Chapter 19 - Electric Potential Energy and Electric Potential
... One electron volt is the magnitude of the amount by which the potential energy of an electron changes when the electron moves through a potential difference of one volt. W or Potential Energy (U) qV ...
... One electron volt is the magnitude of the amount by which the potential energy of an electron changes when the electron moves through a potential difference of one volt. W or Potential Energy (U) qV ...
Electric Potential Energy and Electric Potential
... In chapter 17, we defined and used the concept of electric field so we could easily analyze the force experienced by a charge of any magnitude or sign placed at a point. It is useful to develop an analogous concept for determining changes in potential energy of any charge. Similar to electric field ...
... In chapter 17, we defined and used the concept of electric field so we could easily analyze the force experienced by a charge of any magnitude or sign placed at a point. It is useful to develop an analogous concept for determining changes in potential energy of any charge. Similar to electric field ...
1/24/11 - Bibb County Schools
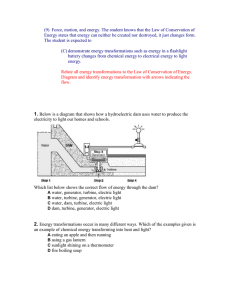
... c. Relate falling objects to gravitational force d. Explain the difference in mass and weight. e. Calculate amounts of work and mechanical advantage using simple machines. ...
... c. Relate falling objects to gravitational force d. Explain the difference in mass and weight. e. Calculate amounts of work and mechanical advantage using simple machines. ...
Scaling laws in the macro-, micro- and nanoworlds
... In recent years, interest in the domains of the microworld and the nanoworld has increased rapidly. The advent of so-called mesoscopic physics, the development of micromachines or micro-electrical mechanical systems (MEMS), the synthesis of nanotubes, the development of nanotechnology, etc… are amon ...
... In recent years, interest in the domains of the microworld and the nanoworld has increased rapidly. The advent of so-called mesoscopic physics, the development of micromachines or micro-electrical mechanical systems (MEMS), the synthesis of nanotubes, the development of nanotechnology, etc… are amon ...
17588_free-electron-theory
... Classical free electron theory of metals This theory was developed by Drude and Lorentz and hence is also known as DrudeLorentz theory. According to this theory, a metal consists of electrons which are free to move about in the crystal like molecules of a gas in a container. Mutual repulsion between ...
... Classical free electron theory of metals This theory was developed by Drude and Lorentz and hence is also known as DrudeLorentz theory. According to this theory, a metal consists of electrons which are free to move about in the crystal like molecules of a gas in a container. Mutual repulsion between ...
potential energy.
... At time ti, the kinetic energy of a particle is 30.0 J and the potential energy of the system to which it belongs is 10.0 J. At some later time tf, the kinetic energy of the particle is 18.0 J. (a) If only conservative forces act on the particle, what are the potential energy and the total energy at ...
... At time ti, the kinetic energy of a particle is 30.0 J and the potential energy of the system to which it belongs is 10.0 J. At some later time tf, the kinetic energy of the particle is 18.0 J. (a) If only conservative forces act on the particle, what are the potential energy and the total energy at ...
Energy
... impact, transforming KE to thermal energy when it is caught. • The player catching the ball absorbs the energy of the ball and this energy is turned to heat. • The total heat energy produced in the first baseman is equal to the energy used to throw the ball by the catcher. ...
... impact, transforming KE to thermal energy when it is caught. • The player catching the ball absorbs the energy of the ball and this energy is turned to heat. • The total heat energy produced in the first baseman is equal to the energy used to throw the ball by the catcher. ...
Milestones Master Study 2017
... Newton’s Third Law - whenever one object exerts a force on a second object, the second object exerts an equal and opposite force on the first (This law can simply be stated as follows: all forces act in pairs) Momentum - a quantity defined as the product of the mass and velocity of an object A. The ...
... Newton’s Third Law - whenever one object exerts a force on a second object, the second object exerts an equal and opposite force on the first (This law can simply be stated as follows: all forces act in pairs) Momentum - a quantity defined as the product of the mass and velocity of an object A. The ...
Meeting Next Generation Science Standards using STARLAB
... from point A to point be can be determined using: S W = F x d x cos Φ As the force is aligned with the A direction of travel, cosine Φ equals 1. Inserting values: ...
... from point A to point be can be determined using: S W = F x d x cos Φ As the force is aligned with the A direction of travel, cosine Φ equals 1. Inserting values: ...
Electric Potential Energy
... increases the potential energy of the object by the same amount. One does “ten floors” worth of work and increased the potential energy “ten floors” worth. An even more general description looks at ∆PE per kilogram. That way the object’s mass is irrelevant. This would be like considering changes in ...
... increases the potential energy of the object by the same amount. One does “ten floors” worth of work and increased the potential energy “ten floors” worth. An even more general description looks at ∆PE per kilogram. That way the object’s mass is irrelevant. This would be like considering changes in ...
Bandgap, chemical potential, nondegenerate approximation
... (The figure below shows two possible particular configurations corresponding to the case N=3). N Since many configurations are possible (Fig.9 shows two of them), let’s call E the energy associated to a given -configuration (or stationary state). ...
... (The figure below shows two possible particular configurations corresponding to the case N=3). N Since many configurations are possible (Fig.9 shows two of them), let’s call E the energy associated to a given -configuration (or stationary state). ...
Document
... If the work is done on a system and it is positive, energy is transferred to the system. If the work done on the system is negative, energy is transferred from the system. If a system interacts with its environment, this interaction can be described as a transfer of energy across the system boundary ...
... If the work is done on a system and it is positive, energy is transferred to the system. If the work done on the system is negative, energy is transferred from the system. If a system interacts with its environment, this interaction can be described as a transfer of energy across the system boundary ...
x - De Anza
... When work is done on a system and the only change in the system is in its speed, the net work done on the system equals the change in kinetic energy of the system. § The speed of the system increases if the work done on it is positive. § The speed of the system decreases if the net work is negative. ...
... When work is done on a system and the only change in the system is in its speed, the net work done on the system equals the change in kinetic energy of the system. § The speed of the system increases if the work done on it is positive. § The speed of the system decreases if the net work is negative. ...
Lesson 1: Forms of Energy and Energy Transformations
... energy a body possesses by virtue of its motion. A moving body of mass, m Kg and velocity v m/s possesses kinetic energy of magnitude mv2 joules. Thus, the magnitude of the kinetic energy of an object depends both the mass and the velocity of the object. Flowing water and winds have kinetic energy. ...
... energy a body possesses by virtue of its motion. A moving body of mass, m Kg and velocity v m/s possesses kinetic energy of magnitude mv2 joules. Thus, the magnitude of the kinetic energy of an object depends both the mass and the velocity of the object. Flowing water and winds have kinetic energy. ...
Dissipation effects in mechanics and thermodynamics
... that force — we even suggest to suppress the denomination “static” force if the body is reduced to its centre-of-mass. The right hand side of equation (13) is not work but it (artificially) “becomes” work if the extended body is reduced, from the outset, to a point-like object. There are several ide ...
... that force — we even suggest to suppress the denomination “static” force if the body is reduced to its centre-of-mass. The right hand side of equation (13) is not work but it (artificially) “becomes” work if the extended body is reduced, from the outset, to a point-like object. There are several ide ...
energy
... Chemical energy in food is converted to ……… 1. Mechanical energy when you are moving, 2. Heat as a result of the movement to maintain body temperature (homeostasis) ...
... Chemical energy in food is converted to ……… 1. Mechanical energy when you are moving, 2. Heat as a result of the movement to maintain body temperature (homeostasis) ...