Life Science-Plants Part 2 of 2
... • Some plants grow from a piece of stem put into water. New roots grow from the bottom of the stem. The new stem with roots is planted in soil. ...
... • Some plants grow from a piece of stem put into water. New roots grow from the bottom of the stem. The new stem with roots is planted in soil. ...
Ch.24 - Jamestown School District
... lightweight, allowing them to be carried in the air or to float on the surface of the water ...
... lightweight, allowing them to be carried in the air or to float on the surface of the water ...
plants - Cloudfront.net
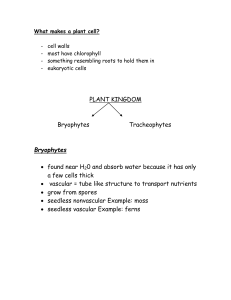
... their own food using sunlight - their cells are designed for this, as they have chloroplasts, an organelle that only plant cells have ...
... their own food using sunlight - their cells are designed for this, as they have chloroplasts, an organelle that only plant cells have ...
Chpt 22 Plants with seeds - Kingdom Plantae
... o Without water, the pollen needs methods to get to the female gametophytes – called pollination o Seeds are the structures that protect the zygote after fertilization o The zygote grows into a tiny embryo, then stops growing and it is covered by a seed coat protecting it and a food supply for its l ...
... o Without water, the pollen needs methods to get to the female gametophytes – called pollination o Seeds are the structures that protect the zygote after fertilization o The zygote grows into a tiny embryo, then stops growing and it is covered by a seed coat protecting it and a food supply for its l ...
plant class notes
... Gymnosperm - vascular plants that produce seeds on scales of female cones - (naked seed) not protected by a fruit - Do not produce flowers - Most leaves are needle-like - Include: conifers, cycads, gingkoes and gnetophytes Most produce male and female cones on ...
... Gymnosperm - vascular plants that produce seeds on scales of female cones - (naked seed) not protected by a fruit - Do not produce flowers - Most leaves are needle-like - Include: conifers, cycads, gingkoes and gnetophytes Most produce male and female cones on ...
Multiple Choice Unit 7 Plants Unit Test A
... a. flower during short days. b. increase their rate of photosynthesis. c. produce less ethylene and more auxin. d. form waxy scales around new leaf buds. ____15. Like parasites, carnivorous plants have a. specialized cells to pump out salt. b. extensive root systems. c. specialized features to obtai ...
... a. flower during short days. b. increase their rate of photosynthesis. c. produce less ethylene and more auxin. d. form waxy scales around new leaf buds. ____15. Like parasites, carnivorous plants have a. specialized cells to pump out salt. b. extensive root systems. c. specialized features to obtai ...
Study guide for Quiz # 1
... a. Like cellulose, but structure is branched out instead of being a long chain i. Makes it not as strong as cellulose b. Important to plant texture iii. Fibrous composition due to 3 carbohydrates 1. humans do not have enzyme to brake down these carbs a. keep you regular 2. Chicory a. Basic Info ...
... a. Like cellulose, but structure is branched out instead of being a long chain i. Makes it not as strong as cellulose b. Important to plant texture iii. Fibrous composition due to 3 carbohydrates 1. humans do not have enzyme to brake down these carbs a. keep you regular 2. Chicory a. Basic Info ...
Flowering Plants - Science with Ms. C
... • Plants have structures that allow them to survive in their habitats when the conditions are not suitable. • Examples of parts of flowering plants that function for survival may be: ▫ Leaves function as the site of photosynthesis, respiration, and transpiration in plants. ▫ Stems support the plant ...
... • Plants have structures that allow them to survive in their habitats when the conditions are not suitable. • Examples of parts of flowering plants that function for survival may be: ▫ Leaves function as the site of photosynthesis, respiration, and transpiration in plants. ▫ Stems support the plant ...
BIOCHEMICAL ASPECTS OF BIODIVERSITY
... Wind dispersal of their lightweight spores has distributed mosses throughout the world. These plants are particularly common and diverse in moist forests and wetlands Some mosses colonize bare, sandy soil, where researchers have found they help retain nitrogen in the soil. Other mosses inhabit su ...
... Wind dispersal of their lightweight spores has distributed mosses throughout the world. These plants are particularly common and diverse in moist forests and wetlands Some mosses colonize bare, sandy soil, where researchers have found they help retain nitrogen in the soil. Other mosses inhabit su ...
