Nature With Nurture - College Test bank
... 89. Psychologists and anthropologists who study cross-cultural differences in child development are investigating the differences in children’s A. mesosystems. B. chronosystems. C. microsystems. D. macrosystems. ...
... 89. Psychologists and anthropologists who study cross-cultural differences in child development are investigating the differences in children’s A. mesosystems. B. chronosystems. C. microsystems. D. macrosystems. ...
מצגת של PowerPoint
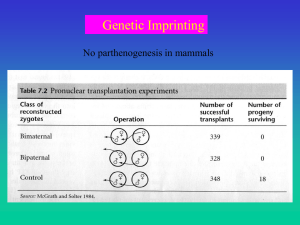
... Garfield AS…Ward A. Nature. 469(7331):534-8 (2011) Imprinted genes, defined by their preferential expression of a single parental allele, represent a subset of the mammalian genome and often have key roles in embryonic development, but also postnatal functions including energy homeostasis and behavi ...
... Garfield AS…Ward A. Nature. 469(7331):534-8 (2011) Imprinted genes, defined by their preferential expression of a single parental allele, represent a subset of the mammalian genome and often have key roles in embryonic development, but also postnatal functions including energy homeostasis and behavi ...
04/01/08 Lecture - UCLA Human Genetics
... roles of genetic factors and their interaction with environmental factors in the occurrence of a trait or disease. Gene = the basic unit of heredity. It is a sequence of DNA that encodes polypeptides (part of a protein) or controls them. It determines the nature of an individuals inherited traits. M ...
... roles of genetic factors and their interaction with environmental factors in the occurrence of a trait or disease. Gene = the basic unit of heredity. It is a sequence of DNA that encodes polypeptides (part of a protein) or controls them. It determines the nature of an individuals inherited traits. M ...
Quantitative Genetics
... You should note that polygenic inheritance can only be studied in populations because there are multiple genes and multiple alleles being studied. Two individuals cannot account for all the alleles controlling the phenotype. In order to assess the influence of all the alleles available, multiple ind ...
... You should note that polygenic inheritance can only be studied in populations because there are multiple genes and multiple alleles being studied. Two individuals cannot account for all the alleles controlling the phenotype. In order to assess the influence of all the alleles available, multiple ind ...
Genetics Review 1. Describe Mendel`s experiments and know terms
... 1. Describe Mendel’s experiments and know terms relating to the experiment (P, F1, F2, cross pollination, true-breeding) Mendel took two plants who differed in one trait (purple vs white flowers), these were called the Parent (P) generation. Using cross-pollination, he bred those plants to create th ...
... 1. Describe Mendel’s experiments and know terms relating to the experiment (P, F1, F2, cross pollination, true-breeding) Mendel took two plants who differed in one trait (purple vs white flowers), these were called the Parent (P) generation. Using cross-pollination, he bred those plants to create th ...
Introduction - Università degli Studi di Roma "Tor Vergata"
... Infertility affects up to 15% of the potentially fertile human population (WHO, 1990). This is in obvious contrast with the genetic program of any individual which is expected to work towards a peak of efficiency to achieve the reproduction. Modern individuals are made up of a range of heritable cha ...
... Infertility affects up to 15% of the potentially fertile human population (WHO, 1990). This is in obvious contrast with the genetic program of any individual which is expected to work towards a peak of efficiency to achieve the reproduction. Modern individuals are made up of a range of heritable cha ...
Everything you need to know about Genetics
... does not dominant over the other, but both phenotypes are present. A roan horse will have red and white hair, instead of being all white, or all red. ...
... does not dominant over the other, but both phenotypes are present. A roan horse will have red and white hair, instead of being all white, or all red. ...
equal expression of both alleles
... •The inheritance of biological characteristics is determined by individual units known as genes. In organisms that reproduce sexually, genes are passed from parents to their offspring. •In cases in which two or more forms of the gene for a single trait exist, some forms of the gene may be dominant a ...
... •The inheritance of biological characteristics is determined by individual units known as genes. In organisms that reproduce sexually, genes are passed from parents to their offspring. •In cases in which two or more forms of the gene for a single trait exist, some forms of the gene may be dominant a ...
The principles and methods formulated by Gregor Mendel provide
... To answer the following questions, remember that each zygote undergoes repeated mitosis to become a child, so the child will have the same genetic makeup as the zygote. 3. What fraction of this couple's children would you expect to be AA? ____ 4. What fraction of this couple's children would you exp ...
... To answer the following questions, remember that each zygote undergoes repeated mitosis to become a child, so the child will have the same genetic makeup as the zygote. 3. What fraction of this couple's children would you expect to be AA? ____ 4. What fraction of this couple's children would you exp ...
Genetics
... Dominant: always expresses the trait Rr, RR Recessive: needs both recessive alleles to express the trait rr Phenotype – physical characteristic Ex. White fur, blue eyes, green skin Genotype – genetic makeup Ex. FF, Bb, or gg ...
... Dominant: always expresses the trait Rr, RR Recessive: needs both recessive alleles to express the trait rr Phenotype – physical characteristic Ex. White fur, blue eyes, green skin Genotype – genetic makeup Ex. FF, Bb, or gg ...
Introduction to Genetics
... Probability • Probability: the likelihood that an event will occur • i.e.: coin flip = ½ or 50% • Determined by: • Probability = # times expected to occur ...
... Probability • Probability: the likelihood that an event will occur • i.e.: coin flip = ½ or 50% • Determined by: • Probability = # times expected to occur ...
