The Action Potential, Synaptic Transmission, and Maintenance of
... efflux of K⫹ when the neuron is in its resting state. Ligandgated ion channels are directly or indirectly activated by chemical neurotransmitters binding to membrane receptors. In this type of channel, the receptor itself forms part of the ion channel or may be coupled to the channel via a G protein ...
... efflux of K⫹ when the neuron is in its resting state. Ligandgated ion channels are directly or indirectly activated by chemical neurotransmitters binding to membrane receptors. In this type of channel, the receptor itself forms part of the ion channel or may be coupled to the channel via a G protein ...
The Nervous System - 1
... • So…. How does all of this action potential stuff allow for communication between excitable tissues? – It allows for the release of neurotransmitters from the terminal button (synaptic bulb) • No action potential, no release, no communication ...
... • So…. How does all of this action potential stuff allow for communication between excitable tissues? – It allows for the release of neurotransmitters from the terminal button (synaptic bulb) • No action potential, no release, no communication ...
Neurons in Action: Passive Axon Tutorial
... Do the results match your prediction of how membrane capacitance should affect the axon length constant? What “constant” is affected by the membrane capacitance? ...
... Do the results match your prediction of how membrane capacitance should affect the axon length constant? What “constant” is affected by the membrane capacitance? ...
23 Comp Review 1
... • What is a sodium channel? Proteins embedded in the cell membranes form channels which only allow certain ions to cross the cell membrane. • A sodium ion can only get into the cell by way of a sodium channel. A potassium ion can only get in by way of a potassium channel, etc. • Charged ions, such ...
... • What is a sodium channel? Proteins embedded in the cell membranes form channels which only allow certain ions to cross the cell membrane. • A sodium ion can only get into the cell by way of a sodium channel. A potassium ion can only get in by way of a potassium channel, etc. • Charged ions, such ...
No Slide Title
... – regeneration tube guides the growing sprout back to the original target cells and reestablishes synaptic contact ...
... – regeneration tube guides the growing sprout back to the original target cells and reestablishes synaptic contact ...
Supplement to: Modulation of Intracortical Synaptic Potentials by
... the whole cell pipette were 0.2 mM EGTA for axonal recordings and either 1 or 10 mM EGTA or 0.025 mM BAPTA for recording from synaptically connected pairs of pyramidal cells, as stated in the main text. Alexa Fluo 488 (100 µM; for axonal recording experiments only) and biocytin (0.2%) were added to ...
... the whole cell pipette were 0.2 mM EGTA for axonal recordings and either 1 or 10 mM EGTA or 0.025 mM BAPTA for recording from synaptically connected pairs of pyramidal cells, as stated in the main text. Alexa Fluo 488 (100 µM; for axonal recording experiments only) and biocytin (0.2%) were added to ...
Supplement: Modulation of Intracortical Synaptic Potentials by
... the whole cell pipette were 0.2 mM EGTA for axonal recordings and either 1 or 10 mM EGTA or 0.025 mM BAPTA for recording from synaptically connected pairs of pyramidal cells, as stated in the main text. Alexa Fluo 488 (100 M; for axonal recording experiments only) and biocytin (0.2%) were added to ...
... the whole cell pipette were 0.2 mM EGTA for axonal recordings and either 1 or 10 mM EGTA or 0.025 mM BAPTA for recording from synaptically connected pairs of pyramidal cells, as stated in the main text. Alexa Fluo 488 (100 M; for axonal recording experiments only) and biocytin (0.2%) were added to ...
Voltage-Gated Ion Channels and the Propagation of Action
... proteins work together to absorb nutrients across the intestinal epithelium and to acidify the stomach. The nervous system, however, provides the most striking example of the interplay of various ion channels, transporters, and ion pumps in carrying out physiological functions. Neurons (nerve cells) ...
... proteins work together to absorb nutrients across the intestinal epithelium and to acidify the stomach. The nervous system, however, provides the most striking example of the interplay of various ion channels, transporters, and ion pumps in carrying out physiological functions. Neurons (nerve cells) ...
Ch48(2) - ISpatula
... 32) Assume that excessive consumption of ethanol increases the influx of negative chloride ions into ʺcommon senseʺ neurons whose action potentials are needed for you to act appropriately and not harm yourself or others. Thus, any resulting poor decisions associated with ethanol ingestion are likely ...
