The Inheritance of Complex Traits
... Identical twins have 100% of their genes in common (correlation coefficient = 1.0) • When raised in separate environments identical twins provide an estimate of the degree of environmental influence on gene expression ...
... Identical twins have 100% of their genes in common (correlation coefficient = 1.0) • When raised in separate environments identical twins provide an estimate of the degree of environmental influence on gene expression ...
PSY 226 Nature_Nurture_Mahoney_revised_9_9_2015
... “The only adoption study that would avoid such [problems] would be one in which adoptees were randomly assigned to parents, with both groups blind to the treatment (i.e., not knowing whether they were adopted or not) – all while prenatal environment was held constant. In other words, it is an imposs ...
... “The only adoption study that would avoid such [problems] would be one in which adoptees were randomly assigned to parents, with both groups blind to the treatment (i.e., not knowing whether they were adopted or not) – all while prenatal environment was held constant. In other words, it is an imposs ...
The Principle Methods of Identifying Twins for Research
... that makes the difference. It is the environment shared by children (in) the same peer group. Judith Rich Harris, 1998 ...
... that makes the difference. It is the environment shared by children (in) the same peer group. Judith Rich Harris, 1998 ...
7.1 The Inheritance of Traits Offspring resemble their parents, but not
... § Each with more than one allele Interaction of multiple genes with multiple alleles results in many phenotypes. Example: human eye color Heritability: proportion of the variation within a population due to genetic differences among individuals ...
... § Each with more than one allele Interaction of multiple genes with multiple alleles results in many phenotypes. Example: human eye color Heritability: proportion of the variation within a population due to genetic differences among individuals ...
SR6e Chapter 3 - Flip Flop Ranch
... are traits passed from parents to offspring? What is an example of how a child could inherit a trait through each of the three mechanisms described in the text? ...
... are traits passed from parents to offspring? What is an example of how a child could inherit a trait through each of the three mechanisms described in the text? ...
SR6e Chapter 3
... – Degree of trait similarity Shared environmental influence – Living in the same home Non-shared environmental influences – Unique experiences ...
... – Degree of trait similarity Shared environmental influence – Living in the same home Non-shared environmental influences – Unique experiences ...
definition - Humble ISD
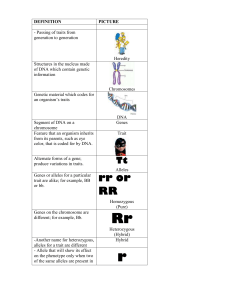
... -Another name for heterozygous, alleles for a trait are different - Allele that will show its effect on the phenotype only when two of the same alleles are present in ...
... -Another name for heterozygous, alleles for a trait are different - Allele that will show its effect on the phenotype only when two of the same alleles are present in ...
Behavior Genetics and Evolutionary Psychology
... similarities can be found between strangers. Researchers point out that differences between fraternal twins are greater than identical twins. ...
... similarities can be found between strangers. Researchers point out that differences between fraternal twins are greater than identical twins. ...
Chapter Four Part One - K-Dub
... has more older siblings and has older (wiser? more tired?) parents. ...
... has more older siblings and has older (wiser? more tired?) parents. ...
Chapter Four Part One - K-Dub
... has more older siblings and has older (wiser? more tired?) parents. ...
... has more older siblings and has older (wiser? more tired?) parents. ...
File
... Sources of human psychological differences: the Minnesota Study of Twins Reared Apart TJ Bouchard Jr, DT Lykken, M McGue, NL Segal, and A Tellegen Department of Psychology, University of Minnesota, Minneapolis 55455. Since 1979, a continuing study of monozygotic and dizygotic twins, separated in in ...
... Sources of human psychological differences: the Minnesota Study of Twins Reared Apart TJ Bouchard Jr, DT Lykken, M McGue, NL Segal, and A Tellegen Department of Psychology, University of Minnesota, Minneapolis 55455. Since 1979, a continuing study of monozygotic and dizygotic twins, separated in in ...
AP Psychology - Coshocton High School
... Besides the functioning of the endocrine and nervous system, genetics is another biological factor that affects human behavior and thought • Behavioral Genetics – Genetic and environmental contributions to personality and behavior • Human traits are usually caused by genes ...
... Besides the functioning of the endocrine and nervous system, genetics is another biological factor that affects human behavior and thought • Behavioral Genetics – Genetic and environmental contributions to personality and behavior • Human traits are usually caused by genes ...
Nature and Nurture
... produced by body…which may affect genes What is the difference between our genotype and our phenotype and what accounts for those differences??? Why identical twins are NOT identical in every way!!! Canalization: growth rates that are mostly genetically determined; When affected by environmental ...
