Organisms can be classified into two major groups
... • Some produce flowers while others do not. • Flowering plants are plants that make seeds within flowers (ex: grass, roses, fruit trees) • Some flowers become fruit. • Non-flowering plants are plants that make seeds within cones or produce spores instead of seeds. (ex: ferns, mosses, cedar trees ...
... • Some produce flowers while others do not. • Flowering plants are plants that make seeds within flowers (ex: grass, roses, fruit trees) • Some flowers become fruit. • Non-flowering plants are plants that make seeds within cones or produce spores instead of seeds. (ex: ferns, mosses, cedar trees ...
4/20 & 4/21 - 7th Grade Agenda
... What are the characteristics of Nonvascular Plants? • Mosses, Liverworts, Hornworts • Low growing • Can pas materials only from one cell to the next • Cell walls provide support • They get water directly from their surroundings. ...
... What are the characteristics of Nonvascular Plants? • Mosses, Liverworts, Hornworts • Low growing • Can pas materials only from one cell to the next • Cell walls provide support • They get water directly from their surroundings. ...
the process of converting light energy into chemical energy using
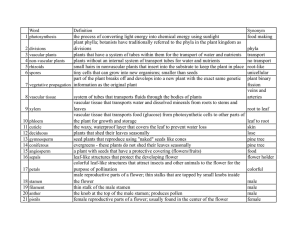
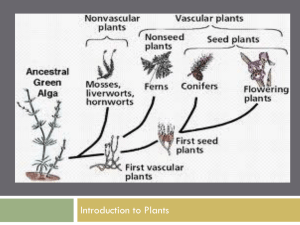
... plant phylla; botanists have traditionally referred to the phyla in the plant kingdom as divisions divisions vascular plants plants that have a system of tubes within them for the transport of water and nutrients non-vascular plants plants without an internal system of transport tubes for water and ...
... plant phylla; botanists have traditionally referred to the phyla in the plant kingdom as divisions divisions vascular plants plants that have a system of tubes within them for the transport of water and nutrients non-vascular plants plants without an internal system of transport tubes for water and ...
Plants I
... Increasingly (evolution) dominated by sporophytes Heterosporous: a few large, sessile, female spores and many small motile male spores ...
... Increasingly (evolution) dominated by sporophytes Heterosporous: a few large, sessile, female spores and many small motile male spores ...
PLANT KINGDOM
... deep in the ground & smaller, more numerous fibrous roots spread to control erosion. ...
... deep in the ground & smaller, more numerous fibrous roots spread to control erosion. ...
AP Biology 11 LO Cards: Plants
... AP Biology 11 LO Cards: Plants Chapter 29: Plant Diversity I 1. Define the following terms: cuticle, secondary compounds, stomata, vascular tissue (xylem and phloem), lignin, rhizoids, roots, leaves, megaspore, microspore 2. Compare and contrast the life cycle of the fern with that of the moss. Chap ...
... AP Biology 11 LO Cards: Plants Chapter 29: Plant Diversity I 1. Define the following terms: cuticle, secondary compounds, stomata, vascular tissue (xylem and phloem), lignin, rhizoids, roots, leaves, megaspore, microspore 2. Compare and contrast the life cycle of the fern with that of the moss. Chap ...
File - Ms. Poole`s Biology
... Adaptations for Moving on To Land • Prevention from dehydration-Evolution of waxy cuticle • Method of gas exchange for photosynthesis-Evolution of stomata and lenticels. • Method to obtain water and minerals-Evolution of roots • Increase in size and support-Evolution of xylem ...
... Adaptations for Moving on To Land • Prevention from dehydration-Evolution of waxy cuticle • Method of gas exchange for photosynthesis-Evolution of stomata and lenticels. • Method to obtain water and minerals-Evolution of roots • Increase in size and support-Evolution of xylem ...
Unit 4 Powerpoint
... In order to prevent water loss on dry land, plants have a cuticle (waxy covering). Some have roots, stems and leaves to help obtain, transport, and use water and nutrients efficiently. Use spores and seeds to protect reproductive cells. ...
... In order to prevent water loss on dry land, plants have a cuticle (waxy covering). Some have roots, stems and leaves to help obtain, transport, and use water and nutrients efficiently. Use spores and seeds to protect reproductive cells. ...
Plant Adaptation Pop Quiz
... ____ 27. The haploid form in a plant’s life cycle is called the gametophyte. ____ 28. A haploid stage following a diploid stage in a plant’s life cycle is called alternation of generations. ____ 29. In plants, haploid gametes are produced as a result of mitosis. ____ 30. The seed coat protects the ...
... ____ 27. The haploid form in a plant’s life cycle is called the gametophyte. ____ 28. A haploid stage following a diploid stage in a plant’s life cycle is called alternation of generations. ____ 29. In plants, haploid gametes are produced as a result of mitosis. ____ 30. The seed coat protects the ...
Obj. 8: Describe characteristics of marine plant and algae divisions
... coastal areas with little wave action 2. Trees and shrubs ...
... coastal areas with little wave action 2. Trees and shrubs ...
Fun Facts About Plants
... -Since non-vascular plants don’t have tubes’ the water and nutrients are transported from cell to cell. ...