Candlestick Point Native Plant Nursery
... partners, agencies, and individuals to realize their large and small scale efforts to cultivate sustainable native plant habitats. ...
... partners, agencies, and individuals to realize their large and small scale efforts to cultivate sustainable native plant habitats. ...
Document
... They are the “factories of the plant”. 2 major parts The Blade & Petiole, Blade- is the flatten part expanded part of a leaf Petiole – is the cylindrical part that attaches to the stem ...
... They are the “factories of the plant”. 2 major parts The Blade & Petiole, Blade- is the flatten part expanded part of a leaf Petiole – is the cylindrical part that attaches to the stem ...
Plants
... • strawberry plants and other vine like plants send out runners, which grow into new plants • some plant clippings will grow into new plants • a Potato will grow into a new plant ...
... • strawberry plants and other vine like plants send out runners, which grow into new plants • some plant clippings will grow into new plants • a Potato will grow into a new plant ...
Kingdom Plantae
... Mosses and ferns rely on rain and dew to transport the male gametes. Seed producing plants rely on wind and insects to carry the male gametes to the female parts of plants. After fertilization the zygote develops in the seed where it can remain dormant for long periods of time and survive drou ...
... Mosses and ferns rely on rain and dew to transport the male gametes. Seed producing plants rely on wind and insects to carry the male gametes to the female parts of plants. After fertilization the zygote develops in the seed where it can remain dormant for long periods of time and survive drou ...
Common name - Center for Aquatic and Invasive Plants
... 2. Programs to educate homeowners about the problems associated with these plants and proper identification 3. Maintain good ground cover and mixture of plant species to reduce establishment ...
... 2. Programs to educate homeowners about the problems associated with these plants and proper identification 3. Maintain good ground cover and mixture of plant species to reduce establishment ...
Kingdom Plantae
... Mosses and ferns rely on rain and dew to transport the male gametes. Seed producing plants rely on wind and insects to carry the male gametes to the female parts of plants. After fertilization the zygote develops in the seed where it can remain dormant for long periods of time and survive drou ...
... Mosses and ferns rely on rain and dew to transport the male gametes. Seed producing plants rely on wind and insects to carry the male gametes to the female parts of plants. After fertilization the zygote develops in the seed where it can remain dormant for long periods of time and survive drou ...
alstroemeria - Super Floral Retailing
... are planted outdoors in the fall and winter, from November through February. ...
... are planted outdoors in the fall and winter, from November through February. ...
The Land Plants: Adaptation for Terrestrial life
... Vascular system * It is plant tissue consisting of cells joined into tubes that transport water and nutrients throughout the plant body (in all but bryophytes). *xylem is the tube-shaped, nonliving portion of the vascular system in plants that carries water and minerals from the roots to the rest o ...
... Vascular system * It is plant tissue consisting of cells joined into tubes that transport water and nutrients throughout the plant body (in all but bryophytes). *xylem is the tube-shaped, nonliving portion of the vascular system in plants that carries water and minerals from the roots to the rest o ...
What Do Plants Need?
... amount of water: A cactus grows in a dry dessert. It doesn’t need plenty of water to grow. ...
... amount of water: A cactus grows in a dry dessert. It doesn’t need plenty of water to grow. ...
PLANT JUDGING COMPETITION
... was particularly tricky as the "best" potted plant did NOT have a single open bloom BUT it was completely covered in buds! Floral Arrangement Division At the last table they had to pick out the best florist arrangement as to form and shape, balance and color, and also judge the freshness of e ...
... was particularly tricky as the "best" potted plant did NOT have a single open bloom BUT it was completely covered in buds! Floral Arrangement Division At the last table they had to pick out the best florist arrangement as to form and shape, balance and color, and also judge the freshness of e ...
PLANT TROPISMS WHAT ARE TROPISMS? Plants can respond to
... Abscisic acid is responsible for the growth of roots the earth. Abscisic acid is also responsible for abscission which is the dropping of leaves or fruit. Dicotyledons have leaves with both petiole (stalk) and blade. An area of weakness grows across the base of the stalk. Eventually only the vei ...
