Nervous System
... Na+ so that K+ diffuses out faster than Na+ diffuses in 3.Cell membrane is basically impermeable to large negatively charged anions present inside the neuron, therefore fewer negative particles move out than positive ...
... Na+ so that K+ diffuses out faster than Na+ diffuses in 3.Cell membrane is basically impermeable to large negatively charged anions present inside the neuron, therefore fewer negative particles move out than positive ...
phys chapter 45 [10-24
... transmitters open these Anion channels mostly size permissive (cations larger than anions, so they can’t fit); inhibitory transmitters open these When transmitter substance activates channel, it opens fast; when transmitter substance no longer present, channel closes fast Second messenger syst ...
... transmitters open these Anion channels mostly size permissive (cations larger than anions, so they can’t fit); inhibitory transmitters open these When transmitter substance activates channel, it opens fast; when transmitter substance no longer present, channel closes fast Second messenger syst ...
amy-2a-2016-cryders-rmp-and-generation-of-action
... resting at -70mV to 30mV and back to resting again. AP begins at the axon hillock, where voltage-gated Na+ channels are greatest. Signals from dendrites and the cell body cause the membrane potential to be more positive. This is known as depolarization. Depolarization opens Na+ channels allowing sod ...
... resting at -70mV to 30mV and back to resting again. AP begins at the axon hillock, where voltage-gated Na+ channels are greatest. Signals from dendrites and the cell body cause the membrane potential to be more positive. This is known as depolarization. Depolarization opens Na+ channels allowing sod ...
Nervous System Structure and Function Pt 1
... • As a result of active transport (K+ in, Na+ out) and diffusion (K+ out, Na+ in), a negative charge builds up on the inside of the membrane and a positive charge builds up on the outside of the membrane. • The difference in electrical charge across the cell membrane of a resting neuron is called is ...
... • As a result of active transport (K+ in, Na+ out) and diffusion (K+ out, Na+ in), a negative charge builds up on the inside of the membrane and a positive charge builds up on the outside of the membrane. • The difference in electrical charge across the cell membrane of a resting neuron is called is ...
Lessons 1
... It is a very simple system, and the axon has a large diameter (up to 1 mm), allowing to insert the electrodes into the axon ...
... It is a very simple system, and the axon has a large diameter (up to 1 mm), allowing to insert the electrodes into the axon ...
Action Potentials & Nerve Conduction
... Gated Channels Are Involved in Neuronal Signalling • In the nervous system, different channel types are responsible for transmitting electrical signals over long and short distances: •A) Graded potentials travel over short distances and are activated by the opening of mechanically or chemically gat ...
... Gated Channels Are Involved in Neuronal Signalling • In the nervous system, different channel types are responsible for transmitting electrical signals over long and short distances: •A) Graded potentials travel over short distances and are activated by the opening of mechanically or chemically gat ...
突觸與神經訊號傳遞 - 國立交通大學開放式課程
... (a) Graded hyperpolarizations produced by two stimuli that increase membrane permeability to K ...
... (a) Graded hyperpolarizations produced by two stimuli that increase membrane permeability to K ...
Slide 1
... and go into solution as magnesium ions. The electrons will be left behind on the magnesium In a very short time, there will be a build-up of electrons on the magnesium, and it will be surrounded in the solution by a layer of positive ions (Helmholtz double layer). This produces a potential defferenc ...
... and go into solution as magnesium ions. The electrons will be left behind on the magnesium In a very short time, there will be a build-up of electrons on the magnesium, and it will be surrounded in the solution by a layer of positive ions (Helmholtz double layer). This produces a potential defferenc ...
THE PHYSICAL BASIS FUNCTION OF NEURONAL
... them without decrement as the result of the movement of charged particles (ions). The properties of electrical signals allow neurons to carry information rapidly and accurately to coordinate actions involving many parts, or even all, of an animal's body. All of the neurons in an organism's body, alo ...
... them without decrement as the result of the movement of charged particles (ions). The properties of electrical signals allow neurons to carry information rapidly and accurately to coordinate actions involving many parts, or even all, of an animal's body. All of the neurons in an organism's body, alo ...
Issue 22_Pump Up the Volume
... tectorial membrane above. This causes the stereocilia to bend to one side, a bit like a sea current brushing the tentacles of a sea anemone in the direction of the current. The brushing movement opens pores in the stereocilia letting potassium ions seep in, which create an electric current. There i ...
... tectorial membrane above. This causes the stereocilia to bend to one side, a bit like a sea current brushing the tentacles of a sea anemone in the direction of the current. The brushing movement opens pores in the stereocilia letting potassium ions seep in, which create an electric current. There i ...
Chapter Two Line Title Here and Chapter Title Here and Here
... VI. Basic Concepts of Neural Integration (pp. 421–423; Figs. 11.22–11.24) A. Organization of Neurons: Neuronal Pools (p. 421; Fig. 11.22) 1. Neuronal pools are functional groups of neurons that integrate incoming information from receptors or other neuronal pools and relay the information to other a ...
... VI. Basic Concepts of Neural Integration (pp. 421–423; Figs. 11.22–11.24) A. Organization of Neurons: Neuronal Pools (p. 421; Fig. 11.22) 1. Neuronal pools are functional groups of neurons that integrate incoming information from receptors or other neuronal pools and relay the information to other a ...
Chapter Two Line Title Here and Chapter Title Here and Here
... VI. Basic Concepts of Neural Integration (pp. 421–423; Figs. 11.22–11.24) A. Organization of Neurons: Neuronal Pools (p. 421; Fig. 11.22) 1. Neuronal pools are functional groups of neurons that integrate incoming information from receptors or other neuronal pools and relay the information to other a ...