... -Since non-vascular plants don’t have tubes’ the water and nutrients are transported from cell to cell. ...
Ferns, Club Mosses, and Horsetails Guided Reading
... 3.When the gametophytes produce egg cells and sperm cells, there must be enough water available for the sperm to swim to the eggs. 4.false 5.underground, upward, downward 6.The developing leaves are coiled at first and resemble the top of a violin. 7. a, d 8. fronds 9. The cuticle helps the plant re ...
... 3.When the gametophytes produce egg cells and sperm cells, there must be enough water available for the sperm to swim to the eggs. 4.false 5.underground, upward, downward 6.The developing leaves are coiled at first and resemble the top of a violin. 7. a, d 8. fronds 9. The cuticle helps the plant re ...
2. No vascular tissue
... adaptations that allow sperm to meet egg without water (e.g. spores that have waterproof coverings, seeds) ...
... adaptations that allow sperm to meet egg without water (e.g. spores that have waterproof coverings, seeds) ...
Notes Chapter
... 6.3 Vascular Plants • Xylem cells that carry water and dissolved mineral UP the roots to the leaves. • Phloem cells that carry food made in the leaves DOWN to all parts of the plant. • Fern vascular plant the reproduces with ...
... 6.3 Vascular Plants • Xylem cells that carry water and dissolved mineral UP the roots to the leaves. • Phloem cells that carry food made in the leaves DOWN to all parts of the plant. • Fern vascular plant the reproduces with ...
Unit VI Exam Study Guide
... Alternation of generations in seed plants Pollen, pollination Properties of gymnosperms Cones(types, location) Microsporangium, megasporangium Characteristics of angiosperms Flower structure Fruit(types) ...
... Alternation of generations in seed plants Pollen, pollination Properties of gymnosperms Cones(types, location) Microsporangium, megasporangium Characteristics of angiosperms Flower structure Fruit(types) ...
Plants with Seeds
... • depend on osmosis and diffusion • plants are small • live in wet environments Mosses and Liverworts • live in wet environments • rhizoids are root like structures to anchor ...
... • depend on osmosis and diffusion • plants are small • live in wet environments Mosses and Liverworts • live in wet environments • rhizoids are root like structures to anchor ...
MSdoc - Stevens County
... Cultural – Good vegetative cover helps prevent initial infestations; can invade and dominate healthy sites Mechanical – Very difficult because breaking up of roots serves to increase the number of plants; regular cutting or tillage can wear down plant reserves and reduce population and vigor but res ...
... Cultural – Good vegetative cover helps prevent initial infestations; can invade and dominate healthy sites Mechanical – Very difficult because breaking up of roots serves to increase the number of plants; regular cutting or tillage can wear down plant reserves and reduce population and vigor but res ...
Learn About Plants
... •Is called a carnivorous (meat eating) plant •Grows in wet, damp bogs •Can reach 1 foot in heighth Let's see other plants ...
... •Is called a carnivorous (meat eating) plant •Grows in wet, damp bogs •Can reach 1 foot in heighth Let's see other plants ...
Kingdom Plantae - Porterville Unified School District
... • Eukaryotes • Autotrophs (producers) • Multicellular • Cell walls made of cellulose • 2nd most complex kingdom – May have evolved from algae ...
... • Eukaryotes • Autotrophs (producers) • Multicellular • Cell walls made of cellulose • 2nd most complex kingdom – May have evolved from algae ...
Kingdom Plantae - Cloudfront.net
... • Eukaryotes • Autotrophs (producers) • Multicellular • Cell walls made of cellulose • 2nd most complex kingdom – May have evolved from algae ...
... • Eukaryotes • Autotrophs (producers) • Multicellular • Cell walls made of cellulose • 2nd most complex kingdom – May have evolved from algae ...
Kingdom Plantae
... holes that allow for the two-way flow of the food Transpiration: the release of water vapor form the leaves that is a result of cellular respiration-draws water up through the xylem. Xylem is like a straw with a one way flow of water and minerals ...
... holes that allow for the two-way flow of the food Transpiration: the release of water vapor form the leaves that is a result of cellular respiration-draws water up through the xylem. Xylem is like a straw with a one way flow of water and minerals ...
Seed dispersal
... Seed Bank in the UK. The UK has about 1400 different types of flowering plants, which we want to collect from all the different areas in which they grow. It is quite windy and wet here, but perhaps this is why the plants are growing well as all plants like to have water! I have been looking out for ...
... Seed Bank in the UK. The UK has about 1400 different types of flowering plants, which we want to collect from all the different areas in which they grow. It is quite windy and wet here, but perhaps this is why the plants are growing well as all plants like to have water! I have been looking out for ...
PLANTS - MrsRyan
... Vascular system – roots and shoots (tracheophytes) Mycorrhizae – fungal associations Stomata and cuticle Lignin – hardens cell walls – preventing water loss Vascular tissues – xylem and phloem ...
... Vascular system – roots and shoots (tracheophytes) Mycorrhizae – fungal associations Stomata and cuticle Lignin – hardens cell walls – preventing water loss Vascular tissues – xylem and phloem ...