... Abscisic acid is responsible for the growth of roots the earth. Abscisic acid is also responsible for abscission which is the dropping of leaves or fruit. Dicotyledons have leaves with both petiole (stalk) and blade. An area of weakness grows across the base of the stalk. Eventually only the vei ...
ground, but they don`t absorb water like
... Angiosperms are vascular plants which have flowers, fiuits and seeds. Angiosperms include herbs, shrubs and trees. Most angiosperm trees lose their leaves in autumn and they don't grow new leaves until spring. These trees are deciduous. Other trees lose only a few of their leaves and produce new lea ...
... Angiosperms are vascular plants which have flowers, fiuits and seeds. Angiosperms include herbs, shrubs and trees. Most angiosperm trees lose their leaves in autumn and they don't grow new leaves until spring. These trees are deciduous. Other trees lose only a few of their leaves and produce new lea ...
Plant Reading Guide - Tea Area School District
... Cereals are grasses that contain grains. Grains are the edible, dry fruits of a cereal, such as rice, wheat, corn, oats, sorghum, rye, and millet. Root crops are roots of underground stems that are rich in carbohydrates. Root crops include potatoes, beets, carrots, and radishes. Legumes are members ...
... Cereals are grasses that contain grains. Grains are the edible, dry fruits of a cereal, such as rice, wheat, corn, oats, sorghum, rye, and millet. Root crops are roots of underground stems that are rich in carbohydrates. Root crops include potatoes, beets, carrots, and radishes. Legumes are members ...
Plants!!!
... plants!! - Their seeds are surrounded by a fruit. - They make up 90% of all plants alive today ...
... plants!! - Their seeds are surrounded by a fruit. - They make up 90% of all plants alive today ...
poisonous plants - Humber Nurseries Ltd.
... If you cannot identify the plants in and around your home and garden, you cannot know whether they are dangerous or not. Qualified horticulturists can often help you identify plants, at which time you should write the names down (preferably on tags attached to the plants) and keep them on hand for f ...
... If you cannot identify the plants in and around your home and garden, you cannot know whether they are dangerous or not. Qualified horticulturists can often help you identify plants, at which time you should write the names down (preferably on tags attached to the plants) and keep them on hand for f ...
Botany

Botany, also called plant science(s) or plant biology, is the science of plant life and a branch of biology. A botanist or plant scientist is a scientist who specializes in this field of study. The term ""botany"" comes from the Ancient Greek word βοτάνη (botanē) meaning ""pasture"", ""grass"", or ""fodder""; βοτάνη is in turn derived from βόσκειν (boskein), ""to feed"" or ""to graze"". Traditionally, botany has also included the study of fungi and algae by mycologists and phycologists respectively, with the study of these three groups of organisms remaining within the sphere of interest of the International Botanical Congress. Nowadays, botanists study approximately 400,000 species of living organisms of which some 260,000 species are vascular plants and about 248,000 are flowering plants.Botany originated in prehistory as herbalism with the efforts of early humans to identify – and later cultivate – edible, medicinal and poisonous plants, making it one of the oldest branches of science. Medieval physic gardens, often attached to monasteries, contained plants of medical importance. They were forerunners of the first botanical gardens attached to universities, founded from the 1540s onwards. One of the earliest was the Padua botanical garden. These gardens facilitated the academic study of plants. Efforts to catalogue and describe their collections were the beginnings of plant taxonomy, and led in 1753 to the binomial system of Carl Linnaeus that remains in use to this day.In the 19th and 20th centuries, new techniques were developed for the study of plants, including methods of optical microscopy and live cell imaging, electron microscopy, analysis of chromosome number, plant chemistry and the structure and function of enzymes and other proteins. In the last two decades of the 20th century, botanists exploited the techniques of molecular genetic analysis, including genomics and proteomics and DNA sequences to classify plants more accurately.Modern botany is a broad, multidisciplinary subject with inputs from most other areas of science and technology. Research topics include the study of plant structure, growth and differentiation, reproduction, biochemistry and primary metabolism, chemical products, development, diseases, evolutionary relationships, systematics, and plant taxonomy. Dominant themes in 21st century plant science are molecular genetics and epigenetics, which are the mechanisms and control of gene expression during differentiation of plant cells and tissues. Botanical research has diverse applications in providing staple foods and textiles, in modern horticulture, agriculture and forestry, plant propagation, breeding and genetic modification, in the synthesis of chemicals and raw materials for construction and energy production, in environmental management, and the maintenance of biodiversity.