- Philsci
... level approximate—for that energy level and lower—arbitrarily well another quantum field theory at a higher energy scale. If one theory posits a particle of mass m, the other theory may, at energies below the scale set by this mass, calculate accurate physical quantities assuming that this particle ...
... level approximate—for that energy level and lower—arbitrarily well another quantum field theory at a higher energy scale. If one theory posits a particle of mass m, the other theory may, at energies below the scale set by this mass, calculate accurate physical quantities assuming that this particle ...
Teacher guide Teacher guide: Particle Physics
... all thought to be caused through exchange of particles, referred to as carriers or exchange particles. For example, two electrons interact with each other through the exchange of one or more virtual photons. In the photoelectric effect, an emitted electron absorbs a photon and acquires its energy; i ...
... all thought to be caused through exchange of particles, referred to as carriers or exchange particles. For example, two electrons interact with each other through the exchange of one or more virtual photons. In the photoelectric effect, an emitted electron absorbs a photon and acquires its energy; i ...
Diapositive 1
... […] one can generalize a gauge variant nonlocal operator […] to more than one gauge invariant expressions, raising the problem of deciding which is the “true” one. [Bashinsky, Jaffe (1998)] ...
... […] one can generalize a gauge variant nonlocal operator […] to more than one gauge invariant expressions, raising the problem of deciding which is the “true” one. [Bashinsky, Jaffe (1998)] ...
Analysis of the Large Gamma Ray Flares of Mkn 421
... Every second about 1000 high energy cosmic particles (integrates flux above 10 GeV) per square meter hit the Earth’s atmosphere. Up to an energy of approximately 1 PeV the chemical composition has been measured directly (for an overview see [LON97/1]). Most of them are ionized nuclei. Approximately ...
... Every second about 1000 high energy cosmic particles (integrates flux above 10 GeV) per square meter hit the Earth’s atmosphere. Up to an energy of approximately 1 PeV the chemical composition has been measured directly (for an overview see [LON97/1]). Most of them are ionized nuclei. Approximately ...
Interactions of Particles in Matter
... of the energy loss with the residual energy as the ‘Bragg curve’. However, all the particles with a given kinetic energy do not have exactly the same range. This is due to the statistical nature of the energy loss process. There are fluctuations on the range called range straggling. ...
... of the energy loss with the residual energy as the ‘Bragg curve’. However, all the particles with a given kinetic energy do not have exactly the same range. This is due to the statistical nature of the energy loss process. There are fluctuations on the range called range straggling. ...
( ) New Faculty Bruce Knuteson
... Experiments performed over the past two decades confirm the Standard Model of particle physics as the correct theory of fundamental interactions down to a distance scale of 10 −18 meters. Despite this remarkable success, inadequacies inherent in the theory suggest that a qualitatively new descriptio ...
... Experiments performed over the past two decades confirm the Standard Model of particle physics as the correct theory of fundamental interactions down to a distance scale of 10 −18 meters. Despite this remarkable success, inadequacies inherent in the theory suggest that a qualitatively new descriptio ...
The Physics of Energy sources Nuclear Fusion
... ! Initially we give some energy in order to initiate fusion ! Then we need to create enough energy for the fusion to be self-sustained • We also have to take into account the energy losses • The main one is through Bremsstrahlung radiation – Emitted when charged particles interact with each o ...
... ! Initially we give some energy in order to initiate fusion ! Then we need to create enough energy for the fusion to be self-sustained • We also have to take into account the energy losses • The main one is through Bremsstrahlung radiation – Emitted when charged particles interact with each o ...
AP Physics – More Electric Fields - Ms. Gamm
... difference of 12 V, the other end will also have a potential of 12 V. We physics types say that all points in a conductor are at an equipotential. When conductors are joined together, the charge ends up being evenly distributing throughout the newly formed conductive system. The new conductor system ...
... difference of 12 V, the other end will also have a potential of 12 V. We physics types say that all points in a conductor are at an equipotential. When conductors are joined together, the charge ends up being evenly distributing throughout the newly formed conductive system. The new conductor system ...
Particles and Fields
... consisting of gold atoms; see fig. 5. In this experiment a source of α particles R is placed in a vacuum chamber with a target consisting of a gold foil F . The scattered α particles are observed by their impact on a ZnS scintillation screen S in front of the microscope M . During the experiment th ...
