uncharged particle in the nucleus of an atom. An electron is a negatively charged particle that occupies the space in an atom outside the nucleus. ...
From Superconductors to Supercolliders
... the analogy between a superconductor and the Higgs mechanism. We imagine that there is a Bose condensate permeating all of space, the occupied quantum state of some boson that carries a charge under the weak interactions, just as the Cooper pairs carry an electric charge (2e). A quark or lepton carr ...
... the analogy between a superconductor and the Higgs mechanism. We imagine that there is a Bose condensate permeating all of space, the occupied quantum state of some boson that carries a charge under the weak interactions, just as the Cooper pairs carry an electric charge (2e). A quark or lepton carr ...
... very close. This behavior is kept for structures W2 and W3 considered below. The optical absorption results for the W2-DQW are shown in Fig. 2. Comparing with Fig. 1 it is seen that the absorption edge is also a function of the DQW dimensions since this leads to different values for the maximum bind ...
Hydrogen balloon - Oxford Physics
... The demonstration This demonstration involves high voltages, and so it should never be done by anyone with a pacemaker or other internal electrical device, or who thinks they might be pregnant. The first part of this demo requires a volunteer from the audience. It works best on someone with long, li ...
... The demonstration This demonstration involves high voltages, and so it should never be done by anyone with a pacemaker or other internal electrical device, or who thinks they might be pregnant. The first part of this demo requires a volunteer from the audience. It works best on someone with long, li ...
F33OT2 Symmetry and Action and Principles in Physics Contents
... The idea of the least-action principle, which you studied in F33OT1 in the context of Classical Mechanics, originates with Fermat in the 1660s. Fermat’s principle states that the path followed by a ray of light between two points is the one that takes the least time. This variational principle allow ...
... The idea of the least-action principle, which you studied in F33OT1 in the context of Classical Mechanics, originates with Fermat in the 1660s. Fermat’s principle states that the path followed by a ray of light between two points is the one that takes the least time. This variational principle allow ...
Charge radii of medium-mass nuclei using the atomic physics
... 2nd order field shifts Due to 2nd-order contributions and from relativistic effects ...
... 2nd order field shifts Due to 2nd-order contributions and from relativistic effects ...
Exploring the fundamental properties of matter with
... “… The vast majority of the nucleon’s mass is due to quantum fluctuations of quark-antiquark pairs, the gluons, and the energy associated with quarks moving around at close to the speed of light. …” ...
... “… The vast majority of the nucleon’s mass is due to quantum fluctuations of quark-antiquark pairs, the gluons, and the energy associated with quarks moving around at close to the speed of light. …” ...