... VI. Basic Concepts of Neural Integration (pp. 421–423; Figs. 11.22–11.24) A. Organization of Neurons: Neuronal Pools (p. 421; Fig. 11.22) 1. Neuronal pools are functional groups of neurons that integrate incoming information from receptors or other neuronal pools and relay the information to other a ...
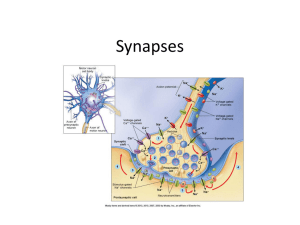
4. Nervous System: Synapses
... – Neurotransmitters: chemicals that move from one cell to the next to carry the signal across a space to the next cell • Examples: acetylcholine serotonin norepinephrine histamine dopamine ...
... – Neurotransmitters: chemicals that move from one cell to the next to carry the signal across a space to the next cell • Examples: acetylcholine serotonin norepinephrine histamine dopamine ...
Student Guide Chapter 11
... b. Bipolar neurons have a single axon and dendrite. c. Unipolar neurons have a single process extending from the cell body that is associated with receptors at the distal end. 5. There are three functional classes of neurons. a. Sensory, or afferent, neurons conduct impulses toward the CNS from rece ...
... b. Bipolar neurons have a single axon and dendrite. c. Unipolar neurons have a single process extending from the cell body that is associated with receptors at the distal end. 5. There are three functional classes of neurons. a. Sensory, or afferent, neurons conduct impulses toward the CNS from rece ...
Neuroglia - wsscience
... “Medications for Parkinson's fall into three groups. The first group includes drugs that increase the level of dopamine in the brain. The second group affects other neurotransmitters in the body in order to ease some of the symptoms of the disease. The third group includes medications that help cont ...
... “Medications for Parkinson's fall into three groups. The first group includes drugs that increase the level of dopamine in the brain. The second group affects other neurotransmitters in the body in order to ease some of the symptoms of the disease. The third group includes medications that help cont ...
Name________________________ Midterm #1 Biology 3330, Fall
... This must involve a malfunction in a rate-limiting step of the epinephrine synthesis!” So he looked at the epinephrine synthesis pathway. ...
... This must involve a malfunction in a rate-limiting step of the epinephrine synthesis!” So he looked at the epinephrine synthesis pathway. ...
General Physiology
... organs are different types of tissues that work together to perform a particular function • Organ systems are the next level of organization An organ system is a group of organs that work together to perform a major function There are 11 organ systems in the human body. These are: ...
... organs are different types of tissues that work together to perform a particular function • Organ systems are the next level of organization An organ system is a group of organs that work together to perform a major function There are 11 organ systems in the human body. These are: ...
Physio lecture 9 Membrane and Action Potentials
... K+ would diffuse down its concentration gradient until the electrical potential across the membrane countered diffusion. As K leaves the cell, it takes a positive charge outside with it, so the inside is more negative. However, as the inside of the cell is becoming more negative, the outside of the ...
... K+ would diffuse down its concentration gradient until the electrical potential across the membrane countered diffusion. As K leaves the cell, it takes a positive charge outside with it, so the inside is more negative. However, as the inside of the cell is becoming more negative, the outside of the ...
Shier, Butler, and Lewis: Hole`s Human Anatomy and Physiology
... 1. The trigger zone of an axon is the first part or initial segment of an axon. 2. The trigger zone contains many voltage-gated sodium channels. 3. At the resting membrane potential, sodium channels are closed but when threshold is reached, sodium channels open. 4. As sodium ions rush into the cell, ...
... 1. The trigger zone of an axon is the first part or initial segment of an axon. 2. The trigger zone contains many voltage-gated sodium channels. 3. At the resting membrane potential, sodium channels are closed but when threshold is reached, sodium channels open. 4. As sodium ions rush into the cell, ...
(一)Functional Anatomy of the Retina
... The membrane of the receptor region is, however, electrically inexcitable; it contains no voltage-gated ionic channels and does not generate spikes. If the receptor region generated action potentials, the graded nature of the generator potential would be destroyed because as soon as the generator p ...
... The membrane of the receptor region is, however, electrically inexcitable; it contains no voltage-gated ionic channels and does not generate spikes. If the receptor region generated action potentials, the graded nature of the generator potential would be destroyed because as soon as the generator p ...
6419982_1441921514
... between the inside and outside of cells, each cell acts as a tiny battery with the positive pole outside the plasma membrane and the negative pole inside. The magnitude of this charge difference is measured in voltage. Although the voltage of this battery is very small (less than a tenth of a volt), ...
... between the inside and outside of cells, each cell acts as a tiny battery with the positive pole outside the plasma membrane and the negative pole inside. The magnitude of this charge difference is measured in voltage. Although the voltage of this battery is very small (less than a tenth of a volt), ...
Patch clamp

The patch clamp technique is a laboratory technique in electrophysiology that allows the study of single or multiple ion channels in cells. The technique can be applied to a wide variety of cells, but is especially useful in the study of excitable cells such as neurons, cardiomyocytes, muscle fibers, and pancreatic beta cells. It can also be applied to the study of bacterial ion channels in specially prepared giant spheroplasts.The patch clamp technique is a refinement of the voltage clamp. Erwin Neher and Bert Sakmann developed the patch clamp in the late 1970s and early 1980s. This discovery made it possible to record the currents of single ion channel molecules for the first time, which improved understanding of the involvement of channels in fundamental cell processes such as action potentials and nerve activity. Neher and Sakmann received the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1991 for this work.