... produced by body…which may affect genes What is the difference between our genotype and our phenotype and what accounts for those differences??? Why identical twins are NOT identical in every way!!! Canalization: growth rates that are mostly genetically determined; When affected by environmental ...
Heredity Important terms and concepts
... One of the problems in early studies was the assumption that effects of genetics and environment can be separated in an individual and studied. It cannot. Modern Behavioral genetics uses groups that differ in genetics and environments to estimate how much each of these determine behavior. • In the ...
... One of the problems in early studies was the assumption that effects of genetics and environment can be separated in an individual and studied. It cannot. Modern Behavioral genetics uses groups that differ in genetics and environments to estimate how much each of these determine behavior. • In the ...
9/06 Pedigrees and Human Genetics
... • 6.1 The Study of Genetics in Humans Is Constrained by Special Features of Human Biology and Culture, 135 • 6.2 Geneticists Often Use Pedigrees to Study the Inheritance of Characteristics in Humans, 136 • 6.3 Analysis of Pedigrees Requires Recognizing Patterns Associated with Different Modes of ...
... • 6.1 The Study of Genetics in Humans Is Constrained by Special Features of Human Biology and Culture, 135 • 6.2 Geneticists Often Use Pedigrees to Study the Inheritance of Characteristics in Humans, 136 • 6.3 Analysis of Pedigrees Requires Recognizing Patterns Associated with Different Modes of ...
Child Psychology, Second Canadian Edition
... – Explores the contribution of shared genes versus shared environment to a trait ...
... – Explores the contribution of shared genes versus shared environment to a trait ...
Quantitative Genetics Polygenic inheritance
... • F1 intermediate • F2 intermediate, normal distribution ...
... • F1 intermediate • F2 intermediate, normal distribution ...
Chapter 4 - Nature v. Nurture and Evolution
... Develop from single egg Develop from separate eggs Person’s characteristic emotional reactivity and intensity Proportion of variation among individuals that we can attribute to genes Effect of one factor (environment) depends on another factor (heritability) Studies the molecular structure and funct ...
... Develop from single egg Develop from separate eggs Person’s characteristic emotional reactivity and intensity Proportion of variation among individuals that we can attribute to genes Effect of one factor (environment) depends on another factor (heritability) Studies the molecular structure and funct ...
Memory
... Separated Twins Critics of separated twin studies note that such similarities can be found between strangers. Researchers point out that differences between fraternal twins are greater than identical twins. ...
... Separated Twins Critics of separated twin studies note that such similarities can be found between strangers. Researchers point out that differences between fraternal twins are greater than identical twins. ...
Chapter 10
... Genes (DNA) are dependent- collaborate with other sources of information Gene expression/activity is affected by context or environment Context is affected by hormones, light, nutrition, etc. ...
... Genes (DNA) are dependent- collaborate with other sources of information Gene expression/activity is affected by context or environment Context is affected by hormones, light, nutrition, etc. ...
Twin study

Twin studies reveal the absolute and relative importance of environmental and genetic influences on individuals in a sample. Twin research is considered a key tool in behavioral genetics and in content fields, from biology to psychology. Twin studies are part of the methods used in behavior genetics, which includes all data that are genetically informative – siblings, adoptees, pedigree data etc.Twins are a valuable source for observation because they allow the study of varying family environments (across pairs) and widely differing genetic makeup: ""identical"" or monozygotic (MZ) twins share nearly 100% of their genes, which means that most differences between the twins (such as height, susceptibility to boredom, intelligence, depression, etc.) is due to experiences that one twin has but not the other twin. ""Fraternal"" or dizygotic (DZ) twins share only about 50% of their genes. Thus powerful tests of the effects of genes can be made. Twins share many aspects of their environment (e.g., uterine environment, parenting style, education, wealth, culture, community) by virtue of being born in the same time and place. The presence of a given genetic trait in only one member of a pair of identical twins (called discordance) provides a powerful window into environmental effects.The classical twin design compares the similarity of monozygotic (identical) and dizygotic (fraternal) twins. If identical twins are considerably more similar than fraternal twins (which is found for most traits), this implicates that genes play an important role in these traits. By comparing many hundreds of families of twins, researchers can then understand more about the roles of genetic effects, shared environment, and unique environment in shaping behavior.Modern twin studies have shown that almost all traits are in part influenced by genetic differences, with some characteristics showing a strong influence (e.g. height), others an intermediate level (e.g. personality traits) and some more complex heritabilities, with evidence for different genes affecting different aspects of the trait — as in the case of autism.