Issues and Debates Essays
... As psychological knowledge has deepened, the naturenurture debate has grown increasingly complex, to the point where some psychologists believe that it is now a meaningless distinction, and a pointless distraction from more important matters. Plomin et al. (1977) have suggested the idea of “passive ...
... As psychological knowledge has deepened, the naturenurture debate has grown increasingly complex, to the point where some psychologists believe that it is now a meaningless distinction, and a pointless distraction from more important matters. Plomin et al. (1977) have suggested the idea of “passive ...
Name Date Class
... 1. ________________ The body cells of humans contain 46 pairs of chromosomes. 2. ________________ A widow’s peak is a trait controlled by many genes. 3. ________________ In the case of sex-linked traits, only females can be carriers. 4. ________________ In females, a recessive allele on the X chromo ...
... 1. ________________ The body cells of humans contain 46 pairs of chromosomes. 2. ________________ A widow’s peak is a trait controlled by many genes. 3. ________________ In the case of sex-linked traits, only females can be carriers. 4. ________________ In females, a recessive allele on the X chromo ...
Chapter 2: Conception, Heredity, and Environment
... reactions that turn genes on or off as they are needed but that do not change the underlying genetic code. o This phenomenon is called epigenesis. Epigenesis works via chemical molecules, or “tags,” attached to a gene that affect the way a cell “reads” the gene’s DNA. Because every cell in the b ...
... reactions that turn genes on or off as they are needed but that do not change the underlying genetic code. o This phenomenon is called epigenesis. Epigenesis works via chemical molecules, or “tags,” attached to a gene that affect the way a cell “reads” the gene’s DNA. Because every cell in the b ...
Human Genetic Disorders PPT
... Caused by a recessive allele on the X chromosome Sex-linked disorder – occurs more frequently in males ...
... Caused by a recessive allele on the X chromosome Sex-linked disorder – occurs more frequently in males ...
Name - O. Henry Science
... People inherit two genes for every characteristic, and they get one gene from each parent. Sometimes the two genes for one trait contain different codes. This affects how the trait appears in the child. For example, maybe both parents have brown eyes. Let's say that they each have one gene for brown ...
... People inherit two genes for every characteristic, and they get one gene from each parent. Sometimes the two genes for one trait contain different codes. This affects how the trait appears in the child. For example, maybe both parents have brown eyes. Let's say that they each have one gene for brown ...
FRQ - mendels laws
... A. Discuss Mendel's laws of segregation and independent assortment. Relate to inheritance patterns of alleles B. Explain how the events of Meiosis I and Meiosis II account for the observations that led Mendel to formulate these laws. STANDARDS: maximum = 10 points total (no more than 6 points for ei ...
... A. Discuss Mendel's laws of segregation and independent assortment. Relate to inheritance patterns of alleles B. Explain how the events of Meiosis I and Meiosis II account for the observations that led Mendel to formulate these laws. STANDARDS: maximum = 10 points total (no more than 6 points for ei ...
Mendelian Genetics
... fertilized egg that splits shortly after fertilization Since they developed from the same egg they have exactly the same genetic makeup ...
... fertilized egg that splits shortly after fertilization Since they developed from the same egg they have exactly the same genetic makeup ...
BIOL Unit 5
... • Genes are chemical factors that determine traits. • Alleles segregate from each other and each gamete carries a single copy of each gene. This is the law of segregation – the second law Mendel observed during his pea plant experiments. • TT is homozygous (“homo” = same; “zygous” = zygote) dominant ...
... • Genes are chemical factors that determine traits. • Alleles segregate from each other and each gamete carries a single copy of each gene. This is the law of segregation – the second law Mendel observed during his pea plant experiments. • TT is homozygous (“homo” = same; “zygous” = zygote) dominant ...
Inherited Traits and Learned Behaviors
... Learned Behaviors • Are you better at something than other members of your family? – You learned how to do this, you did not inherit it from your parents – We learn many behaviors: • Riding a bike, making a sandwich, using good manners ...
... Learned Behaviors • Are you better at something than other members of your family? – You learned how to do this, you did not inherit it from your parents – We learn many behaviors: • Riding a bike, making a sandwich, using good manners ...
Twin study

Twin studies reveal the absolute and relative importance of environmental and genetic influences on individuals in a sample. Twin research is considered a key tool in behavioral genetics and in content fields, from biology to psychology. Twin studies are part of the methods used in behavior genetics, which includes all data that are genetically informative – siblings, adoptees, pedigree data etc.Twins are a valuable source for observation because they allow the study of varying family environments (across pairs) and widely differing genetic makeup: ""identical"" or monozygotic (MZ) twins share nearly 100% of their genes, which means that most differences between the twins (such as height, susceptibility to boredom, intelligence, depression, etc.) is due to experiences that one twin has but not the other twin. ""Fraternal"" or dizygotic (DZ) twins share only about 50% of their genes. Thus powerful tests of the effects of genes can be made. Twins share many aspects of their environment (e.g., uterine environment, parenting style, education, wealth, culture, community) by virtue of being born in the same time and place. The presence of a given genetic trait in only one member of a pair of identical twins (called discordance) provides a powerful window into environmental effects.The classical twin design compares the similarity of monozygotic (identical) and dizygotic (fraternal) twins. If identical twins are considerably more similar than fraternal twins (which is found for most traits), this implicates that genes play an important role in these traits. By comparing many hundreds of families of twins, researchers can then understand more about the roles of genetic effects, shared environment, and unique environment in shaping behavior.Modern twin studies have shown that almost all traits are in part influenced by genetic differences, with some characteristics showing a strong influence (e.g. height), others an intermediate level (e.g. personality traits) and some more complex heritabilities, with evidence for different genes affecting different aspects of the trait — as in the case of autism.