... 32) Assume that excessive consumption of ethanol increases the influx of negative chloride ions into ʺcommon senseʺ neurons whose action potentials are needed for you to act appropriately and not harm yourself or others. Thus, any resulting poor decisions associated with ethanol ingestion are likely ...
Learn about synapses
... For another explanation of the synapse, the Society for Neuroscience has written a short summary called How do nerve cells communicate? Play the Lost Synapse Game from the Nobel e-Museum. Happy 106th Birthday to the word "SYNAPSE". In 2003, the word "synapse" turned 106 years old. The word synapse w ...
... For another explanation of the synapse, the Society for Neuroscience has written a short summary called How do nerve cells communicate? Play the Lost Synapse Game from the Nobel e-Museum. Happy 106th Birthday to the word "SYNAPSE". In 2003, the word "synapse" turned 106 years old. The word synapse w ...
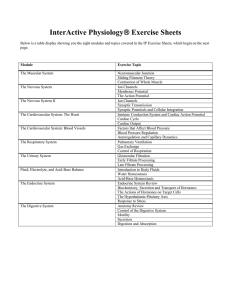
MS Word Version - Interactive Physiology
... a. If the membrane reaches the trigger point, known as __________________, what electrical potential will be generated? __________________________________________ b. During the depolarization phase, voltage-gated __________ channels open and _______ enters the cell. ...
... a. If the membrane reaches the trigger point, known as __________________, what electrical potential will be generated? __________________________________________ b. During the depolarization phase, voltage-gated __________ channels open and _______ enters the cell. ...
File
... ions across the neuron membrane. • The action potential is an explosion of electrical activity that is created by a depolarizing current ...
... ions across the neuron membrane. • The action potential is an explosion of electrical activity that is created by a depolarizing current ...
File
... Graded potentials are local changes in membrane potential that occur in varying grades or degrees of magnitude or strength. For example, membrane potential could change from -70 mV to -60 mV (a 10mV graded potential). The stronger a triggering event, the larger the resultant graded potential: 1. The ...
... Graded potentials are local changes in membrane potential that occur in varying grades or degrees of magnitude or strength. For example, membrane potential could change from -70 mV to -60 mV (a 10mV graded potential). The stronger a triggering event, the larger the resultant graded potential: 1. The ...
25. Organ of balance and hearing
... Dynamic equilibrium: needed to maintain balance when the head or body is rotated or suddenly moved; able to detect changes in direction and rate at which movement occurs (Figure 15-15) Depends on the functioning of the cristae ampullaris, located in the ampulla of each semicircular duct Cupula ...
... Dynamic equilibrium: needed to maintain balance when the head or body is rotated or suddenly moved; able to detect changes in direction and rate at which movement occurs (Figure 15-15) Depends on the functioning of the cristae ampullaris, located in the ampulla of each semicircular duct Cupula ...
Bioelectric Phenomena
... of a cell membrane at rest consisting of resistors, capacitors, and voltage sources is described in Section 12.5. Section 12.6 describes the Hodgkin-Huxley model of a neuron and includes a brief description of their experiments and the mathematical model describing an action potential. Finally, Sect ...
... of a cell membrane at rest consisting of resistors, capacitors, and voltage sources is described in Section 12.5. Section 12.6 describes the Hodgkin-Huxley model of a neuron and includes a brief description of their experiments and the mathematical model describing an action potential. Finally, Sect ...
CH 8 Nervous System - Belle Vernon Area School District
... Chuck was not seriously injured, but when he was revived, he could not remember how many balls and strikes the batter had. This was because A. sensory memory had not been converted to short-term memory. B. short-term memory had not been converted to sensory memory. C. he lost both sensory and short- ...
... Chuck was not seriously injured, but when he was revived, he could not remember how many balls and strikes the batter had. This was because A. sensory memory had not been converted to short-term memory. B. short-term memory had not been converted to sensory memory. C. he lost both sensory and short- ...
Lab #6: Neurophysiology Simulation
... negative, and the membrane potential moves back towards the resting potential. Once the membrane potential is repolarized below threshold, the voltage-gated K+ channels close. Although the resting potential has been restored, the concentration gradients for Na+ and K+ are now different from resting ...
... negative, and the membrane potential moves back towards the resting potential. Once the membrane potential is repolarized below threshold, the voltage-gated K+ channels close. Although the resting potential has been restored, the concentration gradients for Na+ and K+ are now different from resting ...