... consisting of gold atoms; see fig. 5. In this experiment a source of α particles R is placed in a vacuum chamber with a target consisting of a gold foil F . The scattered α particles are observed by their impact on a ZnS scintillation screen S in front of the microscope M . During the experiment th ...
The Nucleus - American School of Milan
... Following this break, the subjects were tested on their ability to recall the pair of images and on their confidence level regarding the accuracy of their recollections. Three months later, the participants were asked to take a surprise test similar to the one they have taken after the rest period. ...
... Following this break, the subjects were tested on their ability to recall the pair of images and on their confidence level regarding the accuracy of their recollections. Three months later, the participants were asked to take a surprise test similar to the one they have taken after the rest period. ...
The Origin of Mass - Massachusetts Institute of Technology
... we were able to predict the results of these experiments before theywere performed. As a historical matter, we discovered QCD and asymptotic freedom by trying to come to terms with the MIT-SLAC “scaling” experiments done at the Stanford Linear Collider in the late 1960s, for which Jerome Friedman, ...
... we were able to predict the results of these experiments before theywere performed. As a historical matter, we discovered QCD and asymptotic freedom by trying to come to terms with the MIT-SLAC “scaling” experiments done at the Stanford Linear Collider in the late 1960s, for which Jerome Friedman, ...
MC2521062109
... suggested such a particle in 1964. He was the only one to explicitly predict the massive particle (125– 127 GeV/c2) and identify some of its theoretical properties. In mainstream media it is often referred to as the "God particle", after the title of Leon Lederman's book on the topic. It is also ver ...
... suggested such a particle in 1964. He was the only one to explicitly predict the massive particle (125– 127 GeV/c2) and identify some of its theoretical properties. In mainstream media it is often referred to as the "God particle", after the title of Leon Lederman's book on the topic. It is also ver ...
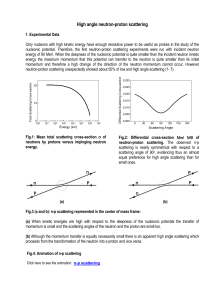
High angle neutron-proton scattering
... 3.c. Orbital Model Let us now make the phenomenological description of the proton-neutron inversion from the orbital standpoint. It provides a straightforward answer (expressed in form of an animation of the scattering process) based on the neutron shell which is easily interchanged between protons. ...
... 3.c. Orbital Model Let us now make the phenomenological description of the proton-neutron inversion from the orbital standpoint. It provides a straightforward answer (expressed in form of an animation of the scattering process) based on the neutron shell which is easily interchanged between protons. ...
Introducing many-body physics using atomic
... Using states that are based on HF orbitals leads to the interesting and useful side effect that V̂ ee does not couple the ground state |Φ0 i to singly excited configurations |Φai i. This is known as Brillouin’s theorem.11 It allows for a straightforward study of photoabsorption, as the atomic ground ...
... Using states that are based on HF orbitals leads to the interesting and useful side effect that V̂ ee does not couple the ground state |Φ0 i to singly excited configurations |Φai i. This is known as Brillouin’s theorem.11 It allows for a straightforward study of photoabsorption, as the atomic ground ...
Section 19.1 Radioactivity A. Radioactive Decay
... • Atomic Number (Z) – number of protons in the nucleus • Mass Number (A) – sum of the number of protons and neutrons • Isotopes – atoms with identical atomic numbers but different mass numbers • Nuclide – each unique atom ...
... • Atomic Number (Z) – number of protons in the nucleus • Mass Number (A) – sum of the number of protons and neutrons • Isotopes – atoms with identical atomic numbers but different mass numbers • Nuclide – each unique atom ...
The Maximal Invariance Group of Newton's Equations for a Free Point Particle
... Almost all introductory books on the special theory of relativity mention, at least in passing, that Newton’s equations of motion for a classical free nonrelativistic point particle are invariant under Galilei transformations. Probably not many eyebrows would be raised if we jumped from this fact to ...
... Almost all introductory books on the special theory of relativity mention, at least in passing, that Newton’s equations of motion for a classical free nonrelativistic point particle are invariant under Galilei transformations. Probably not many eyebrows would be raised if we jumped from this fact to ...