Chapter 8
... Figure 6-10 At the potassium equilibrium potential: buildup of positive charge in Compartment 1 produces an electrical potential that exactly offsets the K+ chemical concentration gradient. ...
... Figure 6-10 At the potassium equilibrium potential: buildup of positive charge in Compartment 1 produces an electrical potential that exactly offsets the K+ chemical concentration gradient. ...
34. Organ of balance and hearing
... Dynamic equilibrium: needed to maintain balance when the head or body is rotated or suddenly moved; able to detect changes in direction and rate at which movement occurs (Figure 15-15) Depends on the functioning of the cristae ampullaris, located in the ampulla of each semicircular duct Cupula ...
... Dynamic equilibrium: needed to maintain balance when the head or body is rotated or suddenly moved; able to detect changes in direction and rate at which movement occurs (Figure 15-15) Depends on the functioning of the cristae ampullaris, located in the ampulla of each semicircular duct Cupula ...
ION-SELECTIVE ELECTRODES - Clayton State University
... Types of indicator electrodes - Metallic electrodes (metal wire, mesh, or strip) - Metal coated with its sparingly soluble salt (Ag/AgCl) - Electrode whose equilibrium reaction responds to nalyte cation - Redox indicator electrode (measures redox reactions) ...
... Types of indicator electrodes - Metallic electrodes (metal wire, mesh, or strip) - Metal coated with its sparingly soluble salt (Ag/AgCl) - Electrode whose equilibrium reaction responds to nalyte cation - Redox indicator electrode (measures redox reactions) ...
Chapter 7 - Faculty Web Sites
... Step 4: Neurotransmitter molecules bind to receptors on the postsynaptic neuron. Step 5: Sodium ion channels open. Step 6: Sodium ions enter the Postsynaptic neuron, causing Depolarization and possible action potential. Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... Step 4: Neurotransmitter molecules bind to receptors on the postsynaptic neuron. Step 5: Sodium ion channels open. Step 6: Sodium ions enter the Postsynaptic neuron, causing Depolarization and possible action potential. Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
lab six: spike referencing
... the figure to the right, the spike is represented as a ‘+’ on a surface of all ‘-‘s within the nerve. As the recording electrode encounters the spike, the result is an upward slash on our voltage-measuring scope. Then, when the spike is in between both the recording electrode and the ground electrod ...
... the figure to the right, the spike is represented as a ‘+’ on a surface of all ‘-‘s within the nerve. As the recording electrode encounters the spike, the result is an upward slash on our voltage-measuring scope. Then, when the spike is in between both the recording electrode and the ground electrod ...
lab seven: spike referencing
... the figure to the right, the spike is represented as a ‘+’ on a surface of all ‘-‘s within the nerve. As the recording electrode encounters the spike, the result is an upward slash on our voltage-measuring scope. Then, when the spike is in between both the recording electrode and the ground electrod ...
... the figure to the right, the spike is represented as a ‘+’ on a surface of all ‘-‘s within the nerve. As the recording electrode encounters the spike, the result is an upward slash on our voltage-measuring scope. Then, when the spike is in between both the recording electrode and the ground electrod ...
Chap 9 Redox Review Q`s
... Which processes occur during the electrolysis of molten sodium chloride? I. Sodium and chloride ions move through the electrolyte. II. Electrons move through the external circuit. III. Oxidation takes place at the positive electrode (anode). ...
... Which processes occur during the electrolysis of molten sodium chloride? I. Sodium and chloride ions move through the electrolyte. II. Electrons move through the external circuit. III. Oxidation takes place at the positive electrode (anode). ...
Neurons Part 1
... An electrical current and Voltage changes are created across the membrane Copyright © 2004 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
... An electrical current and Voltage changes are created across the membrane Copyright © 2004 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
Patch clamp

The patch clamp technique is a laboratory technique in electrophysiology that allows the study of single or multiple ion channels in cells. The technique can be applied to a wide variety of cells, but is especially useful in the study of excitable cells such as neurons, cardiomyocytes, muscle fibers, and pancreatic beta cells. It can also be applied to the study of bacterial ion channels in specially prepared giant spheroplasts.The patch clamp technique is a refinement of the voltage clamp. Erwin Neher and Bert Sakmann developed the patch clamp in the late 1970s and early 1980s. This discovery made it possible to record the currents of single ion channel molecules for the first time, which improved understanding of the involvement of channels in fundamental cell processes such as action potentials and nerve activity. Neher and Sakmann received the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1991 for this work.